As a victim of an Advanced Persistent Threat (APT), you’re dealing with a very skilled and well-equipped cyber attacker. They use complex tactics to get what they want, including stealing sensitive information, gaining more privileges, and manipulating systems.
Attackers try various methods to get into your system, often by posing as legitimate communications. They monitor your online activities, looking for vulnerabilities to exploit. Their goal is to take control of your system and gain administrative access, all while avoiding detection.
These attackers are highly skilled and use various techniques to stay under the radar. They can even manipulate your system’s rules and roles to their advantage. They’re quick to adapt and use new tactics to evade detection.
The biggest danger of APTs is that they’re often carried out by organized groups with significant resources. These groups use sophisticated methods to gather intelligence on their targets, including researching their victims’ habits and weaknesses.
To make matters worse, APTs can go undetected for a long time, giving attackers ample opportunity to steal sensitive information or disrupt systems.
What Can We Do to Understand APTs?
The key to understanding APTs is to recognize that they’re not just random attacks. They’re carefully planned and executed by skilled attackers who know exactly what they’re doing. Their goal is to get ahead of their targets and stay one step ahead of security measures.
So, what can you do to protect yourself from APTs? Be aware of the risks and take steps to secure your online activities. This includes using strong passwords, keeping your software up to date, and being cautious when clicking on links or opening emails from unknown sources.
Remember, APTs are a serious threat, and it’s essential to take proactive measures to protect yourself and your organization from these types of attacks.
By understanding what APTs are and how they work, you can take steps to protect your organization from these sophisticated cyber threats.
Key Takeaways
- Prolonged, targeted attacks. APTs are sustained and aim at specific targets for long-term infiltration.
- Sophisticated techniques. Utilize advanced methods like zero-day exploits and multi-vector attacks.
- Data exfiltration. Primary goal is to steal sensitive information stealthily.
- Human element. Often exploit human errors and lapses in judgment.
Understanding Advanced Persistent Threats

When you’re dealing with Advanced Persistent Threats, it’s essential to know what makes the people behind these attacks tick. You need to understand their motivations and how they work. This knowledge will help you defend against them.
To start, let’s break down the characteristics of these threat actors. What drives them? How do they operate? By understanding these factors, you’ll get a better grasp of the APT landscape.
Next, you’ll want to know about the life cycle of these attacks. What’re the different stages? How do the attackers move from one stage to the next? By examining the attack life cycle, you’ll be better equipped to protect your organization.
Understanding the Actors Behind Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs)
Have you ever wondered what makes the actors behind Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs) so successful at carrying out complex cyber attacks? The answer lies in their unique characteristics, which set them apart from other cyber threats.
What Makes APT Actors So Effective?
| Characteristic | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Well-Resourced and Highly Skilled | APT actors have a deep understanding of the targeted organization’s security and vulnerabilities. | They can infiltrate even the most secure networks. |
| Clear Objectives | APT actors have a specific goal, such as stealing sensitive information or disrupting critical infrastructure. | They can focus their efforts and resources on achieving their objective. |
| Multiple Attack Vectors | APT actors use various tactics, including cyber, physical, and deception, to gain and maintain access. | It’s challenging for organizations to detect and respond to the attack. |
| Adaptive and Evolving | APT actors adjust their tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) in response to changes in the targeted organization’s security. | They can stay one step ahead of security measures and maintain access. |
| Autonomous and Flexible | APT actors can pivot and adjust their operations in real-time to achieve their objectives. | They can respond quickly to changes in the targeted organization’s security. |
Why is it Important to Understand APT Actors?
Understanding these characteristics is crucial in developing effective security measures to prevent and detect APTs. By knowing what to look for, you can better protect your organization’s sensitive information and prevent cyber espionage.
So What Are APT Actors?
APT actors are highly skilled and well-resourced, with clear objectives and multiple attack vectors. They are adaptive, evolving, autonomous, and flexible, making them a significant threat to organizations. By understanding these characteristics, you can develop effective security measures to prevent and detect APTs.
