Introduction: The Rising Importance of IoT in 2023
In the digital age, the Internet of Things (IoT) has emerged as a revolutionary force, reshaping how businesses operate and individuals live. From smart thermostats regulating our home temperatures to intricate sensors optimizing supply chains, IoT devices have seamlessly woven themselves into the fabric of our daily lives. As highlighted in Guide to IoT, the evolution of IoT has been nothing short of transformative, with billions of devices now interconnected, communicating, and sharing data in real-time. It is critical to consider what the best practices for IoT security are.
Yet, with this immense power and potential comes a pressing responsibility. For small businesses, in particular, IoT security isn’t just a technical concern—it’s a business imperative. As discussed in Introduction to IoT Security, the increasing reliance on IoT devices brings forth a myriad of security challenges.
A single vulnerability can lead to data breaches, operational disruptions, and significant financial losses. Moreover, for small businesses that often lack the vast resources of larger corporations, the stakes are even higher. A compromised IoT device can erode customer trust, tarnish reputations, and jeopardize the very survival of the business.
In 2023, as the IoT landscape continues to expand and evolve, understanding and implementing best practices for IoT security is not just a recommendation—it’s a necessity. Small businesses stand at the forefront of this digital frontier, and ensuring the security of their IoT devices is paramount to harnessing the full potential of this technological marvel.
Why Every Small Business Manager Should Prioritize IoT Security
The transformative power of the Internet of Things (IoT) for businesses is undeniable. By seamlessly integrating physical devices with digital systems, IoT has unlocked new avenues for innovation, efficiency, and growth. For small businesses, this transformation is particularly profound.
The Transformative Power of IoT for Business Operations
- Supply Chain Optimization: Consider a local retailer that uses IoT sensors to monitor inventory levels in real-time. These sensors can automatically reorder stock when levels are low, ensuring that the business never runs out of essential products. This not only improves customer satisfaction but also streamlines operations and reduces overhead costs.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: Take the example of a small cafe that employs smart thermostats and lighting systems. By adjusting the ambiance based on customer preferences and external factors like weather, the cafe can offer a personalized and comfortable environment, leading to increased customer loyalty and repeat visits.
However, the benefits of IoT come with significant responsibilities. The interconnected nature of these devices means that a security lapse in one area can have cascading effects throughout the business.
Real-world Consequences of Neglecting the Best Practices for IoT Security
- Data Breaches: A compromised IoT device can provide hackers with a gateway to a business’s entire network. This can lead to unauthorized access to sensitive customer data, financial records, and proprietary information. The aftermath of such breaches can be devastating, with legal repercussions, financial losses, and a tarnished reputation.
- Operational Disruptions: An insecure IoT system can be exploited to disrupt business operations. Imagine a smart manufacturing unit being remotely shut down by a hacker, leading to production halts, missed deadlines, and lost revenue.
While we’ll delve deeper into specific real-world examples later in this article, these brief instances underscore the urgency of prioritizing IoT security. For small business managers, understanding and addressing these vulnerabilities is not just about safeguarding operations—it’s about ensuring the long-term viability and success of the business in an increasingly digital world.
Challenges in IoT Security: Beyond the Basics
The realm of cybersecurity has always been a dynamic and evolving field. However, with the advent of the Internet of Things (IoT), the challenges have multiplied, introducing complexities that traditional cybersecurity measures weren’t initially designed to address.
Traditional Cybersecurity vs. IoT Security: A Comparative Look
| Aspect | Traditional Cybersecurity | IoT Security |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Protecting centralized servers and databases | Safeguarding a decentralized network of interconnected devices |
| Threat Landscape | Malware, phishing, DDoS attacks | Device tampering, data interception, unauthorized device access |
| Scale of Devices | Limited to computers and servers | Billions of diverse devices from wearables to industrial sensors |
| Update Mechanism | Regular software updates and patches | Challenges in updating embedded systems in real-time |
| Data Flow | Predominantly one-way data flow | Multi-directional data flow between devices, local networks, and the cloud |
| User Interaction | Direct user interaction with most devices | Many devices operate autonomously without regular user interaction |
The table above underscores the fundamental differences between traditional cybersecurity and the challenges posed by IoT. While traditional measures focus on safeguarding centralized systems, IoT security must address a vast, decentralized network of diverse devices, each with its unique vulnerabilities.
