Introduction

In the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity, few terms evoke as much concern as “zero-day vulnerabilities.” These are the hidden flaws within software that, when exploited, can wreak havoc before anyone even realizes there’s a problem. This article seeks to answer the question, what is a zero-day vulnerability, and how to protect yourself from it.
In the past year, a zero-day attack dubbed “Linux Polkit” sent shockwaves through the small business community. This exploit targeted Linux systems, a cornerstone for many small enterprises, leaving them vulnerable to unauthorized access and data breaches.
What is a Zero-Day Vulnerability: Breaking it Down
A zero-day vulnerability is a software flaw that is unknown to those who should be interested in mitigating the vulnerability, including the vendor of the target software. The “zero-day” term implies that developers have “zero days” to fix the issue. Thus, leaving systems exposed until a patch is developed and deployed.
But how does this differ from other types of vulnerabilities? Unlike known vulnerabilities, which are publicly disclosed and often have patches available, zero-day vulnerabilities are undisclosed and unpatched. This makes them a prime target for cybercriminals who exploit these flaws before a fix becomes available.
Why Small Businesses Should Be Concerned
Small businesses often think they’re too small to be targeted, but that’s a misconception. Zero-day vulnerabilities can affect any business, regardless of its size. In fact, small businesses can be more susceptible due to limited cybersecurity resources.
Understanding the sectors most affected can help small business managers and IT personnel prioritize their cybersecurity strategies effectively.
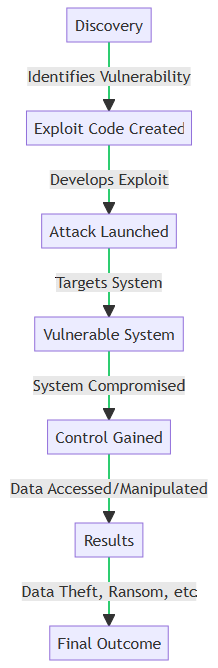
The Anatomy of a Zero-Day Attack
At its core, a zero-day attack is a sequence of events that unfolds like a well-planned heist. First, a hacker discovers a hidden flaw or “loophole” in a software. This is the vulnerability that hasn’t been found by the software’s creators yet.
Next, the hacker crafts a special code, known as an “exploit,” designed to take advantage of this flaw. Think of it as a digital lockpick.
Once the exploit is ready, the attacker launches it against the target system. If successful, they gain unauthorized access, essentially “breaking in” to the system.
Finally, the attacker can do what they came for—whether it’s stealing sensitive data, installing malware, or setting the stage for future attacks.
Real-World Examples: Zero-Day Attacks You Should Know
Case Study 1: The SolarWinds Attack
In late 2020, SolarWinds, a company that provides software to numerous small businesses, fell victim to a zero-day attack. The attackers cleverly inserted malicious code into the company’s software updates. Small businesses that updated their software unknowingly invited the attackers into their systems. This leads to data breaches, compromised security, and financial loss. This incident serves as a stark reminder to always verify the source of your software updates and to employ multi-layered security measures.
Case Study 2: The Kaseya Ransomware Attack
In July 2021, Kaseya, a provider of IT management software, was hit by a ransomware attack. The attackers exploited a zero-day vulnerability to deploy ransomware across Kaseya’s client base, many of whom were small businesses. The attack led to a disruption of services, data loss, and ransom payments. The key takeaway here is the importance of regularly updating your cybersecurity protocols and educating your team on cybersecurity hygiene.
These case studies offer valuable insights into the real-world impact of zero-day attacks on small businesses. These cases serve as cautionary tales that underscore the need for robust cybersecurity measures.
How Are Zero-Day Vulnerabilities Discovered?
Zero-day vulnerabilities are often discovered in a variety of ways, ranging from accidental findings to intentional research. Security researchers play a pivotal role in this process. They actively probe software and systems to identify potential weaknesses. They often work in ethical hacking environments known as “bug bounty programs.”
Software vendors also contribute to the discovery process. They regularly conduct internal audits and tests to identify vulnerabilities in their own products. However, despite these efforts, some vulnerabilities escape detection and become zero-day threats.
The relationship between security researchers and software vendors is crucial. Researchers often report their findings to vendors. This initiates a race against time to develop and deploy a patch before hackers can exploit the vulnerability.
