Today, cyber threats are not just frequent they also increasingly sophisticated. Therefore, businesses can no longer afford to be complacent about their cybersecurity measures. According to Statista, the number of data breaches in the United States has been on a steady rise. Data breaches have reached an alarming 1,473 incidents in 2019 alone. These breaches exposed nearly 165 million records. This underscores the urgency for robust security solutions. Now, let’s explore how Intrusion Detection Systems can help and what types of these are available.
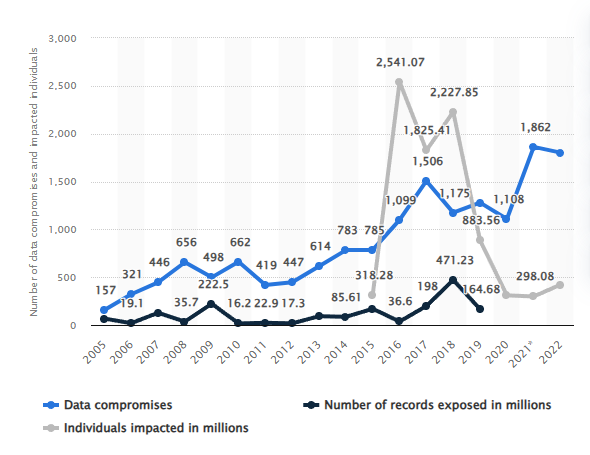
This graph, illustrating the increase in data compromises from 2005 to 2022, is sourced from Statista.
Key Takeaways
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) are essential for monitoring and securing networks against cyber threats.
- IDS can detect malicious activities in real-time, providing a proactive layer of security.
- Different types of IDS, including Network-based (NIDS) and Host-based (HIDS), cater to various security needs.
- Implementing IDS involves steps like risk assessment, configuration, and continuous monitoring.
Enter Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS). These are more than just another layer of security. An IDS is a critical component in a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy. The IDS monitors your network and system activities for malicious exploits or vulnerabilities. It acts as a vigilant watchdog that never sleeps. Whether you’re a small business manager, an IT personnel, or someone concerned about data security, understanding the intricacies of IDS is no longer optional—it’s a necessity.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore intrusion detection systems. We will explore their types, detection methods, and how they fit into the broader landscape of cybersecurity. So, let’s get started!
The Evolution of Cyber Threats: Why Traditional Measures Are No Longer Enough
The threat landscape has evolved dramatically over the past few decades. Gone are the days when simple firewalls and antivirus software were enough to protect your business.
Today, cybercriminals employ a myriad of sophisticated techniques, from ransomware to social engineering, to compromise your systems and data.
Take, for instance, the unsettling rise of vehicle hacking. A New York Times article highlighted how modern cars are becoming increasingly vulnerable to cyberattacks. Hackers can remotely control various car functions, from steering and brakes to the air conditioning. Thus, turning your vehicle into a potential weapon. If something as tangible and life critical as a car can be compromised, imagine the vulnerabilities that exist in your digital systems.
This evolution of cyber threats necessitates a more dynamic and proactive approach to security. Traditional measures like firewalls and antivirus programs are reactive in nature. These measures act after the threat has already infiltrated your system. In contrast, Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) are designed to be proactive, identifying potential threats before they can cause significant damage.
The bottom line is clear: as cyber threats evolve, so must our methods of defense. Relying solely on traditional security measures is akin to bringing a knife to a gunfight. In the following sections, we’ll explore how Intrusion Detection Systems offer a more advanced and proactive solution to modern cybersecurity challenges.
What Are Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS)?
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) serve as a critical line of defense against a wide array of cyber threats. But what exactly is an IDS? How does it fit into your overall cybersecurity strategy? Let’s explore the details.
The Role of IDS in Cybersecurity
At its core, an IDS is designed to monitor network traffic and system activities continuously. It scans for suspicious patterns or anomalies that could indicate a security breach. Unlike traditional security measures like firewalls and antivirus software, an IDS is proactive. It aims to identify potential threats before they can wreak havoc on your system.
