The Survival of your Business Could Be at Stake!
In today’s digital age, the threat landscape for small businesses is constantly evolving. Cyber threats, such as targeted attacks and malicious code, are becoming more sophisticated and frequent. As a small business manager, it’s crucial to have threat protection in place.
Navigating the Cyber Threat Maze: What Small Business Managers Need to Know
Cyber threats are any potential malicious attempts to damage, disrupt, or gain unauthorized access to your computer systems. These threats often involve targeted attacks where cybercriminals specifically target your business. They use malicious code to exploit vulnerabilities in your systems. Thus leading to data breaches that can have devastating consequences for your business.

Why Antivirus Software is Your Business’s Cyber Shield
Antivirus software plays a crucial role in your business threat protection strategy. It scans your computer systems for malicious code and removes it before it can cause damage. Many antivirus software solutions also offer real-time protection. Thus, they can continuously monitor your systems for threats and act immediately when detected.
Scanning for Malicious Code
Antivirus software scans directories or specific files against a library of known malicious signatures. By doing so, the software can detect abnormal patterns indicating the presence of malicious software. It enables users to schedule scans, so they run automatically and allows users to initiate new scans at any time.
When it detects malicious software, it either removes it automatically in the background or notifies users of infections. In some cases, it can then prompt the users to clean the files. This comprehensive scanning process is essential to ensure protection against threats.
Real-Time Protection
Real-time protection is a crucial feature of antivirus software. It acts as a real-time shield that scans each inbound file and program.
At some point, a system detects an infected file or program. It then proceeds based on the settings of the antivirus program. It’s either automatically deleted or moved to a quarantine folder for further analysis.
A quarantine prevents a file from interacting with the rest of the machine and its programs to mitigate damage.
Real-time scanning checks files as they are accessed, preventing immediate damage from malware.It detects and quarantines malicious files, like email attachments or installers, before they can harm your system.
Examples of How Antivirus Tools Can Help You
Protection from External Devices
Most people regularly plug in external devices, such as hard drives and USB adapters, to their computers. Antivirus software scans all attached devices and peripherals to thwart potential viruses from entering the system through external sources.
Dark Web Scanning
Most data breaches, such as ransomware attacks, often leak data on the dark web. Many antivirus tools can help organizations discover leaks of their sensitive data on the dark web.
For example, one might find an associated email address or account number on the dark web.. At that point they can notify the user and update the password to a new and more complex one.
Boot-Scan Command
Sophisticated viruses can often duplicate themselves while the system is active. However, an antivirus program can prevent a virus from self-replicating by invoking a boot-scan command.
A boot scan command shuts down the operating system (OS). Then it restarts the computer and scans the entire hard drive for viruses and malware. The virus is detected during the scan. It then is unable to self-replicate due to the deactivation of the OS.

