Introduction: Welcome to the World of Endpoint Security Controls
In today’s digital age, small businesses are increasingly finding themselves in the crosshairs of cybercriminals.
- A concerning 43% of all cyberattacks are directed at small businesses
- businesses with 1,000 or fewer employees are the target of 46% of these attacks.
- The financial implications are profound, with small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) incurring an average loss of $25,000 due to such cyber threats.
- In just 2020, the cumulative impact of over 700,000 attacks on small businesses amounted to a staggering $2.8 billion in damages.
This surge in cyber threats underscores the critical importance of endpoint security in safeguarding a business’s digital assets and operations in our interconnected world.
Such statistics underscore a critical reality: the digital landscape of 2023 is fraught with threats more sophisticated and relentless than ever before. In this environment, endpoint security emerges as a paramount concern. Every device, from laptops to smartphones, connected to a business’s network can be a potential entry point for cyber threats. As businesses increasingly rely on a myriad of devices to operate, ensuring the security of each endpoint becomes not just an IT concern, but a business imperative. Endpoint security is no longer a luxury or an afterthought—it’s a necessity for safeguarding the very lifeline of a business in today’s interconnected world.
Unraveling the Mystery of Endpoint Security Controls
Endpoint security controls form the backbone of any robust endpoint protection platform. Initially, they are designed to prevent unauthorized access. Subsequently, they detect malicious software, and finally, they respond to security threats in real time. As such, these controls are essential for safeguarding sensitive information and maintaining the integrity of your network.
Why Every Businesses Needs an Endpoint Security Controls Checklist
In the digital realm, the adage “better safe than sorry” has never been more relevant. With the proliferation of devices and the increasing sophistication of cyber threats, a structured approach to endpoint security is not just recommended—it’s essential. A checklist serves as a roadmap, guiding businesses in ensuring that every potential vulnerability is addressed, every device is secured, and every threat is anticipated.
Consider the following real-world incidents that underscore the dire consequences of inadequate endpoint security:
- SolarWinds Supply Chain Attack: In one of the most sophisticated cyberattacks, threat actors compromised the SolarWinds Orion software, affecting thousands of organizations worldwide. This breach was a stark reminder of the vulnerabilities present even in trusted software solutions and the cascading effect a single point of compromise can have.
- Ransomware Attacks on Healthcare Systems: The healthcare sector has been a prime target for ransomware attacks. In one instance, a hospital’s entire system was held hostage, delaying surgeries and redirecting emergency patients. Such attacks not only have financial implications but can also jeopardize human lives. 2
- Compromised Network Management Systems: The reliance on widely-adopted network management systems has its risks. A single compromise can have a pervasive impact, affecting vital processes, from daily operations to critical deliveries.
These incidents are not isolated. They represent the myriad threats that businesses, irrespective of their size or industry, face daily. An endpoint security controls checklist is a proactive measure, ensuring that businesses are not just reacting to threats but are always a step ahead.

Understanding Endpoint Security: A Beginner’s Guide
In the vast world of cybersecurity, understanding the nuances and specifics can be daunting, especially for those new to the field. Let’s break down the basics of endpoint security and how it fits into the broader landscape of IT security.
What is an Endpoint?
An endpoint, in simple terms, is any device that connects to a network. This includes desktop computers, laptops, smartphones, tablets, and even IoT (Internet of Things) devices like smart thermostats or security cameras.
Endpoint Security, Defined
Endpoint security refers to the measures and protocols in place to protect these devices (endpoints) from cyber threats. It ensures that even if a cybercriminal tries to access the network through a device, the attempt would be thwarted.
What is General IT Security?
When we talk about IT security, we’re referring to the overarching strategies and measures to protect an organization’s digital assets, which includes data, software, hardware, and networks. It’s a broad term that encompasses various subfields, including endpoint security, network security, application security, and more.
Endpoint Security vs. General IT Security
While general IT security looks at the bigger picture of protecting an organization’s entire digital infrastructure, endpoint security zeroes in on the devices. Think of general IT security as the security measures for an entire building, while endpoint security is like the individual locks on each door. Both are crucial, but endpoint security focuses specifically on ensuring that each device is a fortress in itself, given that devices can often be the weakest link in the security chain.
In essence, while general IT security provides a holistic approach to safeguarding an organization’s digital realm, endpoint security offers a specialized layer of defense, ensuring that each device connecting to the network is secure and uncompromised.