The Vast and Complex IoT Ecosystem: A Challenge in Itself
The IoT ecosystem is not just vast—it’s staggeringly complex. From simple sensors in a home thermostat to intricate machinery in manufacturing units, the range of devices is vast. Each device generates, transmits, processes, and stores data, often in real-time. This continuous flow of information across a myriad of devices creates a web of interdependencies.
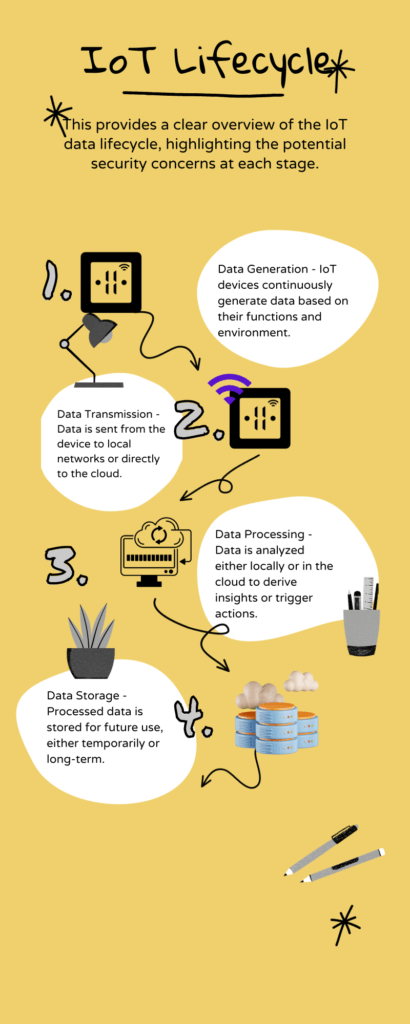
IoT Lifecycle Flowchart: Visualize this complexity through a flowchart showcasing the lifecycle of data in the IoT ecosystem. Start with how data is generated by an IoT device, move to its transmission over networks, illustrate its processing (either locally or in the cloud), and conclude with its storage. At each stage, pinpoint potential security risks, such as “device tampering,” “data interception,” or “unauthorized cloud access.”
This intricate web poses a significant challenge for security professionals. A vulnerability in one device can have cascading effects, compromising the integrity of the entire network. Moreover, the diverse nature of IoT devices, each with its operating systems, protocols, and interfaces, makes standardizing security measures a daunting task.
The IoT Lifecycle
The infographic shows a representation of the IoT lifecycle. The table below gives the security issues associates with each step.
| Step | Description | Security Concern |
| Device Generation | IoT devices continuously generate data based on their functions and environment. | Device Tampering – Physical access to devices can lead to data manipulation or theft. |
| Data Transmission | Data is sent from the device to local networks or directly to the cloud. | Data Interception – Unencrypted data can be intercepted during transmission. |
| Data Processing | Data is analyzed either locally or in the cloud to derive insights or trigger actions. | Unauthorized Access – Inadequate security protocols can allow unauthorized access to data during processing. |
| Data Storage | Processed data is stored for future use, either temporarily or long-term. | Vulnerabilities in storage systems can lead to large-scale data breaches. |
In essence, the very features that make IoT revolutionary—its scale, diversity, and interconnectedness—also make it a formidable challenge from a security standpoint. For small businesses venturing into the IoT landscape, understanding these challenges is the first step towards crafting a robust security strategy.
Real-world Examples: The High Cost of Ignoring The Best Practices for IoT Security
The theoretical discussions around IoT security are essential, but nothing drives home the point more effectively than real-world examples. These incidents underscore the tangible consequences businesses face when they neglect the security of their IoT devices.
1. The Infamous Baby Monitor Hack:
In a chilling incident that made headlines, parents were horrified to discover that their internet-connected baby monitor had been hacked. An unauthorized user gained access to the camera, not only watching the baby but also communicating with the child. This breach highlighted the vulnerabilities of everyday IoT devices and the very real threats to privacy and safety.
Lesson Learned: Even seemingly innocuous devices, like baby monitors, can be gateways for cybercriminals. Ensuring robust password protection and regularly updating device firmware are critical steps in preventing such breaches.
2. The Massive DDoS Attack via IoT Devices:
In 2016, a Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack, one of the largest of its kind, disrupted major websites like Twitter, Netflix, and Reddit. The attack was orchestrated using a botnet comprising thousands of compromised IoT devices, including cameras and routers. By leveraging these devices, hackers were able to flood servers with overwhelming traffic, causing widespread outages.
Lesson Learned: The interconnected nature of IoT devices means that a vulnerability in one can have cascading effects. Businesses must be vigilant about securing every device, understanding that each one can be a potential entry point for cyberattacks.