Fortifying Your Business: Comprehensive Protection Against Cyber Threats
Comprehensive protection against cyber threats involves a multi-layered approach that goes beyond traditional antivirus software. This includes having a cybersecurity checklist.
Let’s explore three sophisticated techniques we can use to detect and respond to cyber threats. We will also look at their potential impact on your system. These techniques, when combined with traditional antivirus software, can provide a more comprehensive protection against cyber threats.
However, it’s important to note that the implementation of these techniques could potentially increase the complexity of the system. Further, it could require additional resources for management and maintenance.
Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR)
EDR is an advanced endpoint security solution that continuously monitors end-user devices. It provides real-time visibility to detect and respond to cyber threats like ransomware and malware. EDR records and analyzes endpoint behaviors, offers threat detection, investigation, and response capabilities, automatically uncovering stealthy attackers through behavioral analytics. The impacts of implementing EDR are:
- enhanced security visibility
- streamlined incident response with automated data collection
- enabled automated remediation for reduced impact and cost of incidents
Threat Detection
This involves IT admins taking timely actions to identify, view, and understand potential cyber threats. It is crucial for safeguarding a company’s network, digital assets, sensitive data, and users. Effective threat detection involves identifying anomalies in network behavior and comparing activity to known threats.
Enhanced visibility and situational awareness, along with SIEM log monitoring software, play key roles in achieving comprehensive threat detection. The impact of implementing threat detection is a more secure network and digital assets, and a reduced risk of undetected threats.
Automation in Cybersecurity
Automation has become an integral component to keep companies protected from the growing number and sophistication of cyberthreats. The use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning in areas with high-volume data streams can help improve cybersecurity in three main categories: threat detection, threat response, and human augmentation.
AI platforms can analyze data and recognize known threats, as well as predict novel threats. They also create and automatically enact security protections.
Furthermore, AI can help eliminate alert fatigue by automatically triaging low-risk alarms. AI can also automate big data analysis and other repetitive tasks. Thus, freeing humans for more sophisticated tasks. Implementing automation in cybersecurity improves threat detection and response, reduces human error, and increases efficiency.
Double Lock Your Data: The Power of Multi-Factor Authentication
Multi-factor authentication is a security measure that requires users to provide two or more forms of identification before they can access your systems. This adds an extra layer of security, making it harder for cybercriminals to gain unauthorized access to your systems.
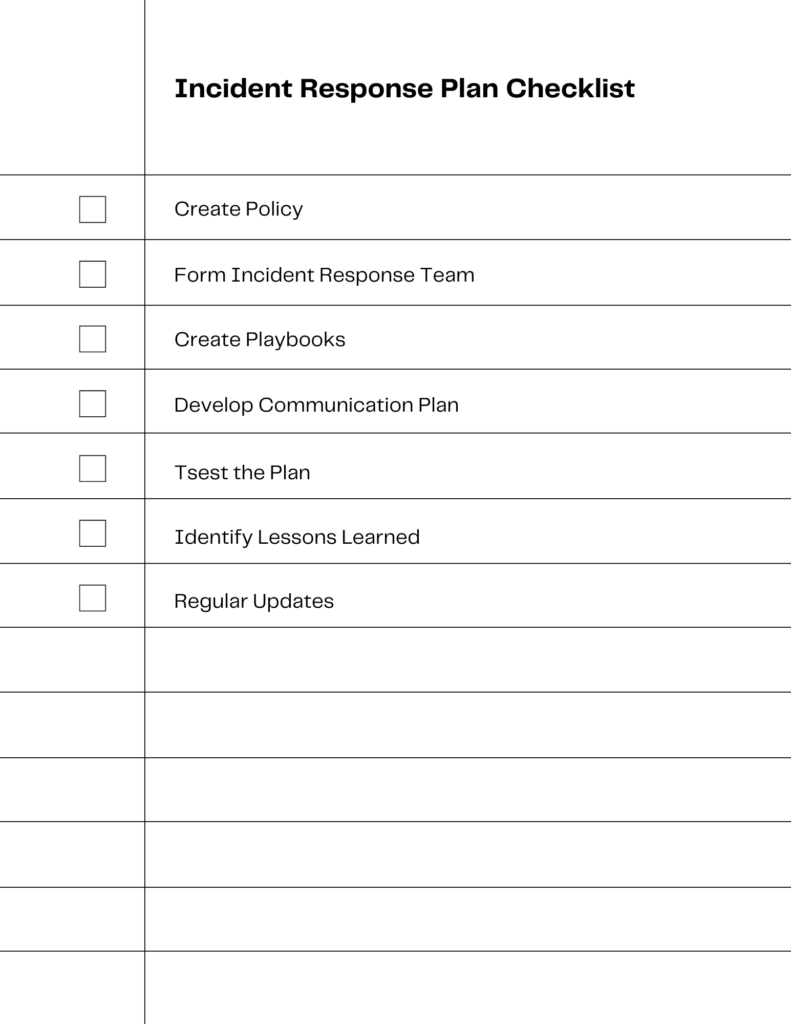
When Cyber Attacks Strike: Crafting Your Incident Response Plan
Crafting an effective incident response plan involves several key procedures. These procedures need to be in place to ensure swift and effective action during a cybersecurity incident. By following these procedures, organizations can ensure they have a robust incident response plan in place. They are then ready to tackle any cybersecurity threats that may arise.
Policy Creation
The first step is to develop or update an incident remediation and response policy. This policy serves as the foundation for all incident handling activities. It provides the authority needed for incident responders to make crucial decisions.
Forming an Incident Response Team
An incident response team should be formed, with each member trained on their responsibilities at various stages of incident handling. The team should include technical staff with platform and application expertise, infrastructure and networking experts, systems administrators, and people with a range of security expertise.
Developing Playbooks
Playbooks are the lifeblood of a mature incident response team. They provide standardized responses for the most common incident types, allowing the team to respond effectively without having to figure out what steps to take every time a similar incident occurs.
Creating a Communication Plan
A communication plan should be in place to ensure effective communication among different groups within an organization, as well as with external stakeholders during an active incident. This plan should also address the involvement of law enforcement.
Testing the Plan
The incident response plan should be tested regularly to ensure its effectiveness. This can be done through simulations and tabletop exercises, which allow teams to talk through the procedures they would apply during a specific security event.
Identifying Lessons Learned
After every major security incident, a formal lessons-learned session should be conducted. This session provides an opportunity to identify security control gaps that contributed to the incident, as well as areas where the incident response plan should be adjusted.
Regular Updates and Reassessments
The incident response plan should be reassessed and updated regularly, at least annually, or whenever changes occur to the company’s IT infrastructure or its business, regulatory, or compliance structure.
Don’t Lose What’s Yours: Techniques for Preventing Data Loss
Data loss prevention strategies involve measures to prevent sensitive data from being accessed, lost, or stolen. This includes both technical measures, such as encryption and access controls, and organizational measures, such as policies and procedures for handling sensitive data.
Sky-High Security: The Benefits of Cloud-Based Solutions
Cloud-based security solutions can offer several benefits for small businesses. They are often more affordable and easier to manage than traditional on-premises solutions. They also offer real-time protection and can be accessed from anywhere, making them a flexible and effective option for business threat protection.

Mobile Fortress: Ensuring the Security of Your Mobile Devices
With the increasing use of mobile devices in business, it’s important to consider their security. Mobile devices can be vulnerable to cyber threats, so it’s important to have measures in place to protect them. This can include using secure mobile device management solutions and educating employees about safe mobile device use.
Leveraging Threat Intelligence
Threat intelligence involves gathering and analyzing information about potential or current threats. This can help you to predict and prevent cyber-attacks, as well as respond more effectively when they occur.
Secure Your Network Against Threats!
Your network could be a playground for hackers unless you take the right precautions.
Endpoint protection is critical in this regard, and there is a lot more to it than installing antivirus software on every laptop.
Block bad traffic coming in and going out of your network. Make sure someone cannot read your data if they are not supposed to. And if all else fails, be sure to have a plan in place to respond to attacks!

Experienced cybersecurity analyst, software engineer, patent attorney, worked with Linux, Windows, AWS, lots of security tools. Hope to help people do the right things and do the things right!