By understanding these foundational concepts, businesses can better appreciate the importance of a robust endpoint security strategy and its role in the broader IT security landscape.
The Comprehensive 2023 Endpoint Security Controls Checklist
Policy Management
In the realm of endpoint security, policy management serves as the foundation, setting the rules and guidelines for both users and devices. Proper policy management ensures that every device and user adheres to a set standard, minimizing the risk of breaches and unauthorized access.
Rules for Users and Devices:
- User Access Control: Define who can access what. For instance, only IT personnel might have the rights to install software, while other employees can only use approved applications.
- Device Authentication: Before any device connects to the network, it should be authenticated. This means only approved devices (like company-issued laptops or phones) can access company data.
- Regular Software Updates: All devices should have the latest security patches and software updates. This can be enforced by setting a policy that checks for updates regularly and prompts users to install them.
Real-world Incidents Highlighting the Consequences of Inadequate Policy Management:
- The Casino’s Fish Tank Incident: In 2017, hackers exploited a casino’s network through a smart thermometer in an aquarium. This IoT device was connected to a networked PC that controlled various aspects of the aquarium. The hackers used this unsecured device to navigate the casino’s broader network, eventually extracting 10GB of data, suspected to be information about the casino’s high-end customers. This breach underscores the importance of having a policy that segregates IoT devices from critical data storage. Read more about the incident here.
- Baby Monitor Breach: In 2018, a family in the United States experienced a chilling incident when their internet-connected baby monitor was hacked. The hacker used the device to broadcast inappropriate messages. This incident highlights the need for stringent device authentication and password policies. Read more about the incident here.
- Canadian Data Breach: In 2018, a laptop containing personal information of over 33,000 Canadian residents was stolen. Shockingly, none of the data on the laptop was encrypted, leaving only the computer password as a barrier. This breach could have been prevented with a strict policy enforcing data encryption on all portable devices. Read more about the incident here.
Effective policy management is not just about setting rules but ensuring they are adhered to. Regular audits, employee training, and stringent enforcement are crucial to make these policies truly effective in safeguarding against potential breaches.
Device Control
Device control is a pivotal aspect of endpoint security, ensuring that only authorized external devices can connect to and interact with a network. By managing and monitoring these devices, businesses can prevent unauthorized data transfers, potential malware infections, and other security threats.
How Device Control Works
- Allow and Deny Device control solutions allow IT administrators to create lists of approved and disapproved devices. Only approved devices can connect to the network, while denied ones are automatically blocked.
- Role-Based Access: Depending on the role or department of an employee, device control can limit the types of devices they can connect. For instance, a graphic designer might have permission to connect a drawing tablet, while a sales representative might not.
- Real-time Monitoring and Alerts: Modern device control solutions continuously monitor the devices connected to the network. If an unauthorized device is plugged in, the system can instantly alert the IT team or even automatically eject the device.
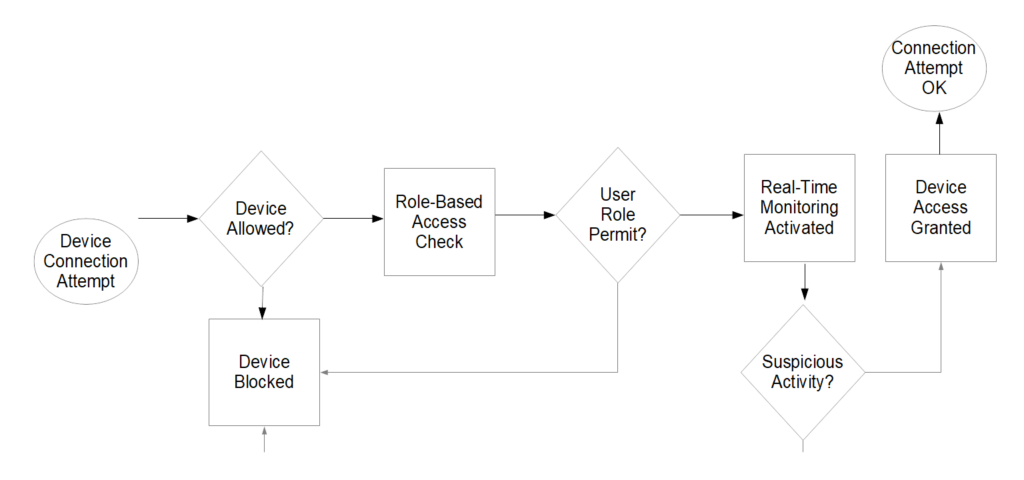
In the device control flowchart below, the process initiates with an attempt to connect a device to the network. The system first checks if the device is on the approved list. If not, the device is immediately blocked, and an alert is dispatched to the IT department. However, if the device is approved, the system then evaluates the user’s role to ascertain if they possess the necessary permissions to connect that specific device.
