Introduction: Why You Can’t Ignore CIS Controls in 2024
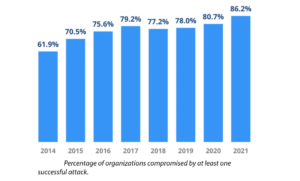
In today’s digital landscape, the rising cybersecurity threats targeting small businesses are more alarming than ever. As depicted in the bar chart, the number of incidents has surged over the past decade. This leaves many small businesses vulnerable. This escalating risk brings us to a crucial question. The question is what are CIS Controls, and how can they fortify your business against these threats?
Designed to offer robust cybersecurity, CIS Controls serve as a comprehensive guide for organizations to navigate the complexities of modern cyber threats. Read on to discover how implementing these controls can be a game-changer for your small business in 2024 and beyond.
What are CIS Controls? A Primer
CIS Controls is short for Center for Internet Security Critical Security Controls. CIS Controls are a set of actionable guidelines designed to bolster cybersecurity. Originating from a collaborative effort among cybersecurity experts, these controls have evolved to become an industry standard.
In a world where cyber threats are increasingly sophisticated, the importance of CIS Controls cannot be overstated. They serve as a roadmap for organizations, especially small businesses, to identify vulnerabilities and take preventive measures. By adhering to these controls, you’re complying with regulations. But you’re also building a resilient cybersecurity infrastructure for the long haul.
The Evolution of CIS Controls: From Inception to v8
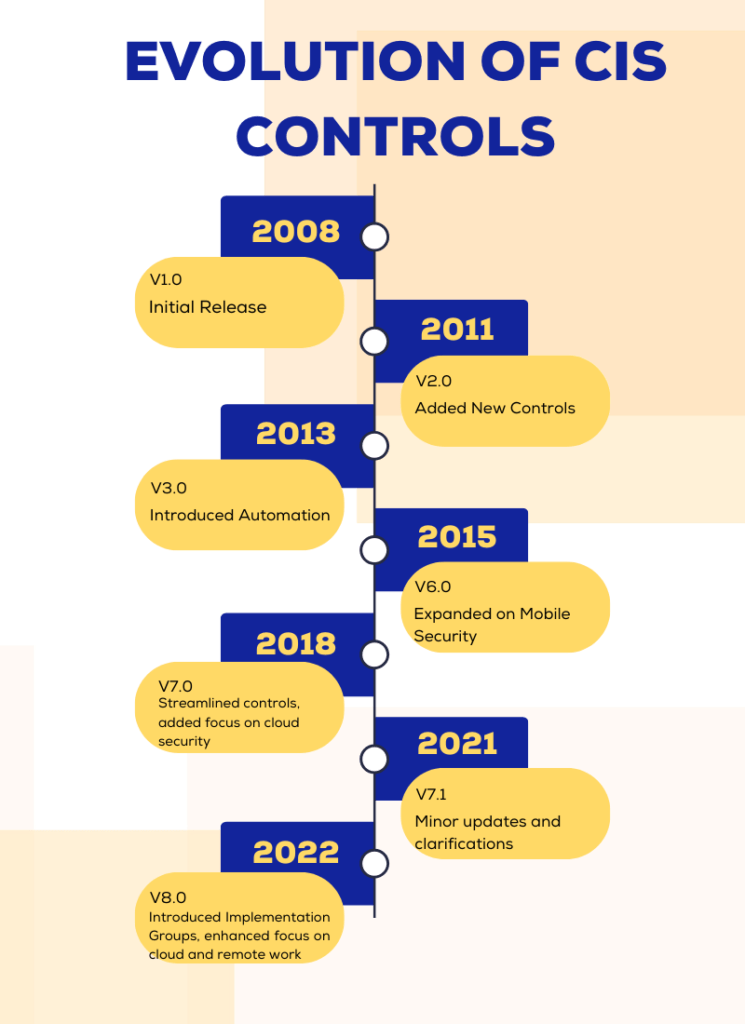
The journey of CIS Controls has been one of continuous evolution, adapting to meet the ever-changing landscape of cybersecurity threats. Our infographic provides a concise timeline. It highlights key versions and their respective features, from the initial release in 2008 to the latest version, v8, in 2022.
Brief History and Versions
Starting as a collaborative initiative among cybersecurity experts, CIS Controls have undergone several updates to stay ahead of emerging threats. Each version aimed to address specific challenges. These challenges were from the introduction of mobile security in v6.0 to the enhanced focus on cloud security in v7.0.
Introduction to CIS Controls v8
The most recent version, CIS Controls v8, brings significant updates tailored for the modern digital environment. One of the standout features is the introduction of Implementation Groups (IGs). IGs are designed to make the controls more adaptable for organizations of different sizes and needs. Additionally, v8 places a heightened focus on securing cloud infrastructure and facilitating remote work. Thus, making it highly relevant for today’s decentralized work settings.
Understand the evolution of CIS Controls. Doing so, you’ll gain a deeper appreciation for their role in shaping a resilient cybersecurity strategy.
