Understanding OWASP and Its Impact on IoT Security
The security of Internet of Things (IoT) devices remain a paramount concern. Various aspects of business and daily life now actively integrate IoT devices. Understanding the vulnerabilities and risks associated with these technologies is crucial. This brings us to the Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP). This project is a beacon of guidance in the murky waters of cybersecurity. The OWASP IoT Top 10 list serves as an essential resource for improving the security of IoT devices. Using this list, we can gain insights into the most pressing vulnerabilities. From that, we can learn how to safeguard our digital ecosystem effectively.
What’s this all about?
Let’s look at IoT security, focusing on the OWASP IoT Top 10 vulnerabilities. We will look at the significance of securing IoT devices. IoT devices have become integral to business operations and everyday life. This will highlight proactive measures against common vulnerabilities. It will stress the importance of regular updates. It will also emphasize the need for robust physical and network security.
We will:
- explore strategies for securing data transfer and storage
- look into managing device lifecycles
- -discuss the significance of privacy protection.

Surviving the Firestorm
This is our new book on Cybersecurity for small businesses. Written in an entertaining format, it is meant for to guide non-technical business owners through the concepts of cybersecurity, planning, and defense tactics. Currently available in Kindle Format.
Overview of the OWASP Top 10 IoT Vulnerabilities
Let’s understand the landscape of IoT security risks through the following infographic. It presents the OWASP Top 10 IoT vulnerabilities last updated in 2018. It highlights the most critical concerns that we must address. Each point on the list corresponds to a potential area of risk for IoT devices. Thus, underlining the importance of strategic security measures.
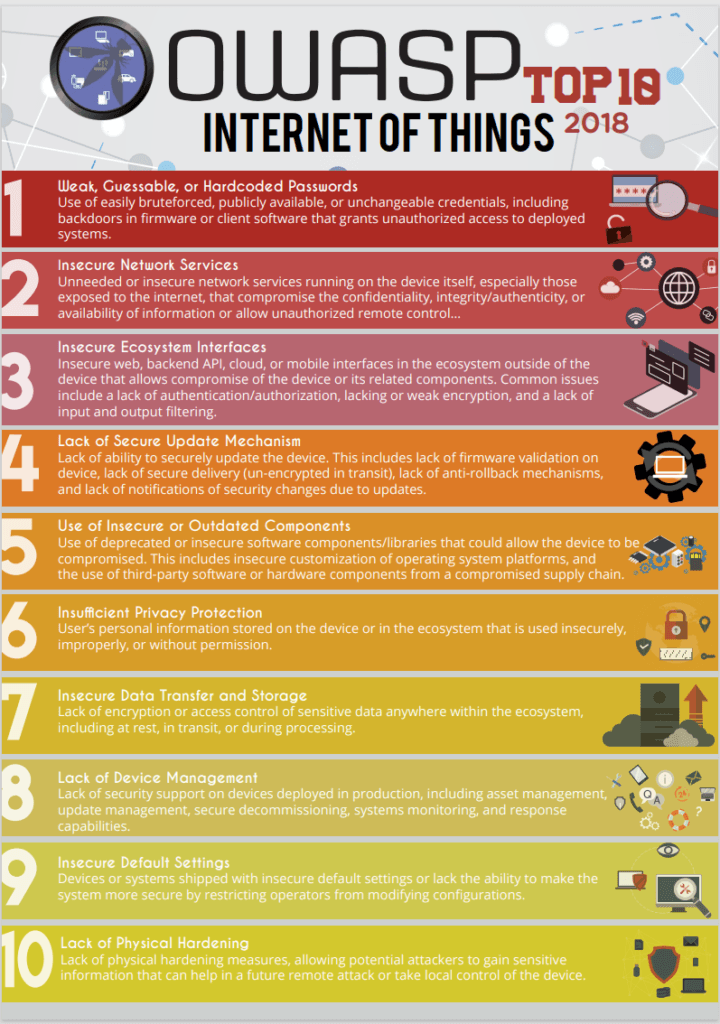
Source: OWASP-IoT-Top-10-2018-final.pdf
The OWASP IoT Top 10 list distills the most critical security vulnerabilities that are common in IoT devices. This list was compiled by security experts and is updated periodically. It reflects the changing landscape of IoT security risks. Each item on the list marks a weak point that malicious actors could exploit in IoT systems. These vulnerabilities include construction issues of IoT devices. Issues like using insecure or outdated components. At the other end of the spectrum are deployment and management challenges. These include things such as lacking secure update mechanisms or device management. Understanding these top 10 vulnerabilities. That is the first step in fortifying the security of IoT devices. Doing so protects sensitive data from unauthorized access.
