Today, robust cybersecurity is essential. This article explores the defense-in-depth strategy. Implementing defense in depth means using multiple security measures to protect against cyber threats. Readers will learn the importance of this approach. They will learn how to implement it effectively. Most importantly, we will explain what the best practices are for maintaining a strong security posture.
Key Takeaways
- Implementing defense-in-depth provides many layers of security to protect against cyber threats.
- A comprehensive risk assessment can identify potential threats and rank security measures.
- There are critical components of a defense-in-depth strategy. Consider controls on the network, endpoints, access controls, and incident response planning
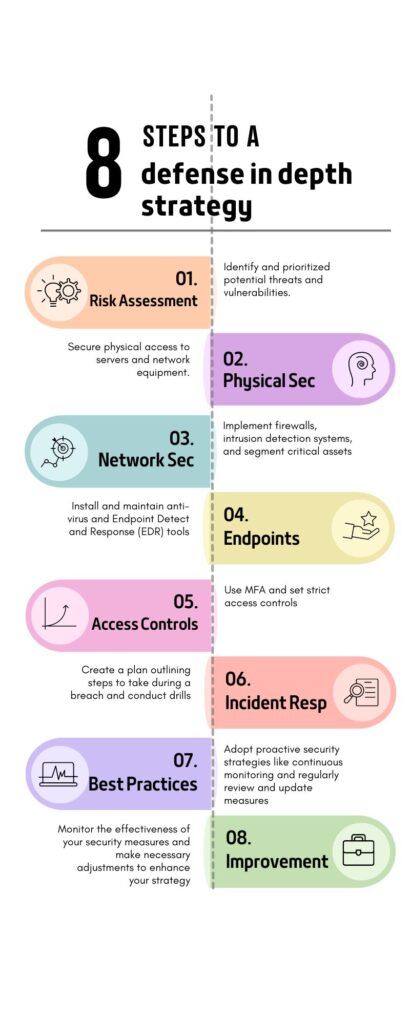
What is Defense-in-Depth?
Defense-in-depth is a cybersecurity strategy that uses multiple layers of security. This strategy can better protect your data. You’re not just relying on one method. Thus, it combines various tools and techniques to keep hackers out.
Understanding the Defense-in-Depth Strategy
Defense-in-depth employs multiple layers of security controls to protect an organization’s assets. This strategy ensures that if one layer is breached, additional layers can still mitigate the risk. This is much safer rather than relying on a single line of defense,
Importance in Modern Cybersecurity
Implementing defense-in-depth is crucial for modern cybersecurity. It provides a comprehensive security posture that can adapt to evolving threats. This strategy ensures that potential security gaps are addressed through a layered approach.
Why Implement Defense-in-Depth?
Implementing defense-in-depth helps protect your business from cyber-attacks. By using several security measures, you can reduce the risk of a breach and keep your data safe.
Benefits of Multiple Layers of Security
Organizations can reduce the risk of cyber-attacks by implementing multiple layers of security. This approach helps safeguard sensitive data. Moreover, it can enhance the organization’s overall security posture.
How It Mitigates Cyber Threats
A defense-in-depth strategy ensures a better response to potential security incidents. This layered security approach helps organizations detect and mitigate threats. Importantly, they can detect threats before they can cause significant harm.
Layers of Security in Defense-in-Depth
Defense-in-depth involves different layers of security to create a strong defense. These layers work to protect your network, devices, and data from potential threats.
Physical Security Measures
Physical security measures are the first layer of defense. These include securing physical access to servers and network equipment. Physical security can prevent unauthorized access and tampering.
Network Security Controls
Multiple types of network security controls are essential for protecting data in transit. The combination can help prevent unauthorized access and detect potential threats. Firewalls can block bad traffic based on rules. Intrusion detection systems look for patterns to detect an ongoing or potential attack. Network segmentation isolates parts of the system to keep problems from spreading.
Endpoint Security Solutions
Endpoint security solutions are critical for protecting individual devices. Antivirus and endpoint detection and response (EDR) tools are examples of these. Another critical solution is regular security updates. The combination of these ensures that endpoints are safeguarded against the latest threats.
Conducting a Comprehensive Risk Assessment
A risk assessment is essential for identifying threats and weaknesses in your security. This process helps determine what needs protection. Then you can prioritize your security efforts.