Why Small Businesses Need CIS Controls
Small businesses often operate under the misconception that they’re too insignificant to be targeted by cybercriminals. However, the reality is quite the opposite. Small businesses are increasingly becoming lucrative targets due to their generally weaker security measures.
Risk Minimization
Implementing CIS Controls can drastically reduce the risk of cyber threats. These controls act as a comprehensive checklist that covers everything from data protection to network security. By following these guidelines, small businesses can identify vulnerabilities and take proactive measures to mitigate risks.
Compliance with Regulations
Beyond risk minimization, CIS Controls also help in achieving compliance with various industry regulations. Whether it’s GDPR in Europe or CCPA in California, these controls align well with the requirements set forth by these regulations. Being compliant not only avoids hefty fines but also builds trust with clients and stakeholders.
In summary, CIS Controls are not just a cybersecurity luxury; they’re a necessity for small businesses aiming to safeguard their assets and reputation.
Breaking Down the 18 CIS Controls
Understanding the 18 CIS Controls can seem daunting at first glance, but they’re organized in a way that makes them approachable and actionable. Let’s break them down into three main categories: Basic, Foundational, and Organizational controls.
Overview of the 18 Controls
The 18 CIS Controls cover a broad spectrum of cybersecurity measures, ranging from inventory and control of hardware assets to data protection and incident response. Each control is designed to address specific vulnerabilities and risks that organizations face.
Basic Controls
These are the essential controls that every organization, regardless of size, should implement. They lay the groundwork for a secure infrastructure and include measures like continuous vulnerability assessment and secure configuration.
The Basic Controls are:
- C01: Inventory and Control of Enterprise Assets
- C02: Inventory and Control of Software Assets
- C03: Data Protection
- C04: Secure Configuration of Assets and Software
- C05: Account Management
- C06: Access Control Management
Foundational Controls
Once the basic controls are in place, the next step is to implement foundational controls. These are more specialized measures that provide a deeper level of security. Examples include data protection and secure data recovery.
The Foundational Controls are:
- C07: Continuous Vulnerability Management
- C08: Audit Log Management
- C09: Email and Web Browser Protections
- C10: Malware Defenses
- C11: Data Recovery
- C12: Network Infrastructure Management
- C13: Network Monitoring and Defense
Organizational Controls
These are advanced controls tailored for organizations with more complex needs. They focus on areas like incident response planning and penetration testing. Implementing these controls requires a higher level of expertise and resources.
By categorizing the controls into these three groups, CIS Controls offer a scalable approach to cybersecurity, making it easier for small businesses to prioritize and implement the most relevant measures.
The Organizational Controls are:
- C14: Security Awareness
- C15: Service Provider Management
- C16: Application Software Security
- C17: Incident Response Management
- C18: Penetration Testing

Implementation Groups: Tailoring CIS Controls to Your Needs
CIS Controls v8 introduces the concept of Implementation Groups (IGs), designed to make cybersecurity more accessible and manageable for organizations of all sizes. These groups—IG1, IG2, and IG3—serve as a framework for tailoring the 18 controls to your specific needs.
Explanation of IG1, IG2, and IG3
- IG1: This group is designed for smaller organizations or those with less sensitive data. It focuses on implementing the Basic Controls to establish a foundational level of security.
- IG2: Aimed at medium-sized organizations, IG2 incorporates both Basic and Foundational Controls. It offers a more robust level of security suitable for businesses with moderate risk profiles.
- IG3: This group is intended for larger organizations or those with high-risk profiles. It encompasses all 18 controls, including the Organizational Controls, providing the most comprehensive level of security.
Choosing the Right Implementation Group for Small Businesses
For small businesses, the choice between IG1, IG2, and IG3 will largely depend on the nature of the data you handle and the level of risk you’re willing to accept.
- If you’re a small retail business with minimal customer data, IG1 may suffice.
- If you’re in healthcare or finance and handle sensitive information, you might consider IG2 or even IG3.
By understanding the nuances of these Implementation Groups, small businesses can make informed decisions on how to best apply CIS Controls, balancing both security needs and resource availability.
Real-world Applications: CIS Controls in Action
CIS Controls aren’t just theoretical guidelines; they have real-world applications that have proven effective in enhancing cybersecurity. Let’s delve into two case studies that demonstrate their impact.
A Midwestern State Credit Union
This credit union used CIS Controls to strengthen its cybersecurity posture. By implementing the controls, they were able to identify vulnerabilities and take proactive measures, thereby safeguarding sensitive financial data.
School District Enhances Cyber Hygiene
A school district successfully used CIS Controls to improve its cyber hygiene. The controls helped them secure student data and protect their network from potential threats.
Testimonials
Prominent figures and organizations have endorsed the effectiveness of CIS Controls:
- Kamala D. Harris, Attorney General, California Department of Justice:“The [CIS Controls] identify a minimum level of information security that all organizations that collect or maintain personal information should meet.”