Key Takeaways on IoT Security
The journey through the OWASP IoT Top 10 (2018) vulnerabilities highlights several key takeaways:
- Proactive Security Measures. Prevention is better than cure. Proactively securing IoT devices against known vulnerabilities is essential. You should address the lack of security that often plagues many IoT systems.
- Regular Updates and Patches. Keeping software and firmware up to date is crucial. It helps to protect against emerging threats and IoT security vulnerabilities.
- Physical and Network Security. Both implementing physical security measures and securing network services are critical. They help to prevent unauthorized access and data breaches.
- Privacy and Data Protection. Implementing strong data security and privacy measures is not just a legal requirement. It is also crucial for maintaining user trust.
- Comprehensive Device Management. Management of IoT devices is key to maintaining their security and functionality.
- Education and Awareness. Implement continual education and awareness about IoT security best practices. This is vital for both users and manufacturers.
Introduction to OWASP in Cybersecurity
OWASP stands as a cornerstone in the world of cybersecurity. OWASP is a non-profit foundation. It provides impartial, practical, and freely available information about computer security. It makes this available to individuals and organizations worldwide. The initiative has earned its reputation primarily for the influential OWASP Top 10 list. This list highlights the most critical web application security risks. OWASP operates under the philosophy that knowledge about security should be freely accessible. Thus, enabling everyone to understand and combat security vulnerabilities. Their work extends beyond traditional web applications. It plays a pivotal role in shaping the security landscape of emerging technologies like IoT.
Effective device management will be underscored as essential for IoT security. We will offer insights on best practices for safeguarding IoT ecosystems.
By addressing each vulnerability, businesses can protect their IoT infrastructure. Thus, a comprehensive plan can ensure these technologies are secure, reliable, and trustworthy.
It’s important to visualize the applications that IoT has in the enterprise setting. The infographic below illustrates key IoT devices. Devices play a pivotal role in operational efficiency. These include such devices as smart sensors, thermostats, and RFID tags. Consequently, we have the necessity for stringent security measures.
OWASP’s Role in IoT Security
OWASP has taken a proactive stance in IoT security. OWASP recognizes the unique challenges and threats posed by these interconnected devices. The OWASP IoT Top 10 list specifically addresses the top 10 IoT vulnerabilities. It provides a framework for understanding and mitigating risks in the IoT ecosystem. This list is not just a theoretical exercise. The top 10 list is grounded in real-world incidents and expert consensus. Explore standardizing IoT security protocols and offering guidance on best practices. OWASP can empower manufacturers, developers, and users to implement robust security measures. Thus, ensuring that IoT devices are more than functional. It also ensures that they are convenient, secure, and trustworthy. The role of OWASP in IoT security goes beyond just listing vulnerabilities. Its’ role is to foster a culture of security awareness and resilience. All this in the face of evolving digital threats.
The OWASP IoT Top 10 List: A Deep Dive into Common Vulnerabilities
Understanding and addressing IoT security vulnerabilities is necessary. It’s also imperative for the safe and efficient operation of these devices. The OWASP IoT Top 10 list plays a crucial role in this endeavor. This list is a comprehensive guide to the most common and impactful IoT security risks. This list allows you to protect your infrastructure against a variety of threats. Thus, it will ensure a more secure IoT ecosystem. The OWASP IoT Top 10 list isn’t just a checklist. The OWASP Top 10 list is a roadmap for building and maintaining secure IoT technologies.
Tackling Insecure Default Settings in IoT Devices
One of the most common yet overlooked vulnerabilities in many IoT devices is the presence of insecure default settings. Manufacturers often prioritize ease of setup and user convenience. This can lead to the deployment of devices with weak default configurations. This oversight makes devices susceptible to a multitude of security threats. These are threats ranging from unauthorized access to data breaches. Addressing these insecure default settings is crucial. Doing so will enhance the overall security of IoT devices.