Understanding the Attack Life Cycle
When a network is under attack by a sophisticated threat, known as an Advanced Persistent Threat (APT), it goes through a series of stages.
As a network administrator, it’s crucial to understand these stages to protect your network from these threats.

Stage 1: Gaining Access
The first stage is when attackers gain unauthorized access to your network. This often happens through emails with malicious links or attachments that exploit weaknesses in software or hardware.
Once inside, they create a backdoor and increase their privileges to move freely within your network.
Stage 2: Reconnaissance
Next, attackers gather information about your network.
They identify important targets and create a map to plan their next moves.
Stage 3: Data Exfiltration
After that, attackers steal sensitive data.
They use encryption and compression to avoid detection.
They also set up command and control servers to maintain access to your network.
Stage 4: Covering Their Tracks
After all is done, the attacker will try to delete all traces of their attack if possible. This way, the target has no way to figure out who the attacker was, or what their process was.
Understanding the Stages of an APT Attack

When you look at the stages of an APT (Advanced Persistent Threat) attack, you’ll realize that getting into the network is just the first step. The attackers then use tactics to move laterally throughout the network. This means they try to gain more control and access to sensitive information.
As you learn about these tactics, you’ll see how attackers try to escalate their privileges. This means they try to get more power and control within the network. They also gather sensitive data, which is a key part of their plan.
Understanding these tactics is crucial to recognizing when an APT has a persistent presence on the network. This includes knowing how they escalate privileges and how they exfiltrate data.
Initial Network Infiltration: The First Step in a Cyber Attack
Imagine someone trying to break into your house. They might try to pick the lock, find an open window, or trick you into letting them in. In a similar way, hackers try to get into your computer network using various tactics. This is called initial network infiltration, and it’s the first step in a type of cyber attack known as an Advanced Persistent Threat (APT).
How Hackers Get In
Hackers often use emails to trick people into opening malicious attachments or clicking on links. These emails are called spear-phishing emails, and they’re designed to look like they’re from someone you trust. Once you open the attachment or click the link, malware is downloaded onto your computer, giving the hacker access to your network.
Another way hackers get in is by using exploit kits. These kits scan your network for vulnerabilities in software or plugins. If they find one, they can use it to gain access to your network. Zero-day vulnerabilities are also a problem. These are vulnerabilities that no one knows about yet, so they’re not patched or detected by security software.
The Goal of Initial Network Infiltration
The goal of initial network infiltration is to establish a foothold in your network. This allows hackers to move around and eventually achieve their objectives. It’s like they’re setting up a base camp in your network, from which they can launch further attacks.
Protecting Your Network
Monitor your network traffic to detect suspicious activity. Use two-factor authentication to make it harder for hackers to get in. Keep your software up-to-date to patch vulnerabilities. Be careful when opening emails and attachments from unknown sources.
Lateral Movement Tactics
Once an attacker gets into your network, they’ll start moving quietly through your systems to gather more information. This is called lateral movement. Their goal is to get closer to achieving their objective, which is often to steal sensitive data or cause harm.
During this stage, attackers use various tools and techniques to explore your network. They want to learn about your internal systems, accounts, and trust relationships. Attackers might use tools like Nmap to scan your network and find vulnerable spots. They can also create a copy of themselves to move laterally and get to a strategic point in your network.
Attackers use special tools to gather information about your accounts and connections. They might use command-line tools or off-the-shelf software to find out what privileges certain accounts have. They can also use these tools to discover different connection channels.
To prevent attackers from spreading through your network, you need to have strong security measures in place. This includes monitoring your network traffic, using application and domain allowlisting, and implementing two-factor authentication. You should also consider using specialized security solutions to stop advanced persistent threats (APTs) from achieving their goals.
How Attackers Gain More Power in Your Network
Imagine a hacker has already gotten into your network. Now, they want to gain more control and access to sensitive information. This is called privilege escalation. It’s a key part of an Advanced Persistent Threat (APT), a type of cyber attack that’s hard to detect.