- Jim Long, Managing Partner, The Long Law Firm, PLLC:“We use the CIS Controls to help our clients achieve compliance…I highly recommend starting with CIS in building your cybersecurity program.”
These case studies and testimonials underscore the practical utility of CIS Controls, especially for small businesses aiming to bolster their cybersecurity measures.
How to Implement CIS Controls: A Step-by-Step Guide
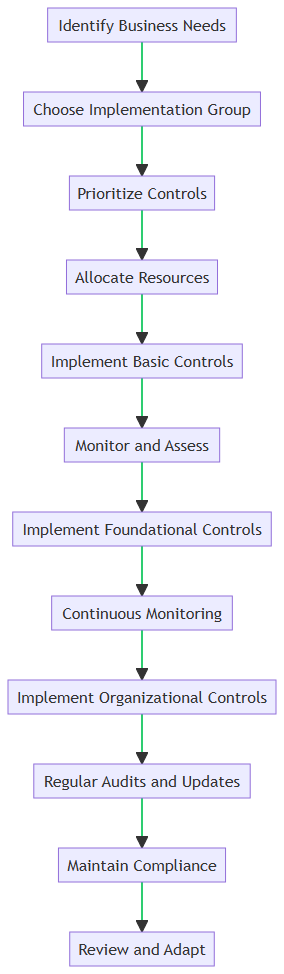
The accompanying flow chart above outlines the practical steps small businesses can take to implement CIS Controls effectively. Here’s a brief explanation of each step:
- Identify Business Needs: Understand the specific cybersecurity needs of your business.
- Choose Implementation Group: Select the appropriate Implementation Group (IG1, IG2, or IG3) based on your risk profile.
- Prioritize Controls: Decide which controls to implement first, based on your chosen Implementation Group.
- Allocate Resources: Assign personnel and budget for the implementation.
- Implement Basic Controls: Start with the Basic Controls like inventory management and data protection.
- Monitor and Assess: Continuously monitor the effectiveness of the implemented controls.
- Implement Foundational Controls: Once Basic Controls are in place, move on to Foundational Controls like vulnerability management.
- Continuous Monitoring: Keep an eye on your security posture and make adjustments as needed.
- Implement Organizational Controls: For those who need advanced security measures, implement Organizational Controls.
- Regular Audits and Updates: Conduct periodic audits to ensure compliance and update controls as necessary.
- Maintain Compliance: Keep up with regulatory requirements to avoid penalties.
- Review and Adapt: Regularly review your cybersecurity strategy and adapt to new threats and business needs.
Overcoming Challenges in Implementing CIS Controls
Implementing CIS Controls is a commendable step toward robust cybersecurity, but it’s not without its challenges. Let’s explore some common obstacles and how to overcome them.
Common Obstacles
- Resource Constraints: Small businesses often operate on limited budgets and manpower.
- Technical Complexity: The technical aspects of implementing controls can be daunting.
- Compliance Overload: Keeping up with various regulations can be overwhelming.
- Resistance to Change: Employees may resist new security measures.
Solutions and Best Practices
Resource Constraints
- Solution: Prioritize controls based on your risk profile and start small.
- Best Practice: Use free or low-cost tools initially, and invest in more advanced solutions as you grow.
Technical Complexity
- Solution: Leverage guides and templates to simplify the implementation process.
- Best Practice: Consider hiring or consulting with a cybersecurity expert for complex controls.
Compliance Overload
- Solution: Use compliance management platforms to keep track of requirements.
- Best Practice: Regularly review and update your compliance documentation.
Resistance to Change
- Solution: Educate employees on the importance of cybersecurity.
- Best Practice: Make cybersecurity training a regular part of employee onboarding and ongoing education.
By understanding these challenges and applying the suggested solutions and best practices, you can navigate the complexities of implementing CIS Controls more effectively.
The Future of CIS Controls: What to Expect
As the landscape of cybersecurity threats continues to evolve, CIS Controls are also expected to undergo changes to stay relevant. You can anticipate new versions that tackle emerging threats, an expanded scope to include controls for new technologies like IoT and AI, and closer alignment with changing regulations. To stay updated on these developments, regularly visit the official CIS website, subscribe to relevant cybersecurity newsletters, and participate in industry webinars and conferences. Social media platforms like LinkedIn and Twitter are also excellent sources for real-time updates from CIS and cybersecurity experts. By staying informed, you can ensure your cybersecurity measures remain effective and up to date.
Conclusion: Your Next Steps in Mastering CIS Controls
In today’s digital age, cybersecurity is more crucial than ever, especially for small businesses. Implementing CIS Controls provides a structured and effective approach to safeguarding your business assets. From understanding the basics and choosing the right implementation group to overcoming challenges and staying updated on future developments, this guide aims to be a comprehensive resource for small businesses. We encourage you to share your experiences or questions in the comment section below. Your insights could be invaluable to others on the same cybersecurity journey.

Experienced cybersecurity analyst, software engineer, patent attorney, worked with Linux, Windows, AWS, lots of security tools. Hope to help people do the right things and do the things right!