While we’ll delve deeper into more specific examples later in this article, these incidents serve as stark reminders of the high stakes involved. For small businesses, the repercussions of such breaches can be even more severe, with potential financial losses, reputational damage, and legal consequences. Prioritizing IoT security isn’t just a technical necessity—it’s a business imperative.
Understanding Common Vulnerabilities in IoT
The rapid proliferation of the Internet of Things (IoT) has ushered in a new era of connectivity, with devices ranging from smart thermostats to industrial sensors becoming integral parts of our daily lives. However, with this expansion comes a myriad of security vulnerabilities that businesses and individuals must be aware of.
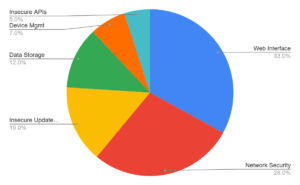
A recent pie chart, based on data up to January 2022, provides a snapshot of the most common security vulnerabilities in IoT devices.
It’s essential to note that these percentages provide a general indication rather than exact numbers. For those seeking a deeper dive into IoT vulnerabilities, authoritative sources like OWASP and NIST offer comprehensive insights and guidelines.
1. Insecure Web Interface
Devices with web interfaces often come with default settings that can be easily exploited if not changed. This category includes vulnerabilities like weak default credentials, lack of password protection, and exposed administrative panels.
2. Insufficient Network Security
This vulnerability pertains to the ways devices communicate with each other and the broader internet. Unencrypted data transmission, open ports, and the use of outdated protocols can leave devices susceptible to attacks.
3. Lack of Secure Update Mechanism
Devices that don’t have a secure way to update their software or firmware are at risk. Outdated software can have known exploits that hackers can use to gain unauthorized access.
4. Insecure Data Storage
Storing sensitive data without proper encryption or in easily accessible locations can lead to data breaches. This vulnerability is especially concerning for devices that store personal or business-critical information.
5. Lack of Device Management
Without proper device management capabilities, users might not be able to change passwords, implement two-factor authentication, or manage multiple devices efficiently.
6. Insecure APIs
APIs, or Application Programming Interfaces, allow devices to communicate with each other. Insecure APIs can lead to unauthorized access, data breaches, and other security incidents.
Outdated software, weak passwords, and other factors play a significant role in these vulnerabilities. Regularly updating devices, using strong, unique passwords, and staying informed about the latest threats are crucial steps in mitigating these vulnerabilities and ensuring the security of IoT devices.
Best Practices for Securing Your IoT Devices
As the Internet of Things (IoT) continues to weave its way into the fabric of our daily lives and business operations, ensuring the security of these devices becomes paramount. While the vulnerabilities are many, the good news is that with proactive measures, many of these threats can be mitigated. Here are some best practices to help secure your IoT devices:
1. Regular Software Updates
One of the most effective ways to protect your IoT devices is by keeping their software up-to-date. Manufacturers often release updates to patch known vulnerabilities and improve device security.
Outdated software can have known exploits that hackers can leverage to gain unauthorized access. Because of this, it is important to enable automatic updates when available. If this isn’t an option, regularly check the manufacturer’s website for updates and apply them promptly.
2. Strong Password Policies
Default passwords or weak passwords are a hacker’s delight. Ensuring that your devices are protected by strong, unique passwords is a simple yet crucial step.
Weak passwords can be easily guessed or cracked, giving attackers easy access to your device and potentially your entire network. Because of this, it is important to make sure that users use passwords that combine uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special symbols. Avoid using easily guessable information like birthdays or names. There is software that will look at passwords to make sure that the name of the site, the user, or other easily guessed passwords are not used as well.
3. Multi-factor Authentication (MFA)
MFA adds an additional layer of security by requiring two or more verification methods: something you know (password), something you have (a smart card or phone), or something you are (fingerprint or facial recognition).
Note that even if a hacker manages to steal your password, MFA can prevent unauthorized access. Therefore, it is important to enable MFA on all devices and platforms that support it. It’s a small inconvenience for a significant security boost.
4. Network Security Measures and Monitoring
Your IoT devices are only as secure as the network they’re connected to. Implementing robust network security measures can shield your devices from potential threats.
An insecure network can be a gateway for hackers to access all connected devices. Therefore, it is recommended that you:
- Use firewalls to block unauthorized access to your network.
- Create separate network segments for your IoT devices, so even if one device is compromised, the attacker can’t easily move to other parts of the network.