Exploiting Weaknesses and Stealing Credentials
Attackers use different techniques to exploit vulnerabilities in your system. They might manipulate settings or steal login credentials to get more privileges. This allows them to move around your network without being detected.
What’s at Risk?
As the attack continues, hackers use privilege escalation to gain administrative access. This means they can install malware, create backdoors, and steal sensitive data.
To prevent this, you need a strong security system that includes:
- Monitoring network traffic
- allowlisting applications and domains
Stay Vigilant
Your security team must be on the lookout for suspicious activity and respond quickly to potential threats. By understanding how attackers escalate their privileges, you can better protect your network and sensitive information.
Understanding Lateral Movement and Data Exfiltration
As attackers gain more control over your network, they can move on to the next stage: lateral movement. This is where they spread across your network, using different techniques to stay hidden and gather data to steal.
Techniques Used in Lateral Movement
| Technique | Description | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Hiding Malware | Attackers hide their malicious software to avoid detection | Stay hidden in the network |
| Exploiting Weaknesses | Attackers use known weaknesses to gain access to more areas | Gain more control over the network |
| Using Elevated Privileges | Attackers use their increased privileges to move across the network | Gather data to steal |
| Using Multiple Exploits | Attackers use multiple weaknesses to gain access and stay hidden | Stay in the network for a long time |
What Happens During Lateral Movement
Attackers use these techniques to stay in your network for a long time. They might use multiple connections, increase their privileges, and exploit weaknesses to gather data and stay hidden. It’s essential to understand these techniques to detect and prevent Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs).
Understanding Persistent Network Presence in Cyber Attacks
Imagine a burglar who breaks into a house, but instead of stealing everything at once, they hide in the attic and come down at night to take what they want. This is similar to what happens in a type of cyber attack called an Advanced Persistent Threat (APT).
How Attackers Get In and Stay In
During an APT attack, hackers try to get into a company’s computer network and stay there for a long time without being detected. They do this by using different techniques to hide their tracks and create secret doors, called backdoors, to get back in if they get kicked out.
What Attackers Do Once They’re In
Once hackers are inside the network, they try to move around and find sensitive areas where they can steal important data. They might use special tools to guess passwords, record what people type on their keyboards, or create fake doors to get to other parts of the network.
Why Persistent Network Presence is a Big Deal
The problem with APT attacks is that hackers can stay in the network for a long time, even if the company finds and closes the door they used to get in. This means that companies need to be extra careful and use strong security measures, like monitoring network traffic and using two-factor authentication, to detect and prevent these types of attacks.
Characteristics of APT Attacks

When dealing with an Advanced Persistent Threat (APT), you’re facing a sophisticated attack designed to go undetected and achieve specific goals. To better prepare your organization, let’s break down the characteristics of APT attacks.
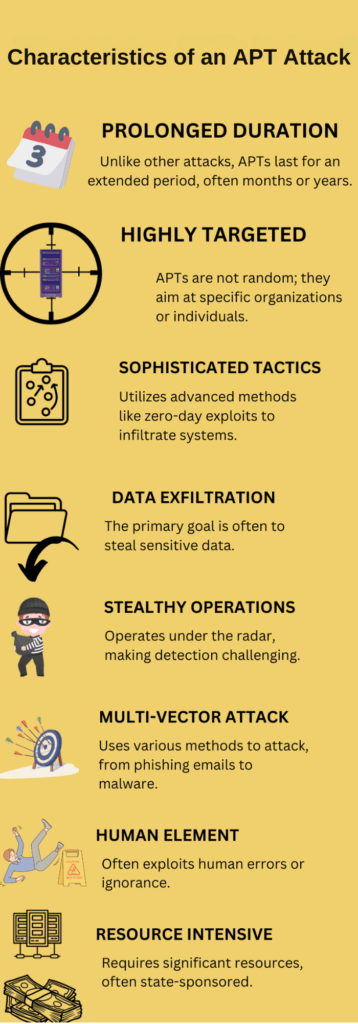
Stealthy Network Infiltration
APTs often involve sneaking into a network without being detected. This can happen through various means, such as exploiting vulnerabilities or using social engineering tactics to trick employees into revealing sensitive information.