Should the user’s role not permit the device’s connection, it’s blocked, and again, an alert is sent to IT. If the user’s role does allow for the device connection, real-time monitoring is activated for that device. During this monitoring phase, if any suspicious activity is detected, the device is promptly blocked. In the absence of any suspicious activity, the device is granted access to the network, completing the device control process.
Examples of Device Control in Action
- USB Drive Restrictions: A company might allow only encrypted USB drives to connect to its systems. If an employee tries to plug in a non-encrypted USB, the system would block access and notify the IT department.
- Printer Controls: In a large office, device control can ensure that only specific departments or teams can access certain high-capacity printers or scanners, optimizing resource usage and preventing unauthorized access.
- Mobile Device Management: For businesses with BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) policies, device control can ensure that personal smartphones or tablets meet specific security standards before they can access company data or apps.
By implementing robust device control measures, businesses can maintain a tight grip on the external devices interacting with their network, significantly reducing potential security vulnerabilities.
Advanced Endpoint Protection
In an era where cyber threats are evolving at an unprecedented rate, relying on traditional security measures is no longer sufficient. Advanced Endpoint Protection (AEP) steps in to fill this gap, offering a more sophisticated and proactive approach to safeguarding devices and networks.
AEP employs a combination of techniques to detect, prevent, and respond to threats. Unlike basic antivirus solutions that rely on signature-based detection, AEP utilizes behavioral analysis, machine learning, and threat intelligence to identify and counteract zero-day attacks, fileless malware, and other advanced threats. This ensures that even if a threat hasn’t been previously identified or cataloged, the system can recognize its malicious behavior and take appropriate action.
One of the standout products in this domain is ESET’s Endpoint Protection Advanced. ESET’s solution is renowned for its multilayered defense mechanism, which not only detects and neutralizes threats but also provides insights into the attack’s origin and its intended impact. This level of detail is invaluable for IT teams, allowing them to fortify their defenses against future attacks.
In conclusion, Advanced Endpoint Protection is not just an upgrade; it’s a necessity in today’s threat landscape. By integrating solutions from trusted affiliates like ESET, businesses can ensure they are equipped with the best tools to fend off even the most sophisticated cyber adversaries.
Machine Learning and Endpoint Security
The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) into endpoint security marks a revolutionary shift in how we approach and combat cyber threats. These technologies are transforming the reactive nature of traditional security measures into proactive, adaptive, and continuously evolving systems.
AI and ML Workflow
Here’s how AI and ML are revolutionizing endpoint protection:
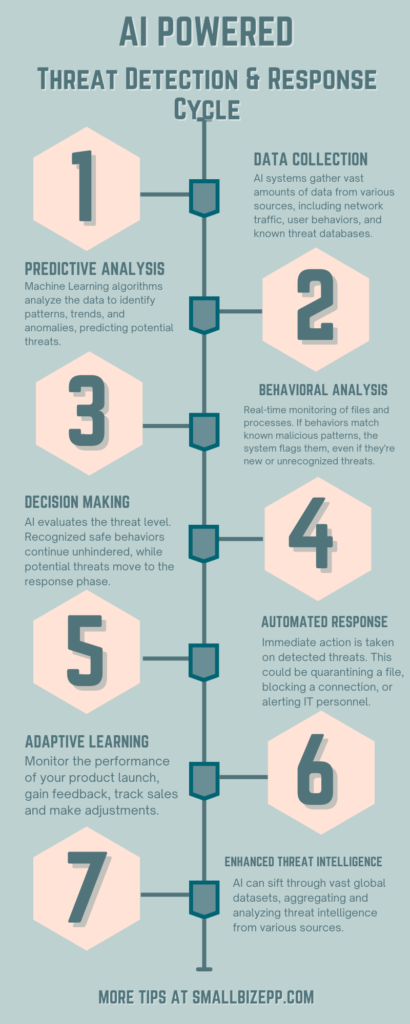
- Data Collection: AI systems gather vast amounts of data from various sources, including network traffic, user behaviors, and known threat databases.