Identifying Potential Threats and Vulnerabilities
A comprehensive risk assessment is the first step in implementing defense-in-depth. Identifying potential threats and vulnerabilities helps organizations prioritize security measures. This helps to focus on the most significant risks.
Prioritizing Security Measures
Now you have identified potential threats. At this point, one can implement security measures to protect against these risks. This proactive approach ensures that resources are allocated effectively. Thus, enhancing overall security capabilities without wasting budget.
Network Security: The First Line of Defense
Network security is the first step in defense-in-depth. It involves using tools to protect your network from unauthorized access.
Firewalls and Intrusion Detection Systems
Firewalls and intrusion detection systems are critical components of network security. These tools help detect and mitigate unauthorized access attempts and potential cyber-attacks.
Network Segmentation
Network segmentation involves dividing a network into smaller, isolated segments. This strategy helps contain potential breaches and prevents unauthorized access to sensitive information.
Strengthening Endpoint Security
Endpoint security focuses on protecting individual devices like computers and smartphones. Using antivirus software and regular updates helps keep these devices secure.
Antivirus and Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR)
Antivirus software and EDR tools are essential for protecting endpoints. EDR solutions detect and mitigate malware and other threats. Thus, ensuring that endpoints remain secure.
Importance of Regular Security Updates
Regular security updates are crucial for maintaining a robust security posture. Ensure that all devices are up-to-date with the latest patches. This helps protect against newly discovered vulnerabilities.
Implementing Access Controls and Authentication
Access controls and authentication ensure that only authorized users can access your data. Using multi-factor authentication adds a layer of security to protect against unauthorized access.
Multi-Factor Authentication
Multi-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security. It acts by requiring multiple forms of verification. This measure helps prevent unauthorized access and strengthens overall security.
Access Controls to Prevent Unauthorized Access
Implementing strict access controls ensures that only authorized individuals can access sensitive data. This security measure helps protect against unauthorized access and potential breaches.
Incident Response Planning
An incident response plan prepares your organization for potential cyber-attacks. It outlines the steps to take if a breach occurs, helping you respond quickly and effectively.
Developing a Robust Incident Response Plan
A well-developed incident response plan is essential for responding to security incidents. This plan outlines the steps to take in the event of a breach and helps minimize the impact of cyber attacks.
Importance of Regular Security Drills
Regular security drills help ensure that the incident response plan is effective. These drills allow organizations to test their response strategies and make necessary improvements.
Best Practices for Implementing Defense-in-Depth
Following best practices for defense-in-depth can strengthen your security. These proactive strategies help protect your data from evolving threats.
Proactive Security Strategies
Proactive security strategies help organizations stay ahead of potential threats. Continuous monitoring looks at real-time streams and alerts when something unusual is detected. Threat hunting is looking for something based on a hypothesis. Implementing these best practices enhances overall security capabilities.
Continuous Monitoring and Improvement
Continuous monitoring and improvement are key to maintaining a strong security posture. Regularly review and update security measures. This ensures that they remain effective against evolving threats.
The Future of Defense-in-Depth
Cyber threats will continue to evolve. Thus, defense-in-depth will remain a crucial strategy for protecting organizations. Organizations need to continuously improve security measures and adopt new technologies. By doing this, organizations can stay ahead of potential threats and maintain a robust security posture.
Questions? We Have Answers.
Get answers to a list of the most Frequently Asked Questions.
To maintain a current defense in depth strategy, organizations should regularly update antivirus signatures, patch operating systems and software, train employees in security awareness, and perform periodic security assessments to identify and mitigate new risks. It’s also vital to stay informed of the latest cyber threats and adjust your strategy accordingly.

Experienced cybersecurity analyst, software engineer, patent attorney, worked with Linux, Windows, AWS, lots of security tools. Hope to help people do the right things and do the things right!

This sounds like the same concept in Naval Warfare, where defense in depth is a layered defense concerning the battle group. The Air Craft Carrier is the HVU or high-value unit in the center of the transiting BG. The surrounding ships are placed in formation using their primary mission and weapons systems as a basis for distance from the HVU. The farthest ship away from the HVU would have the longest-range weapons against the immediate threat, which might be a ballistic missile. It would most likely be a Cruiser or Destroyer, with an Aegis weapons system and three-dimensional radar in today’s Navy. I’ll spare you the similarity in redundancy or contingency systems on each ship compared to cyber systems backup.
Most of the cybersecurity concepts originated with the military, so it makes sense.