Targeted Data Extraction
Once inside, APTs focus on extracting specific data, such as sensitive business information or personal data. This targeted approach helps attackers achieve their goals without raising suspicion.
Evasive Malware Tactics
APTs often use evasive malware tactics to avoid detection. This can include using code that changes frequently or hiding malware in seemingly harmless files.
Stealthy Network Infiltration: A Growing Threat
Imagine a sneaky attacker who can get into your network without being detected. This is what happens in an Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) attack. The attacker uses clever techniques to stay hidden and remain in your network for a long time.
How Do Attackers Get In?
Attackers use different tactics to gain access to your network. Social engineering is a common technique, where attackers trick network staff into giving away sensitive information. This helps them get into the network.
Web Application Firewall (WAF) evasion is another technique, where attackers find ways to bypass security measures, allowing them to inject malicious code. This compromises web applications and gives them access to sensitive data.
Attackers also use stealth operations to remain undetected within the network. This helps them stay in the network for a long time and steal sensitive data. Additionally, attackers use network scanning to scan the network and identify vulnerabilities, finding weak spots to gain access to sensitive areas.
The Impact of APT Attacks
APT attacks often involve multiple attack vectors, making it essential to have robust security measures in place. This includes Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems to detect and prevent APT attacks.
To protect your network, using security measures like SIEM systems is essential. Training network staff to avoid social engineering attacks is also crucial.
Keeping web applications and networks up to date with the latest security patches is another vital step. Monitoring network activity for suspicious behavior helps identify potential threats before they escalate.
The Threat of Targeted Data Extraction
Imagine a hacker who’s not just happy with breaking into your network. They want to dig deeper and steal your most valuable information. This is called targeted data extraction, and it’s a key part of an Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) attack.
What’s at Risk?
Once hackers are inside your network, they start looking for sensitive data. This can include things like trade secrets, intellectual property, and other important business information. They keep searching until they find something valuable enough to make the attack worth their time.
The Consequences
The stolen data can be devastating for your business. You could lose valuable intellectual property, and it could cost you a lot of money. The problem is that APTs are designed to be hard to detect, making them tough to stop.
Understanding the Threat
To protect your business, you need to know how targeted data extraction works. This way, you can prepare your organization to defend against these sophisticated attacks.
Understanding Evasive Malware Tactics
As we’ve seen how targeted data extraction can harm your business, it’s equally important to know about the sneaky tactics used by Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) attackers. These attackers use various methods to stay hidden and achieve their goals.
What are these tactics?
APT attackers use several tactics to evade detection.
- Code Obfuscation: Malicious code is hidden to avoid detection. This makes it hard for security controls to detect malware.
- Anti-Debugging Techniques: These techniques prevent malware from being analyzed. This hinders security researchers from understanding malware.
- Living off the Land: Legitimate system tools are used to carry out malicious activities. This makes it harder to detect and distinguish from normal network activity.
How do these tactics affect your business?
These tactics allow APT attackers to steal sensitive data without being detected. They may also use phishing emails with malicious files or links to gain initial access to the network.
Why is it important to know about these tactics?
Understanding these evasive malware tactics is crucial to protecting your business from APT attacks. By knowing how attackers work, you can take steps to prevent them from succeeding.
Why Should Businesses Care About APT Threats?
The Myth of Immunity
Many small business owners believe that APTs only target large corporations or government entities. This couldn’t be further from the truth. In fact, small businesses are increasingly becoming lucrative targets for APT groups.
They often believe they’re immune to such sophisticated attacks. They think they have nothing worth stealing. This false sense of security can lead to lax cybersecurity measures, making them easy targets.