- Predictive Analysis: Machine Learning algorithms analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and trends. By doing so, they can predict potential threats or vulnerabilities even before they manifest, allowing businesses to take preemptive action.
- Behavioral Analysis: Instead of solely relying on known malware signatures, ML-driven security tools monitor the behavior of files and processes in real-time. If a file or process acts in a way that’s consistent with known malicious behaviors (even if it’s a brand-new, unrecognized threat), the system can flag or quarantine it.
- Decision Making: AI evaluates the threat level. Recognized safe behaviors continue unhindered, while potential threats move to the response phase.
- Automated Response: AI-driven systems can make split-second decisions on potential threats, automatically blocking or quarantining suspicious files or processes without human intervention. This rapid response can be crucial in preventing the spread of malware or stopping a cyberattack in its tracks.
- Adaptive Learning: As new threats emerge and old ones evolve, ML models continuously learn and adapt. This ensures that the endpoint security system remains effective even as the threat landscape changes.
- Enhanced Threat Intelligence: AI can sift through vast global datasets, aggregating and analyzing threat intelligence from various sources. This provides a more holistic view of the global threat landscape, helping businesses understand and prepare for emerging threats.
In essence, the fusion of Machine Learning with endpoint security offers a dynamic, ever-evolving shield against cyber threats. As cyber adversaries employ more sophisticated techniques, the integration of AI ensures that endpoint protection remains several steps ahead, offering not just defense but a strategic advantage in the cybersecurity battleground.
Threat Intelligence
Threat Intelligence is a critical component of modern endpoint security, acting as the system’s eyes and ears in the ever-evolving world of cyber threats. By continuously gathering, analyzing, and disseminating information about emerging threats, vulnerabilities, and malicious actors, Threat Intelligence ensures that the security system is always a step ahead, ready to defend against the latest cyber-attacks.
At its core, Threat Intelligence operates on the principle of proactive defense. Instead of waiting for a threat to manifest and then reacting, it equips the system with the knowledge to anticipate and counteract threats before they can cause harm. This real-time threat data is sourced from a myriad of global channels, including cybersecurity firms, research institutions, and even underground hacker forums, ensuring a comprehensive view of the current threat landscape.
Examples of how Threat Intelligence Helps Security
In recent years, ransomware attacks have surged, with new strains emerging frequently. Threat Intelligence can identify these new strains by analyzing patterns from previous attacks, even before they become widespread. For instance, if a new ransomware variant starts affecting businesses in Europe, Threat Intelligence can alert companies worldwide, allowing them to bolster their defenses before the threat reaches them.
Zero-Day Vulnerabilities are software vulnerabilities unknown to those interested in patching them, making them prime targets for hackers. With Threat Intelligence, as soon as a zero-day vulnerability is discovered and reported somewhere in the world, systems integrated with this intelligence can start implementing protective measures, even before official patches are released.
In essence, Threat Intelligence is not just about gathering data; it’s about transforming this data into actionable insights that fortify endpoint security. In a digital age where threats can emerge from any corner of the globe in an instant, staying updated with real-time threat data is not just beneficial—it’s imperative.
Server Security
Servers, being the backbone of any digital infrastructure, are prime targets for cyber adversaries. Ensuring their security is paramount, not just for the integrity of the data they hold but also for the seamless operation of the businesses they support. Server security encompasses a multi-faceted approach to safeguard these vital systems from a myriad of threats.
Here are some of the key ways server security fortifies servers against attacks:
- Firewalls: Firewalls serve as a protective barrier for your network. They monitor and control incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules. By blocking unauthorized access, they prevent malicious actors from exploiting your network and gaining access to your sensitive data. Firewalls are especially important in managing the security risks associated with devices that connect to your network.
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS): IDS/IPS are advanced threat detection and prevention technologies. They monitor network traffic for suspicious activity in real time. When such activity is detected, they issue alerts and can even take action to block the threats. IDS/IPS are essential tools for identifying and responding to advanced threats that traditional antivirus software might miss.
- Regular Patching and Updates: Cyber adversaries often exploit known vulnerabilities in outdated software. Regularly updating server software and applying patches ensures that known vulnerabilities are addressed, reducing potential entry points for attackers.