Risks of Insecure Default Settings
The risks associated with insecure default settings in IoT devices are multifaceted. Firstly, these settings can provide an easy entry point for attackers. Malicious actors often know default usernames and passwords and can exploit them easily. Moreover, insecure default configurations could disable critical security features. Further, they could expose sensitive data or open network ports to remote access. This jeopardizes the individual device’s security. Further, it also threatens the entire connected network. This is particularly true if attackers use the device as part of a botnet or as a gateway for further attacks.
Securing Default Settings
To mitigate these risks, it’s essential to implement robust measures for securing default settings in IoT devices:
- Change Default Credentials: Always replace default usernames and passwords with strong, unique credentials.
- Update Security Settings. Regularly review and update the security settings of IoT devices. This will ensure they meet current best practices.
- Disable Unnecessary Services. Disable any services or features unnecessary for the device’s operation. This will minimize potential attack surfaces.
- Implement Network Segmentation. Isolate IoT devices on separate network segments to limit the impact in case of a breach.
- Regular Firmware Updates. Keep the device’s firmware updated to patch any known vulnerabilities.
- Educate Users. Educate users about the importance of security. Provide clear instructions on how to configure devices securely.
These steps allow businesses to significantly reduce risks posed by insecure default settings. It further ensures a more secure and resilient IoT environment.
Physical Hardening: A Critical Step in IoT Security
Much attention in IoT security is given to software and network threats,. However, the physical security of IoT devices often gets overlooked. Physical hardening refers to the measures taken to protect IoT devices from physical tampering or damage. Physical tampering or damage can be just as detrimental as cyber threats. This aspect of security is especially crucial in environments where IoT devices are exposed to the public. It is also crucial if the devices are located in physically insecure areas. Understanding and implementing physical hardening strategies are key to creating a comprehensive security plan for IoT devices.
Understanding The Impact of the Lack of Physical Hardening
Let’s look at physical hardening. This is crucial for IoT security because it addresses the physical vulnerabilities of devices. Without proper hardening, IoT devices can be physically accessed and tampered with. This will lead to unauthorized control of the device. It can also lead to extraction of sensitive data, or disruption of its functionality. This is particularly critical for devices that are deployed in public spaces. It is also a problem in environments where the devices are susceptible to physical manipulation. This lack of physical hardening exposes the devices themselves to risks. It further poses a potential threat to the larger network to which they are connected. This is true because compromised devices can be used as entry points for wider network breaches.
Strategies for Physical Hardening
Implementing physical hardening requires a multifaceted approach:
- Durable Device Casings. Use robust and tamper-evident materials for device casings. This will help to resist physical damage and indicate any tampering attempts.
- Secure Installation Locations. Position devices in locations that are less accessible to unauthorized personnel or the public.
- Locks and Seals. Employ locks, seals, or other physical barriers to prevent easy access to the device’s internals.
- Environmental Controls. Ensure devices are protected from environmental threats like extreme temperatures, moisture, or dust.
- Alarm Systems. Incorporate alarm systems that trigger alerts in case of physical tampering.
- Surveillance and Monitoring. Use surveillance cameras or monitoring systems to oversee areas where IoT devices are installed.
Be sure to incorporate these physical hardening strategies. By doing so, the overall security posture of IoT devices can be significantly enhanced. This will protect them from a wide range of physical threats. It will also ensure their integrity and reliability in various deployment scenarios.
The Dangers of Insecure Network Services in IoT
The network services that connect and manage IoT devices play a critical role in overall security. However, these services can often be a significant source of vulnerabilities. Insecure network services in IoT devices can open the door to a range of cyber threats. These threats range from data breaches to unauthorized access. It is essential to identify and address these vulnerabilities. This will ensure the secure operation of IoT devices and the safety of the networks they operate on.
Identifying Insecure Network Issues
Common issues with network services in IoT devices include:
- insufficient encryption
- weak authentication mechanisms,
- unsecured communication channels.
These vulnerabilities can lead to several problems. Problems such as:
- interception of sensitive data
- unauthorized access to device controls
- the potential for devices to be hijacked and used for malicious purposes.