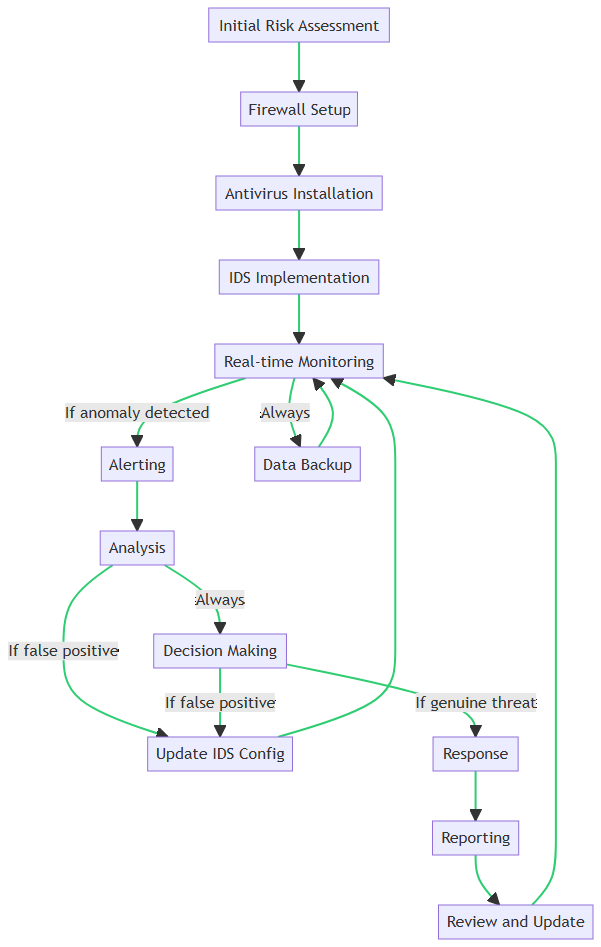
How IDS Works: A Step-by-Step Guide
Based on the above flowchart, let’s break down the steps involved in implementing and operating an IDS within a business environment:
- Initial Risk Assessment: Before setting up any security measures, it’s crucial to evaluate your current security posture. This assessment helps identify vulnerabilities that IDS can address.
- Firewall Setup: Firewalls act as the first line of defense. They filter incoming and outgoing traffic based on predetermined security rules.
- Antivirus Installation: Antivirus software scans for known malware signatures and removes them. Thus, offering another layer of protection.
- IDS Implementation: This is where the IDS comes into play. It’s configured and deployed to monitor network and system activities for any suspicious behavior.
- Real-time Monitoring: The IDS continuously scans network traffic and system activities. If it detects an anomaly, it triggers an alert.
- Alerting: System administrators receive immediate notifications about the detected activity. Thus, allowing for quick intervention.
- Analysis: The nature of the alert is examined to determine whether it’s a false positive or a genuine threat.
- Decision Making: Based on the analysis, appropriate actions are decided. This could range from ignoring the alert to escalating it for further investigation.
- Response: Actions like blocking the IP address or isolating the affected system are implemented.
- Reporting: All incidents and actions are documented for compliance and future reference.
- Review and Update: The incident is reviewed, and security measures, including IDS configurations, are updated as needed.
By understanding these steps, you can appreciate the proactive and comprehensive nature of IDS in cybersecurity. It’s not just another tool in your security arsenal. The IDS is a critical component that works in tandem with other security measures to provide a robust defense mechanism.
In the following sections, we’ll explore the types of IDS. We will also go into how to choose the IDS that best fits your needs.
Types of Intrusion Detection Systems: A Deep Dive
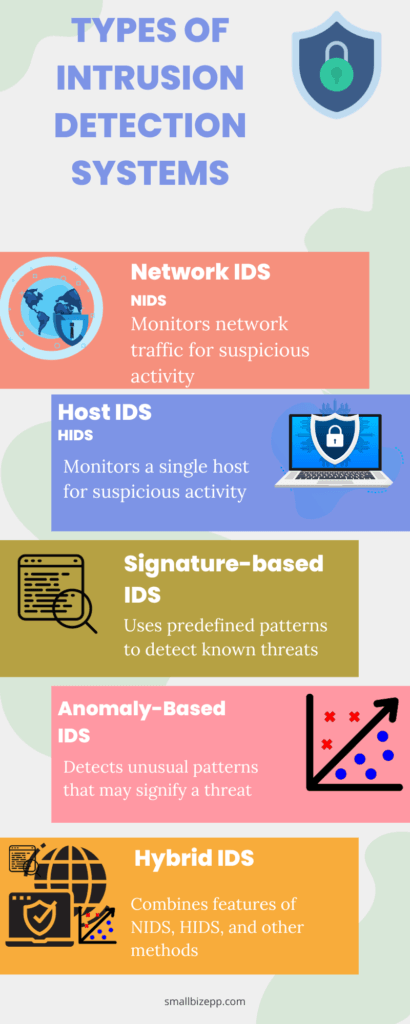
In the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity, one size does not fit all. Different organizations have different needs. Thankfully, the IDS come in various types to cater to these diverse requirements. In this section, we’ll take a deep dive into the types of IDS. This will help you understand which one is the best fit for your organization.