- Secure Configuration: Ensuring that servers are configured securely is crucial. This includes disabling unnecessary services, setting up proper user permissions, and ensuring that default passwords are changed. There are special versions of operating systems that are hardened so that they are more secure; these are useful for production systems as opposed to a development environment where you are making changes sometimes on a daily basis.
- Antivirus and Malware Scanners: This is your first line of defense against malicious software. Antivirus and anti-malware software scan your endpoint devices. Specifically, these devices include mobile devices and IoT devices that connect to your network, for known threats.
Once identified, antivirus and anti-malware software detects, quarantines, and removes malware. Consequently, this helps to protect your sensitive information. Given these points, it’s crucial to keep this software up-to-date to guard against the latest threats. - Encryption: Data, both at rest and in transit, should be encrypted. This ensures that even if data is intercepted or accessed without authorization, it remains unreadable.
- Backup and Recovery: Regular backups ensure that in the event of a cyberattack, like ransomware, data can be restored without paying a ransom. Recovery plans ensure minimal downtime and data loss.
- Physical Security: Beyond digital threats, servers are also vulnerable to physical threats like theft, tampering, or natural disasters. Ensuring servers are housed in secure locations with controlled access is vital.
- Network Segmentation: By segmenting the network, servers holding sensitive information can be isolated from the broader network, reducing the risk of lateral movement by attackers.
- Monitoring and Logging: Continuous monitoring of server activity can detect anomalies or unauthorized access attempts. Logs provide a record of all activities, aiding in post-incident investigations.
In conclusion, server security is a multi-layered discipline, combining both hardware and software solutions to create a fortified defense against both common and advanced threats. In a world where data is the new gold, ensuring the sanctity of servers is of paramount importance.
Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
In the digital age, data is often considered an organization’s most valuable asset. Protecting this data from unauthorized access, breaches, and leaks is of paramount importance. Data Loss Prevention (DLP) focuses on implementing tools and strategies to ensure that sensitive data remains secure and within the confines of the organization.
Here’s how DLP tools and strategies work to prevent data breaches:
- Content Discovery: Before implementing protective measures, it’s essential to know where sensitive data resides. DLP tools scan storage devices, databases, and network locations to identify and categorize sensitive information.
- Data Classification: Once identified, data is classified based on its sensitivity level. This could range from public data to highly confidential information, allowing for tailored protective measures for each classification.
- Access Controls: By setting strict user permissions, DLP ensures that only authorized individuals can access specific data sets. Role-based access controls can be implemented, ensuring employees only access data pertinent to their job functions.
- Encryption: Encrypting sensitive data ensures that even if it’s accessed or intercepted, it remains unreadable without the appropriate decryption key.
- Endpoint Controls: DLP tools monitor data transfer activities on endpoints (like computers and mobile devices). This includes checking if sensitive data is being transferred to external drives, emailed, or uploaded to cloud storage.
- Network Traffic Monitoring: By inspecting network traffic, DLP solutions can detect and block unauthorized data transfers in real-time.
- Incident Response: In the event of a potential data breach, DLP tools can trigger alerts, automatically quarantine sensitive data, or even revoke user access, ensuring swift response to threats.
- Regular Audits and Reporting: Periodic audits of data access and transfer activities provide insights into potential vulnerabilities. Detailed reports can highlight patterns, unauthorized access attempts, or areas that need tighter security controls.
- Employee Training: One of the most significant vulnerabilities in any organization is human error. Regular training sessions ensure that employees are aware of best practices, the importance of data security, and the potential consequences of breaches.
- Integration with Other Security Tools: DLP solutions can be integrated with other security tools like Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS), firewalls, and Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems for a comprehensive security approach.
In essence, Data Loss Prevention is not just about tools but also about fostering a culture of data security within the organization. With the right mix of technology and awareness, organizations can significantly reduce the risk of data breaches and ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of their valuable data.
Examples of Data Loss Incidents
In recent years, even prominent organizations have fallen victim to data breaches, emphasizing the critical importance of data loss prevention.
For instance, in January 2018, the world’s largest ID database, Aadhaar, experienced a breach that exposed the personal and biometric information of over 1.1 billion Indian citizens. This breach, facilitated through the website of a state-owned utility company, Indane, not only exposed names, addresses, and biometric data but also bank account details linked to unique 12-digit numbers. The compromised data was even reportedly sold for as little as $7 in some WhatsApp groups.