Many IoT devices also lack the capability to be updated remotely or securely. This leaves them susceptible to exploitation long after known vulnerabilities have been identified.
Remedying Network Security Vulnerabilities
Let’s explore how to address network security vulnerabilities in IoT devices. There are several key steps should be taken:
- Implement Strong Encryption. Use robust encryption protocols for data transmission. This will serve to protect sensitive information from being intercepted.
- Secure Authentication Protocols. Ensure that devices use secure authentication methods to prevent unauthorized access.
- Regular Security Updates. Keep the device firmware and software updated with the latest security patches.
- Network Segmentation. Segregate IoT devices on separate network segments. This will reduce the risk of broader network exposure if a device is compromised.
- Intrusion Detection Systems. Deploy intrusion detection systems to monitor network traffic for signs of malicious activity.
- Conduct Regular Security Audits. Regularly audit IoT devices and their network connections. This will help to identify and address potential vulnerabilities.
Try to understand and address these network service vulnerabilities. The security of IoT devices can be significantly improved by addressing these vulnerabilities. By doing this, you are protecting them from a variety of cyber threats. Further, you are ensuring the safety and integrity of the networks they are a part of.
Secure Update Mechanisms: Ensuring Continuous Protection
The ability to securely update IoT devices is not just a feature but a necessity. Secure update mechanisms are vital for the longevity and safety of IoT devices. These mechanisms ensure that devices are protected against known vulnerabilities at the time of their deployment. Further, they also remain resilient against emerging threats over their operational lifetime. Secure update processes is a crucial aspect of IoT security strategy.
Importance of Secure Update Mechanisms
Secure update mechanisms are fundamental to the integrity and security of IoT devices. These updates are essential for patching security vulnerabilities. Further, they act to enhance functionality. These update mechanisms also ensure compatibility with evolving network standards and protocols. Without secure update processes, IoT devices can become increasingly vulnerable over time. This is because new security threats emerge and existing vulnerabilities are exploited. Additionally, secure update mechanisms help maintain user trust. They also help to maintain compliance with regulatory standards. These standards often mandate regular security updates to protect sensitive data and ensure the safety of IoT ecosystems.
Implementing Secure Updates
Ensure that IoT devices benefit from secure and effective updates. To do so, the following strategies should be implemented:
- Encrypted Update Files. Encrypt update files to protect against tampering during the transfer process.
- Authentication of Update Source. Verify the authenticity of update sources. This will prevent the installation of malicious or unauthorized updates.
- Automatic Update Notifications. Implement systems to automatically notify users of available updates, ensuring timely installations.
- Rollback Capabilities. Include options for rolling back updates in case of compatibility or performance issues.
- Testing Before Deployment. Thoroughly test updates in controlled environments before widespread deployment. This serves to minimize the risk of introducing new vulnerabilities.
- User-Friendly Update Process. Design the update process to be user-friendly and straightforward. Doing so encourages users to regularly update their devices.
Prioritize these secure update mechanisms. By doing so, one can significantly enhance the overall security and performance of these devices. Thus, ensuring they remain protected against current and future cyber threats.
Privacy Protection in IoT: More Than Just a Buzzword
Privacy protection is a critical concern. It goes well beyond mere compliance or buzzword status. As IoT devices often collect and process vast amounts of sensitive data. Thus, ensuring the privacy and security of this data is paramount. This concern is not just limited to preventing unauthorized access. Further, it also involves responsibly managing and safeguarding user data against misuse. Effective privacy protection in IoT is essential. It helps to maintain user trust and for adhering to legal and ethical standards.
The Need for Privacy Protection
The importance of privacy protection in IoT devices stems from the nature of the data they handle. IoT devices can collect sensitive information. This information ranges from personal health data to details about an individual’s daily routines. Without adequate privacy measures, this data could be exposed to unauthorized entities. This can lead to potential misuse such as identity theft, surveillance, or other forms of privacy invasion. Moreover, privacy breaches can damage a company’s reputation and lead to legal ramifications. Ensuring privacy in IoT devices is not just about securing data from external threats. It is also about implementing responsible data handling and processing practices.