Network Intrusion Detection Systems (NIDS)
Network Intrusion Detection Systems (NIDS) focus on monitoring network traffic. They are usually placed at strategic points within the network to inspect traffic coming in and out of all devices on the network.
- Strengths: Excellent for detecting unauthorized access and large-scale attacks.
- Weaknesses: May not be as effective in detecting attacks that occur within a single host.
- Best For: Large enterprises with complex network architectures.
Host Intrusion Detection Systems (HIDS)
Unlike NIDS, Host Intrusion Detection Systems (HIDS) are installed on individual hosts or devices within the network. They monitor inbound and outbound packets from the device only and alert the user or administrator of suspicious activity.
- Strengths: Highly effective for monitoring individual endpoints.
- Weaknesses: Limited in scope; does not monitor network-wide activity.
- Best For: Small businesses or individual users who need to secure fewer endpoints.
Signature-Based Intrusion Detection Systems (PIDS)
Signature-Based Intrusion Detection Systems (PIDS) rely on predefined patterns or signatures to identify known threats. These systems are highly effective at detecting known malware or attack patterns. However, they may not be effective against new, unknown threats.
- Strengths: Quick detection of known threats.
- Weaknesses: Ineffective against zero-day attacks or new, unknown threats.
- Best For: Organizations that require quick detection and mitigation of known threats.
Anomaly-Based Intrusion Detection Systems (PIDS)
Anomaly-Based Intrusion Detection Systems (PIDS) work by establishing a baseline of normal activities and then flagging any actions that deviate from this norm.
- Strengths: Effective against new, unknown threats.
- Weaknesses: May generate false positives.
- Best For: Research institutions or organizations with unique data patterns.
Hybrid Intrusion Detection Systems
Hybrid Intrusion Detection Systems combine the features of NIDS, HIDS, and other methods to offer a multi-layered approach to cybersecurity.
- Strengths: Comprehensive coverage reduced false positives.
- Weaknesses: Complexity in setup and management.
- Best For: Organizations that require a multi-layered, robust security solution.
Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each type of IDS can help you make an informed decision that aligns with your organization’s specific needs. In the next section, we’ll explore how to implement IDS effectively. Understanding that will ensure you get the most out of your chosen system.
Signature-Based vs. Anomaly-Based: Detection Methods Unveiled
When it comes to intrusion detection systems, the detection method employed plays a pivotal role in the system’s effectiveness. The two primary detection methods are Signature-Based and Anomaly-Based. Each has its own set of advantages and disadvantages, and understanding these can help you make an informed decision. In this section, we’ll delve into the intricacies of these two methods.
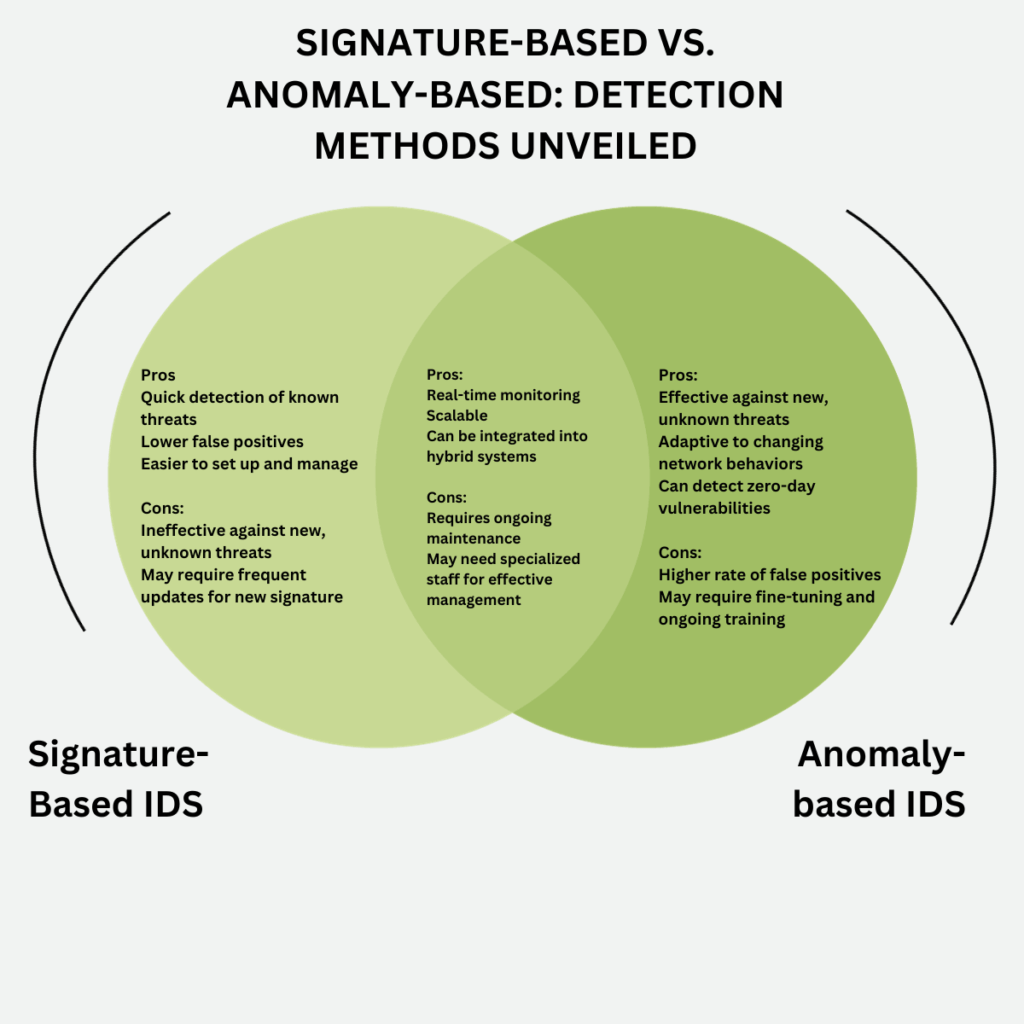
Signature-Based Detection
Signature-Based Detection relies on a database of known attack patterns or “signatures.” When incoming traffic matches one of these signatures, an alert is triggered.