Another significant breach occurred in November 2019 when a developer scraped customer data from Alibaba’s Chinese shopping website, Taobao. Over an eight-month period, the developer managed to compromise 1.1 billion pieces of user data, including usernames and mobile numbers. Although the data wasn’t sold, the incident led to a three-year prison sentence for the developer. These incidents underscore the dire consequences of inadequate data protection, especially for small businesses that might lack the resources to bounce back from such setbacks.
Mobile and Virtual Environment Protection
In today’s interconnected world, the traditional office workspace has evolved. With the rise of remote work, bring-your-own-device (BYOD) policies, and virtual environments, businesses now operate across a diverse range of devices and platforms. This diversity, while offering flexibility and scalability, also presents unique security challenges. Mobile and Virtual Environment Protection focuses on safeguarding these varied endpoints, ensuring consistent security regardless of the device or platform.
Here’s how this feature addresses the challenges of diverse device protection:
- Unified Endpoint Management (UEM): UEM solutions provide a centralized platform to manage and secure all devices, be it smartphones, tablets, laptops, or virtual machines. This ensures consistent application of security policies and rapid response to threats across the board.
- Containerization: Especially relevant for BYOD policies, containerization isolates business applications and data from personal ones. This ensures that even if a personal app or file is compromised, the business data remains secure.
- Virtual Environment Security: Virtual machines (VMs) and cloud environments have their own set of vulnerabilities. Dedicated security tools monitor these virtual environments for anomalies, unauthorized access, and potential breaches, ensuring they remain as secure as physical servers.
- Mobile Device Management (MDM): MDM solutions allow businesses to remotely manage mobile devices. This includes enforcing security policies, remotely wiping data in case of device loss, and ensuring that devices are updated with the latest security patches.
- Network Access Control: This ensures that only devices compliant with the company’s security policies can access the network. Non-compliant or potentially compromised devices are restricted or quarantined.
- Real-time Threat Detection: With mobile devices often connecting to unsecured public networks, real-time threat detection becomes crucial. Security tools continuously monitor for suspicious activities, ensuring threats are neutralized before they can cause harm.
- Encryption: Data stored on mobile devices or transmitted from them is encrypted, ensuring that even if a device is lost or intercepted, the data remains inaccessible.
In conclusion, as the boundaries of the traditional office continue to expand, Mobile and Virtual Environment Protection ensures that security remains consistent and robust. By addressing the unique challenges posed by diverse devices and platforms, businesses can operate flexibly without compromising on security.
IoT Security
The Internet of Things (IoT) has ushered in a new era of connectivity, with billions of devices—from smart thermostats and fridges to industrial sensors—now communicating and sharing data. While this interconnectedness offers unprecedented convenience and efficiency, it also introduces a host of security challenges. Ensuring the safety of IoT devices is paramount, given their increasing prevalence in both personal and professional settings.
Here are some of the primary challenges posed by IoT devices:
- Diverse Device Landscape: Unlike traditional computing devices, IoT encompasses a vast range of devices with varying functionalities, manufacturers, and operating systems. This diversity makes it challenging to implement a one-size-fits-all security solution.
- Limited Built-in Security: Many IoT devices are designed with functionality in mind, often sidelining security. As a result, they might lack essential security features like firewalls, encryption, or even the capability for software updates.
- Lack of Standardization: The IoT industry lacks a universal set of security standards. This means that devices from different manufacturers might have varying levels of security, with some being more vulnerable than others.
- Increased Attack Surface: With every new connected device, there’s a potential entry point for cyber adversaries. This expanded attack surface requires comprehensive monitoring and protection strategies.
- Data Privacy Concerns: IoT devices continuously collect and transmit data. Without proper security, this data—often personal or sensitive in nature—can be intercepted, leading to privacy breaches.
- Physical Threats: Beyond digital vulnerabilities, IoT devices can be physically tampered with, especially if they are located in easily accessible areas.
- Lifecycle Challenges: Many IoT devices have longer operational lifespans than traditional tech products. Ensuring they remain secure throughout their lifecycle, especially when manufacturers stop providing updates, is a significant challenge.
- Complex Ecosystems: IoT devices often operate within intricate ecosystems, interacting with other devices, systems, and networks. A vulnerability in one device can potentially compromise the entire ecosystem.