- If you’re accessing your IoT devices remotely, use a Virtual Private Network (VPN) to encrypt your connection.
- Regularly monitor network traffic for any unusual activity. Tools like intrusion detection systems can alert you to potential threats.
By implementing these best practices, businesses and individuals can significantly reduce the risks associated with IoT devices. In an era where connectivity is king, ensuring the security of our connected devices is not just a technical necessity—it’s a responsibility.
The Role of AI and ML in Enhancing IoT Security
The rapid expansion of the Internet of Things (IoT) has brought forth a plethora of opportunities and, with it, a host of security challenges. As the number of connected devices continues to grow, traditional security measures often fall short. This is where Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) step in, revolutionizing the way we approach IoT security.
Continuous Data Feed
IoT devices are constantly sending a stream of data to the AI system, as depicted by the arrows pointing towards the AI brain. This continuous data feed allows the AI to have a real-time understanding of each device’s state and activities.
Real-time Analysis and Predictive Threat Analysis
Within the AI brain, the lightning bolts or processing symbols indicate the real-time analysis of data patterns. AI doesn’t just passively receive this data; it actively processes and analyzes it. This capability enables predictive threat analysis, where AI can forecast potential security threats before they manifest, offering a proactive approach to security.
Machine Learning and Adaptation
The circular arrow emerging from and returning to the AI brain represents the machine learning feedback loop. ML algorithms learn from the data patterns, continuously refining their threat detection capabilities. Over time, the system becomes more adept at identifying even the subtlest of anomalies, ensuring that security measures evolve in tandem with emerging threats.
Proactive Security Measures
Finally, the arrows from the AI brain pointing back to the IoT devices symbolize the security actions or alerts being dispatched. With its real-time monitoring and predictive analysis, AI can detect anomalies and take immediate measures, whether it’s isolating a device, sending an alert, or patching a vulnerability.
In the vast and intricate world of IoT, AI and ML serve as vigilant guardians, always learning, always adapting, and always ready to defend. Their role in enhancing IoT security is not just beneficial—it’s indispensable.
Building a Secure IoT Ecosystem for Your Business
In today’s interconnected world, businesses cannot afford to be complacent about the security of their IoT devices. Building a secure IoT ecosystem requires a proactive approach, starting with a thorough audit of the current infrastructure and followed by the implementation of tailored security policies. Here’s how to go about it.
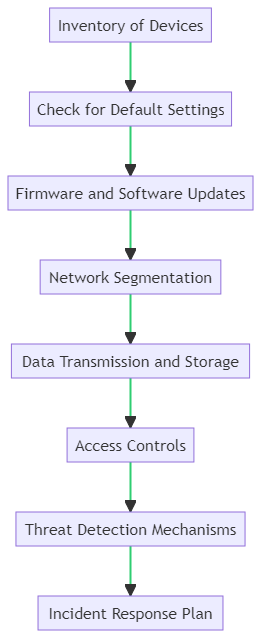
Steps to Audit and Assess Your Current IoT Infrastructure
- Inventory of Devices:
- Description: Begin by creating a comprehensive list of all IoT devices in your organization. This includes everything from smart thermostats to industrial sensors.
- Check for Default Settings:
- Description: Many IoT devices come with default settings that can be easily exploited. Ensure that these have been changed, especially default usernames and passwords.
- Firmware and Software Updates:
- Description: Ensure that all devices are running the latest firmware and software versions. Manufacturers often release updates to patch known vulnerabilities.
- Network Segmentation:
- Description: Check if your IoT devices are on a separate network segment. This can prevent potential attackers from accessing critical business systems if they compromise an IoT device.
- Data Transmission and Storage:
- Description: Assess how data from IoT devices is transmitted and stored. Ensure that data is encrypted both in transit and at rest.
- Access Controls:
- Description: Determine who has access to each IoT device and ensure that access controls are in place. Only authorized personnel should have access.
- Threat Detection Mechanisms:
- Description: Check if there are mechanisms in place to detect unusual activity or potential threats in real-time.
- Incident Response Plan:
- Description: Ensure that there’s a plan in place detailing how to respond if an IoT device is compromised.
Implementing Security Policies Tailored to IoT
IoT devices present unique security challenges, and thus, generic security policies might not be sufficient. Here’s how to tailor your security policies to the IoT landscape:
- Device Authentication: Implement multi-factor authentication for IoT devices, ensuring that only authorized devices can connect to your network.
- Regular Security Training: Organize training sessions for employees to educate them about the unique security challenges posed by IoT devices and how to mitigate them.