The Reality
The truth is that many businesses often lack the robust cybersecurity infrastructure that larger organizations have. This makes small businesses attractive targets for APT groups. Small businesses may hold valuable data, such as customer information or intellectual property. Data that can be exploited or sold on the dark web. Moreover, small businesses can serve as a gateway to larger organizations they may be connected to, such as suppliers or partners.
The Cost of Complacency
Ignoring the threat of APTs can have devastating consequences for small businesses. From financial losses to reputational damage, the impact can be far-reaching and sometimes irreversible.
A Collective Threat
The table of industry sectors targeted by various APT groups shows that no sector is immune. Sectors like Business Services and Financial, often comprising small businesses, are also on the radar of these advanced threat actors.
Proactive Measures
Given the increasing threat landscape, small businesses must take proactive steps to protect themselves. This includes regular cybersecurity training for staff, implementing multi-factor authentication, and keeping all software up-to-date.
Try to understand the risks and taking appropriate measures. This can go a long way in safeguarding your small business against the looming threat of APTs. Ignorance is not an option; it’s a risk you can’t afford to take.
Acknowledge the reality of APT threats and take proactive security measures!
By doing so, small businesses can better protect themselves and their valuable assets. The first step is awareness, and the next is action.
| Industry Sector | APT Groups |
|---|---|
| Telecommunications | APT39, APT35 |
| Travel Industry | APT39 |
| IT | APT39 |
| High-Tech Industry | APT39, APT41 |
| Military | APT35 |
| Diplomatic | APT35 |
| Media | APT35 |
| Energy | APT35, APT34, APT33, ChamelGang |
| Defense Industrial Base | APT35 |
| Engineering | APT35 |
| Business Services | APT35 |
| Financial | APT34 |
| Government | APT34 |
| Chemical | APT34 |
| Aerospace | APT33 |
| Healthcare | APT41 |
| Video Game Industry | APT41 |
| Higher Education | APT41 |
| Aviation | ChamelGang |
| Travel Services | APT41 |
| News/Media | APT41 |
Note that many or most of these APTs are identified in a tool called MITRE ATT&CK which is really helpful to use to understand the attack characteristics and so how to defend against them.
Protecting Against APT Attacks

To keep your organization safe from advanced threats, you need to use a combination of strategies.
Watch for Suspicious Activity
First, set up a system to monitor your network traffic. This helps you detect any unusual activity that might be a sign of an attack.
Add an Extra Layer of Security
Next, use two-factor authentication to make it harder for attackers to get into your network. This adds an extra layer of security to protect your organization.
Use Allowlisting and Specialized Solutions
You should also enforce allowlisting policies, which means only allowing approved software to run on your network. Additionally, use specialized solutions that can help detect and prevent advanced threats. By taking these steps, you can significantly reduce the risk of a successful attack.
Implement Traffic Monitoring
Implementing Traffic Monitoring to Protect Against APT Attacks
Monitoring traffic is a crucial step in protecting against Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs). To do this, you need to keep an eye on all traffic coming in and out of your network, as well as traffic within your network. This helps detect and prevent hackers from installing backdoors and stealing data.
Real-time monitoring is key. It helps you detect and prevent APT attacks by identifying unusual patterns and anomalies. You can use systems like Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) and Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) to get real-time alerts and notifications of potential APT attacks.
When setting up traffic monitoring, use network traffic analysis and threat intelligence to detect and respond to APT attacks. This helps you identify compromised devices and systems within your network, so you can respond quickly and minimize the attack’s impact.
Having a solid incident response plan in place is also important. This plan helps you quickly respond to detected threats and prevent them from becoming incidents.
Use Two-Factor Authentication
Protecting Your Network: Why Two-Factor Authentication Matters
You’ve already taken a great step by keeping an eye on your network. Now it’s time to make it even more secure. This is where two-factor authentication comes in, which is like adding an extra lock on your digital door.
You know how important it’s to protect yourself from Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs), like stolen passwords and fake emails trying to trick you. This is exactly why 2FA is here to save the day.