Enhancing IoT Privacy Measures
To enhance privacy safeguards in IoT systems, consider the following strategies:
- Data Minimization. Collect only the data that is necessary for the device’s function, reducing the amount of sensitive information at risk.
- Strong Encryption. Utilize strong encryption for data at rest and in transit to protect it from interception and unauthorized access.
- User Consent and Control. Implement mechanisms for obtaining user consent for data collection. Also, provide users with control over their data.
- Regular Privacy Audits. Conduct regular audits to assess privacy practices. Also, ensure they align with current regulations and standards.
- Anonymization Techniques. Where possible, anonymize data to prevent it from being linked to specific individuals.
- Privacy by Design. Integrate privacy considerations into the design phase of IoT devices, rather than as an afterthought.
Focusing on these areas can significantly strengthen the privacy protection of systems. This wil build trust with users. It will also ensure compliance with increasingly stringent data privacy regulations.
Combatting Insecure Data Transfer and Storage
In the IoT ecosystem, the way data is transferred and stored plays a crucial role in the overall security posture of the system. Insecure data transfer and storage can lead to significant risks. These risks include data breaches and unauthorized access. These risks threaten the confidentiality and integrity of the data. Further, they also threaten the trustworthiness and reliability of the IoT system as a whole. Therefore, it’s essential to understand these risks. Once you do, you should implement robust security measures. This serves to protect data throughout its lifecycle in the IoT environment.
Risks in Data Transfer and Storage
Insecure data transfer and storage in IoT devices can lead to several critical issues. Data transmitted over unsecured channels can be intercepted by malicious actors. leading to the exposure of sensitive or confidential information. Similarly, data stored without adequate security measures can be easily accessed or tampered with. This compromises the data itself. Further, it can also lead to broader security incidents. Incidents such as device manipulation or network intrusion. Moreover, inadequate data protection can result in non-compliance with data protection regulations. This can lead to legal and financial repercussions.
Securing Data in IoT
To ensure the security of data transfer and storage in IoT devices, consider the following actionable steps:
- Use of Strong Encryption. Implement strong encryption protocols for both data in transit and at rest. This will protect the data from unauthorized access and interception.
- Secure Communication Channels. Utilize secure communication channels, such as VPNs or SSL/TLS, for transmitting data.
- Access Controls. Apply strict access controls to data storage areas. Thus, ensuring that only authorized personnel can access sensitive information.
- Regular Security Assessments. Conduct regular security assessments and audits. This will help to identify and mitigate potential vulnerabilities in data transfer and storage mechanisms.
- Data Integrity Checks. Implement mechanisms for data integrity checks. This will ensure that data has not been altered during transfer or storage.
- Compliance with Regulations. Stay updated with and adhere to relevant data protection regulations and standards.
Focusing on these areas can significantly enhance the security of data transfer and storage in IoT devices. This will serve to protect against a range of potential threats. It also will ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data in the IoT ecosystem.
Navigating the Challenges of Insecure or Outdated Components
The components that make up IoT devices — from software to hardware — are fundamental to their overall functionality and security. However, the use of insecure or outdated components is a common challenge that can significantly compromise the security and effectiveness of these devices. Addressing this issue is crucial for maintaining the integrity and reliability of IoT systems, as well as protecting them from a wide array of cyber threats.
Impact of Insecure/Outdated Components
The use of insecure or outdated components in IoT devices can have far-reaching impacts. Outdated software may contain vulnerabilities that have been resolved in newer versions, leaving devices susceptible to known security threats. Similarly, outdated or low-quality hardware may lack the necessary features to support modern security standards or may fail prematurely, leading to potential security breaches or system failures. Furthermore, insecure components can act as a gateway for attackers to access and manipulate not only the compromised device but also other connected systems and networks. The cumulative effect of these issues can lead to a loss of consumer trust, financial losses, and even legal liabilities for manufacturers and users.
Updating and Securing Components
Ensure that the components of IoT devices are secure and up-to-date. Consider the following recommendations:
- Regular Software Updates. Implement a regular schedule for updating the device’s software. This will help to patch vulnerabilities and enhance functionality.
- Quality Hardware Selection. Choose high-quality hardware components that meet current security standards and are capable of supporting future updates.