How to Protect Your Business: Actionable Steps
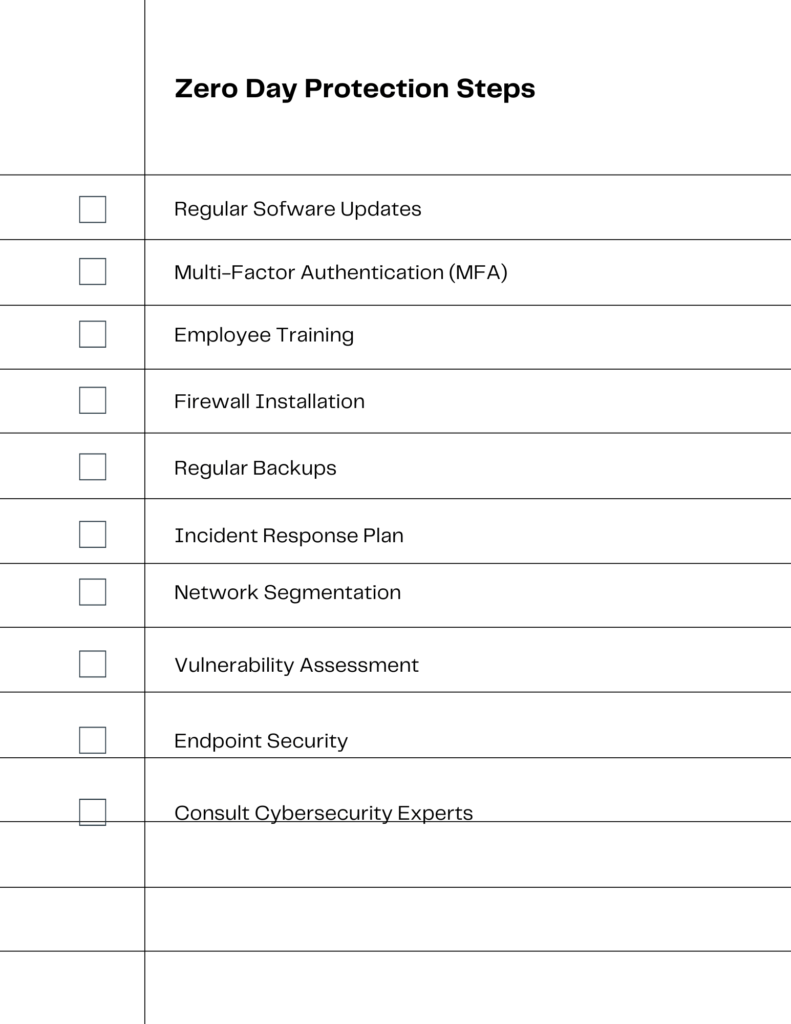
Protecting your business from zero-day vulnerabilities starts with regular software updates to minimize potential risks. Adding an extra layer of security through Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) can further safeguard your systems. Employee training is essential; make sure your team knows cybersecurity best practices and how to spot phishing attempts. A robust firewall can block unauthorized access, while regular backups of critical data offer a safety net. Having an incident response plan in place prepares you for potential cyberattacks. Network segmentation can contain the damage from any breaches. Regular vulnerability assessments help identify weak points in your security. Endpoint security solutions monitor and secure entry points into your network. For tailored solutions, consult cybersecurity experts to assess your specific needs.
The Role of Antivirus Software and Security Patches
Antivirus software and security patches serve as the first line of defense against zero-day vulnerabilities. Antivirus software continuously scans your system for malicious activities and known vulnerabilities, offering real-time protection. While it may not always catch zero-day exploits, it can often detect unusual behavior that could indicate a compromise.
Security patches, on the other hand, are updates released by software vendors to fix known vulnerabilities. These patches are crucial in closing the loopholes that could be exploited in a zero-day attack. It’s essential to apply these patches as soon as they are released to keep your systems secure.
Together, antivirus software and security patches create a multi-layered defense strategy, making it difficult for attackers to penetrate your system. They are indispensable tools in your cybersecurity arsenal.
Conclusion: The Importance of Being Proactive
Understanding zero-day vulnerabilities is not just a matter of technical curiosity; it’s a business imperative. These vulnerabilities can compromise your data, disrupt your operations, and tarnish your reputation. Take proactive steps, such as regular software updates, employee training, and employing antivirus software and security patches. Doing so, you can fortify your business against these unpredictable threats.
We encourage you to share your experiences or questions in the comments section below. Your insights could be invaluable to other small business managers and IT personnel navigating the complex landscape of cybersecurity.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What Is a Zero-Day Vulnerability?
A zero-day vulnerability is a software flaw unknown to the vendor, making it a ripe target for hackers. It’s called “zero-day” because developers have zero days to fix it once it’s discovered by the public.
2. How Do Zero-Day Attacks Affect Small Businesses?
Zero-day attacks can have severe consequences for small businesses, including data breaches, financial loss, and reputational damage. Small businesses often lack the resources for robust cybersecurity, making them attractive targets.
3. How Can I Protect My Business from Zero-Day Vulnerabilities?
Protection involves a multi-layered approach, including regular software updates, employee training, and the use of antivirus software and security patches. It’s crucial to stay vigilant and proactive in your cybersecurity measures.

Experienced cybersecurity analyst, software engineer, patent attorney, worked with Linux, Windows, AWS, lots of security tools. Hope to help people do the right things and do the things right!