Two-Factor Authentication requires an attacker to not just guess your password but also to get through an additional step, which could be anything like getting a verification code sent to your phone, a random code created on a separate device or something unique, like a biometric scan, to ensure the identity is valid.
Types of Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
Option 1: SMS-Based 2FA receives a code from the server. This method uses authenticators that create codes within a digital form, ensuring independence from the server.
Authenticators receive a mode required for cell phones to process, depending on the error rate needed for mobile authentication. This process has been verified to result in a basic personal number that makes every verified core unique.
Other available types of two-factor authentication include:
Option 2: Physical Two-Factor Authentication uses unique signals, such as biometric scans, to verify identity. This method is considered stronger than SMS-based 2FA, as it is more difficult to compromise.
Some users take advantage of physical two-factor authentication, which sends basic signals to verify identity. This process builds on the safety systems already in place, while also providing an additional layer of security.
Physical two-factor authentication can be used in various ways, including:
Using a separate device to create a random code
Using a biometric scan, such as a fingerprint or facial recognition
Using a physical token that generates a unique code
Each of these methods provides a unique way to verify identity and add an extra layer of security to your network.
Enforce Allowlisting Policies
Protecting your network from Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs) requires a multi-layered approach. One crucial step is enforcing allowlisting policies. This helps control the applications and domains that can access your system.
Allowlisting is like creating a guest list for your network. You decide which applications and software are allowed to run, and block all others. This approach can help prevent APT attacks by controlling what’s allowed to run on your network.
There are two types of allowlisting policies: application allowlisting and domain allowlisting. Application allowlisting controls which applications can run on your network. Domain allowlisting controls access to specific domains and websites.
Effective allowlisting policies require regular monitoring and updates. This ensures the list of approved applications and domains stays current and relevant.
To implement effective allowlisting policies:
- Create a list of approved applications and domains
- Regularly monitor and update the list
Boost Your Defense Against Advanced Persistent Threats
To fight back against sneaky online threats like Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs), you need the right security tools in your arsenal. Two such solutions that can detect and stop APTs in their tracks are Web Application Firewalls and endpoint detection tools.
Real-World APT Attack Examples

Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs) are a type of cyber attack that can have serious consequences. To understand how they work, let’s look at some real-life examples.
You might’ve heard of some of the most well-known APT attacks, such as Stuxnet and APT28. These attacks have made headlines in recent years.
By studying these examples, we can learn more about the tactics and techniques used by hackers to infiltrate and exploit vulnerable networks.
Looking at real-life examples can help us understand how APTs work and how they can be prevented. These examples show us what we can do to protect ourselves from these types of attacks.
Notorious APT Attack Examples
The severity and impact of Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs) are best shown through real-life examples. These are high-profile attacks that have compromised governments, international organizations, and private companies worldwide.
One notable example is the Stuxnet worm, which was launched in 2010. This attack targeted Iran’s nuclear program, causing significant damage to the country’s nuclear centrifuges. Another example is the GhostNet operation, discovered in 2009. This operation compromised over 1,200 computers in 103 countries, including government ministries, embassies, and international organizations.
These attacks are often carried out by nation-states or APT groups, such as APT28, also known as Fancy Bear. In 2015, APT28 was linked to a spear-phishing attack on the Pentagon. APT32, also known as OceanLotus, has been active since at least 2014. This group has targeted organizations in Southeast Asia, including those in Vietnam, the Philippines, and Laos.
These groups use clever tactics to gain access to an organization’s network. They exploit weaknesses in web servers and web applications. Once inside, they can conduct database operations and steal sensitive information and intellectual property.
To prevent such attacks, security teams must be vigilant. They must detect and prevent APTs, which can have devastating consequences. This is especially true for organizations that handle sensitive information.
APT groups use various techniques to attack their targets. These include exploiting vulnerabilities in software and using social engineering tactics. Social engineering is a way of tricking people into revealing sensitive information or clicking on malicious links.