- Data Privacy Policies: Given that IoT devices often collect vast amounts of data, ensure that there are strict data privacy policies in place. This includes how data is collected, stored, and shared.
- Remote Access Restrictions: If IoT devices can be accessed remotely, ensure that secure methods like VPNs are used. Also, limit remote access to only essential personnel.
- Device Lifecycle Management: Have policies in place for the entire lifecycle of an IoT device, from procurement and installation to decommissioning and disposal.
By taking a proactive approach to IoT security, businesses can harness the power of interconnected devices without compromising on security. Remember, in the world of IoT, security is not a one-time task but an ongoing commitment.
Looking Ahead: The Future of IoT Security
The realm of the Internet of Things (IoT) is ever-evolving, with each passing year bringing new innovations, challenges, and solutions. As we stand on the cusp of a new era of interconnectedness, it’s essential to look ahead and understand the trajectory of IoT security.
Emerging Trends and Technologies in IoT Security
A Journey Through Time – IoT Security Evolution:
- 2010: Initial IoT Devices: The dawn of the IoT age was marked by excitement and innovation. However, in these early days, security often took a backseat, leading to vulnerabilities that hackers were quick to exploit.
- 2015: Rise of Smart Homes: The mid-2010s saw a surge in the popularity of smart homes. With devices controlling everything from lighting to security, the vulnerabilities became personal. This period marked a shift in manufacturers’ perspectives, emphasizing hardware-level security.
- 2020: Implementation of Standard Security Protocols: As IoT devices permeated industries from healthcare to agriculture, the need for standardized security protocols became paramount. This era saw the establishment of baseline security measures, ensuring a consistent level of protection across devices.
- 2025: Advanced AI-driven Security Measures: The near future promises a synergy between IoT and AI. With AI and machine learning at the helm, we can anticipate real-time threat detection, predictive analytics, and swift response mechanisms, marking a significant leap in proactive security measures.
- 2030: Fully Autonomous IoT Security Systems: Looking further ahead, the vision is of a world where IoT security systems operate with full autonomy. These systems would not just detect and respond to threats but would also learn, adapt, and preemptively counteract potential vulnerabilities, all without human intervention.
The Role of Government Regulations and Industry Standards:
As the IoT landscape expands, so does the scrutiny it falls under. Governments worldwide are recognizing the potential risks associated with insecure IoT devices. Regulations are being put in place to ensure manufacturers adhere to specific security standards, protecting consumers and businesses alike.
Industry standards, on the other hand, are often a step ahead of government regulations. Organizations like the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) are continuously updating their guidelines to reflect the latest in IoT security best practices.
In conclusion, the future of IoT security is a tapestry of technological advancements, regulatory frameworks, and industry-driven standards. As we move forward, the emphasis will be on proactive measures, ensuring that the IoT ecosystem remains resilient in the face of evolving threats.

Conclusion: Embracing The Best Practices for IoT Security with Confidence in 2023
The Internet of Things (IoT) has undeniably transformed the way we live and conduct business. From smart homes to interconnected industries, the possibilities seem endless. However, with great innovation comes great responsibility, especially in the realm of security.
Key Takeaways
- IoT’s Expansive Landscape: The vast and intricate world of IoT presents unique challenges, making it imperative for businesses to understand and address potential vulnerabilities.
- The Role of AI and ML: Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning are not just buzzwords; they’re at the forefront of revolutionizing IoT security, offering real-time threat detection and adaptive learning.
- Building a Secure Ecosystem: It’s not just about securing individual devices; it’s about creating a holistic, secure IoT ecosystem. This involves regular audits, tailored security policies, and staying updated with emerging trends.
- The Future is Proactive: Looking ahead, the emphasis is shifting from reactive to proactive security measures. The future promises systems that can autonomously detect, adapt, and counteract threats.
For businesses, the message is clear: IoT security is not a luxury; it’s a necessity. As we continue to integrate IoT into our operations, we must prioritize its security. It’s not just about protecting devices; it’s about safeguarding our data, our operations, and our future.
To all businesses venturing into the IoT landscape or those already immersed in it: Take a moment to assess your IoT security posture. Are you prepared for the challenges ahead? Remember, in the world of IoT, security is an ongoing commitment. Prioritize it today for a safer, more secure tomorrow.

Experienced cybersecurity analyst, software engineer, patent attorney, worked with Linux, Windows, AWS, lots of security tools. Hope to help people do the right things and do the things right!