In conclusion, while IoT offers transformative potential, it also introduces a complex web of security challenges. Addressing these requires a holistic approach, combining robust security measures with continuous monitoring and timely updates. As the IoT landscape continues to evolve, so must the strategies to protect it.
Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR)
Endpoint Detection and Response, commonly referred to as EDR, is a critical component in the modern cybersecurity arsenal. As cyber threats become more sophisticated and stealthy, traditional defense mechanisms might not catch every malicious activity. EDR fills this gap by providing continuous monitoring and real-time threat response, ensuring that endpoints remain secure even in the face of advanced persistent threats.
Here’s how EDR enhances system security:
- Continuous Monitoring: Unlike traditional antivirus solutions that rely on signature-based detection, EDR continuously monitors all endpoint activities. This means it can detect anomalies or suspicious behaviors, even if they stem from previously unknown threats.
- Behavioral Analysis: EDR solutions utilize advanced algorithms and machine learning to analyze patterns and behaviors. This allows them to identify malicious activities based on how they behave rather than relying on known signatures.
- Real-time Threat Response: Upon detecting a potential threat, EDR solutions can take immediate action. This could range from isolating the affected endpoint, terminating malicious processes, or even rolling back changes made by malware.
- Threat Hunting: Beyond passive monitoring, EDR tools enable proactive threat hunting. Security teams can actively search for signs of compromise or indicators of attack, ensuring threats are neutralized before they can escalate.
- Incident Investigation: In the event of a security incident, EDR provides detailed logs and timelines of endpoint activities. This aids in understanding the scope of the breach, identifying compromised data, and determining the threat actor’s tactics, techniques, and procedures.
- Integration with Other Security Tools: EDR solutions can seamlessly integrate with other security platforms, such as Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems. This ensures a unified and coordinated response to threats.
- Automated Response: Leveraging artificial intelligence, EDR tools can automate responses to common threats. This not only speeds up reaction times but also ensures consistent and effective countermeasures.
In essence, EDR transforms endpoint security from a passive, reactive stance to an active, proactive one. By continuously monitoring, analyzing, and responding to threats in real-time, EDR ensures that endpoints remain secure even as cyber threats evolve in complexity and sophistication.
Choosing the Right Endpoint Security Solution for Your Business
Selecting the right endpoint security solution is crucial for safeguarding your business assets in the digital realm. While a deeper dive is available in another post, here are some high-level factors to consider when making your choice:
- Scalability: Ensure the solution can grow with your business. As you expand, add more devices, or branch into new areas, your security solution should be able to accommodate these changes without compromising on protection.
- Integration Capabilities: Your chosen solution should seamlessly integrate with other tools and systems you have in place. This ensures a unified defense strategy and simplifies management.
- User-Friendliness: A solution that’s easy to deploy, manage, and use ensures that all employees, regardless of their tech proficiency, can adhere to security protocols without feeling overwhelmed.
- Support and Updates: Opt for solutions backed by robust support from the provider. Regular updates, prompt customer service, and access to resources are vital for maintaining optimal security.
- Reputation and Reviews: Consider the reputation of the solution provider. Look for reviews, case studies, and testimonials to gauge the effectiveness and reliability of the product.
Remember, while features and capabilities are essential, the best solution is one that aligns with your business’s unique needs and challenges.
Conclusion: Staying Ahead in the Cybersecurity Game
In the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity, staying static is not an option. As cyber adversaries employ increasingly sophisticated tactics, businesses must be proactive, always looking ahead and anticipating the next potential threat. Endpoint security, while a crucial component, is just one piece of the puzzle. The real key to robust protection lies in continuous learning and adaptation.
The realm of endpoint security is dynamic, with new vulnerabilities, threats, and solutions emerging regularly. To truly safeguard your business assets, it’s imperative to stay updated with the latest trends, technologies, and best practices. This not only ensures that your defenses are up-to-date but also empowers you with the knowledge to make informed decisions.
Our website is dedicated to providing you with the educational resources you need in this journey. From in-depth articles to interactive webinars, we aim to be your go-to source for all things related to endpoint security. We encourage you to explore, engage, and enrich your understanding. After all, in the cybersecurity game, knowledge is not just power—it’s protection.
Stay vigilant, stay informed, and stay ahead.

Experienced cybersecurity analyst, software engineer, patent attorney, worked with Linux, Windows, AWS, lots of security tools. Hope to help people do the right things and do the things right!