To stay safe, organizations must be proactive. They must use advanced security measures, such as intrusion detection systems and incident response plans. They must also educate their employees on how to spot and report suspicious activity.
Recent High-Profile Breaches
The New York Times was breached by Chinese hackers in 2013. This attack lasted for four months and affected 53 employees’ computers. It was similar to the ‘Titan Rain’ operation and showed how important it’s to have strong event management and security measures in place.
The 2017 NotPetya malware attack caused a lot of disruption to critical infrastructure and global companies like Merck and FedEx. The estimated damages were over $10 billion. This attack involved a lot of data and showed how APT groups can evade detection.
The 2017 Equifax breach is another example. It exposed the sensitive data of over 147 million individuals. This breach was attributed to an APT group that exploited a vulnerability in the Apache Struts open-source software.
These recent breaches highlight the need for organizations to prioritize strong security measures to prevent and detect APT attacks.
Another indicator of an APT attack is the presence of unusual data, such as spam and phishing emails, within an organization.
What IS an APT?
Now that you know what Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs) are and how they work, it’s time to take action. You can’t afford to be complacent about your network security.
APTs are a serious threat to your sensitive data and intellectual property. To defend yourself, you need to understand the tactics and techniques used by APT attackers. This knowledge will help you stay one step ahead of these threats.
Stay vigilant and proactive. Take the necessary measures to protect your data. Your reputation depends on it. Remember, APTs are sophisticated attacks that can have serious consequences if not prevented.
By being aware of the risks and taking action, you can reduce the chances of an APT attack. This includes keeping your software up to date, using strong passwords, and being cautious when opening emails or clicking on links.
Summary
- What is an Advanced Persistent Threat? An Advanced Persistent Threat, or APT, is a type of cyber attack that is very sophisticated and involves multiple steps to achieve a specific goal. These attacks are often carried out by highly skilled hackers who have a lot of resources and a deep understanding of the targeted organization’s security and weaknesses.
- The Dangers of APTs APTs can have serious consequences, including stealing sensitive data and taking control of computer systems. Because of their complexity, APTs can be difficult to detect and respond to.
- How APTs Work APTs typically involve several stages, including:
- Getting into the network (initial infiltration)
- Moving around the network to find valuable data (lateral movement)
- Stealing sensitive data (data exfiltration)
- Protecting Against APTs To protect against APTs, you need a comprehensive security strategy that includes:
- Monitoring network traffic to detect suspicious activity
- Using two-factor authentication to make it harder for hackers to get in
- Enforcing allowlisting policies to control what software can run on your network
Don’t wait until it’s too late. Take control of your network security today. Protect your data and reputation from APTs.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is an Advanced Persistent Threat (APT)?
An APT is a prolonged, targeted cyber attack where intruders gain unauthorized access to a network, remaining undetected for extended periods to steal sensitive data.
How do APTs differ from regular cyber threats?
APTs differ in their duration, sophistication, and targeted nature. Unlike regular cyber threats, APTs aim for long-term infiltration and data exfiltration, often employing advanced techniques.
What are common methods used in APT attacks?
Common methods include phishing emails, exploiting zero-day vulnerabilities, social engineering, and deploying malware to maintain prolonged access and move laterally within the network.
Why are APTs challenging to detect?
APTs are designed to operate stealthily, using advanced evasion techniques and remaining dormant for periods to avoid detection, making them challenging to identify and mitigate..
What industries are most targeted by APTs?
Industries frequently targeted by APTs include telecommunications, finance, government, healthcare, and high-tech sectors due to the valuable data they hold.
How can businesses protect against APTs?
Businesses can protect against APTs by implementing robust endpoint security, regular employee training, using advanced detection tools like IDS and SIEM, and leveraging threat intelligence for proactive defense..

Experienced cybersecurity analyst, software engineer, patent attorney, worked with Linux, Windows, AWS, lots of security tools. Hope to help people do the right things and do the things right!