- Vendor Collaboration. Work closely with component vendors to ensure they provide regular updates and support for their products.
- Security-First Design. Incorporate security considerations into the design phase. Select components that are known for their security features.
- Monitoring for Vulnerabilities. Actively monitor for new vulnerabilities in both hardware and software components. Once vulnerabilities are detected, be sure to respond promptly.
- End-of-Life Planning. Have a clear plan for devices or components that reach the end of their life. These plans should include secure decommissioning and replacement.
By focusing on these updating and securing components. By doing so, one can significantly mitigate the risks associated with insecure or outdated components for IoT devices. Thereby enhancing the overall security and longevity of their IoT systems.
Effective Device Management: A Keystone of IoT Security
Device management is a fundamental aspect of maintaining robust IoT security. The complexity and scale of IoT networks make comprehensive management strategies essential. This encompasses not just the initial configuration and deployment of devices. It also includes ongoing monitoring, maintenance, and management throughout their lifecycle. The absence of device management can lead to significant security vulnerabilities and inefficiencies. This often stems from a lack of security support. This makes it a critical area of focus for anyone involved in the IoT space.
The Impact of the Lack of Device Management on Security
The lack of comprehensive device management in IoT can have profound security implications. Unmanaged devices may not receive necessary updates. This leaves them vulnerable to known security threats. Without proper management, IoT devices that are unmonitored become vulnerable. This increases the risk of prolonged and undetected breaches. Furthermore, unmanaged devices can become compliance liabilities in terms of data protection regulations. This is because they may not adhere to required security standards. Effective device management is more than about maintaining the functionality of IoT devices. It is also about safeguarding the entire network they operate within.
Best Practices in Device Management
To ensure effective device management in IoT, the following best practices should be adopted:
- Centralized Management Platform. Utilize a centralized platform for managing all IoT devices. This provides a comprehensive view of the network and facilitating efficient management.
- Regular Device Audits. Conduct regular audits to ensure all devices are functioning correctly. Further, that are in compliance with security policies.
- Automated Updates and Patch Management. Implement systems for automated updates and patch management. This will ensure devices are always running the latest software.
- Real-Time Monitoring. Employ real-time monitoring tools. This allows one to detect and respond to security incidents as they occur.
- Device Authentication and Access Control. Ensure robust authentication and access control mechanisms are in place. This will prevent unauthorized access.
- End-to-End Security Measures. Adopt end-to-end security measures. These security measures should cover all of the device’s lifecycle; from deployment to decommissioning.
By adhering to these best practices the security and efficiency of their IoT devices can be significantly enhanced.

Surviving the Firestorm
This is our new book on Cybersecurity for small businesses. Written in an entertaining format, it is meant for to guide non-technical business owners through the concepts of cybersecurity, planning, and defense tactics. Currently available in Kindle Format.
Securing IoT: A Holistic Approach to Avoid Top 10 Vulnerabilities
We have learned about the complexities of IoT security. As we do, it becomes increasingly clear that a holistic approach is necessary. With that approach, we can effectively mitigate the risks associated with OWASP’s top 10 IoT vulnerabilities. This means not just addressing individual vulnerabilities as they arise. It also means adopting a comprehensive, end-to-end strategy that encompasses all aspects of IoT security. From the physical hardening of devices to the management of network services and the implementation of robust privacy measures, each component plays a vital role in securing the IoT ecosystem.
Embracing a Comprehensive Security Approach
Secure IoT systems amid the various security challenges. To do this, you need to embrace a comprehensive security approach. This approach involves:
- implementing robust security controls
- continuous monitoring, regular assessments
- the willingness to adapt to new threats and technologies
- collaboration between device manufacturers, software developers and users
- collaboration with security experts to share knowledge and best practices.
By embracing this approach, we can mitigate the current OWASP IoT Top 10 vulnerabilities. Further, we can also prepare for future challenges in the ever-evolving landscape of IoT security. Ultimately, the goal is to create a secure and resilient IoT ecosystem. The goal is that the benefits of these technologies can be fully realized without compromising on safety and privacy.

Experienced cybersecurity analyst, software engineer, patent attorney, worked with Linux, Windows, AWS, lots of security tools. Hope to help people do the right things and do the things right!