- Strengths: Quick detection of known threats, lower false positives, and easier to manage.
- Weaknesses: Ineffective against new, unknown threats and may require frequent updates.
Anomaly-Based Detection
Anomaly-Based Detection, on the other hand, establishes a baseline of typical behavior. Then it flags any deviations from this norm as potential threats.
- Strengths: Effective against new, unknown threats, adaptive to changing network behaviors, and can detect zero-day vulnerabilities.
- Weaknesses: Higher rate of false positives and may require fine-tuning.
Comparative Analysis
As illustrated in the Venn diagram, both methods offer real-time monitoring and are scalable. They can also be integrated into hybrid systems for a more comprehensive approach. However, they differ significantly in their effectiveness against known and unknown threats, false positive rates, and management requirements.
- Best For Signature-Based: Organizations that require quick detection and mitigation of known threats.
- Best For Anomaly-Based: Organizations that need a more adaptive system capable of detecting new, unknown threats.
Try to understand the nuances of these detection methods. Then you can choose the one that best aligns with your organization’s specific needs and threat landscape.
In the next section, we’ll explore some common challenges you might face while using IDS and how to overcome them.
The Role of IDS in IoT: Beyond Computers and Networks
In today’s interconnected world, the Internet of Things (IoT) is no longer a buzzword but a reality that’s deeply integrated into our daily lives. From smart homes to industrial automation, IoT devices are everywhere. While these devices offer unprecedented convenience and efficiency, they also present a new set of challenges in cybersecurity. This is where Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) come into play. They extend their role beyond traditional computers and networks to secure the ever-expanding IoT landscape.
A comprehensive study published in Springer’s Cybersecurity Journal delves into the critical role of IDS in the realm of IoT. The research highlights how IDS is instrumental in identifying and mitigating a wide array of threats that IoT devices are susceptible to. These threats range from unauthorized access to data breaches and even physical tampering of the devices.
The article emphasizes the need for specialized IDS solutions for IoT. There is a need for solutions that can adapt to the unique network traffic patterns and vulnerabilities inherent in IoT devices. It also discusses the future of IDS in IoT. It suggests that as IoT technology evolves, so too must the security measures that protect it. Thus, making IDS an indispensable component of IoT cybersecurity strategy.
Why IDS is Crucial for IoT
IoT devices often lack the built-in security measures that are standard in computers and servers. This makes them vulnerable to attacks, and the consequences can be dire given the sensitive nature of the data these devices often handle.
Types of Threats in IoT
Just like traditional networks, IoT is susceptible to a range of threats, including but not limited to:
- Unauthorized access
- Data manipulation
- Physical tampering
How IDS Can Help
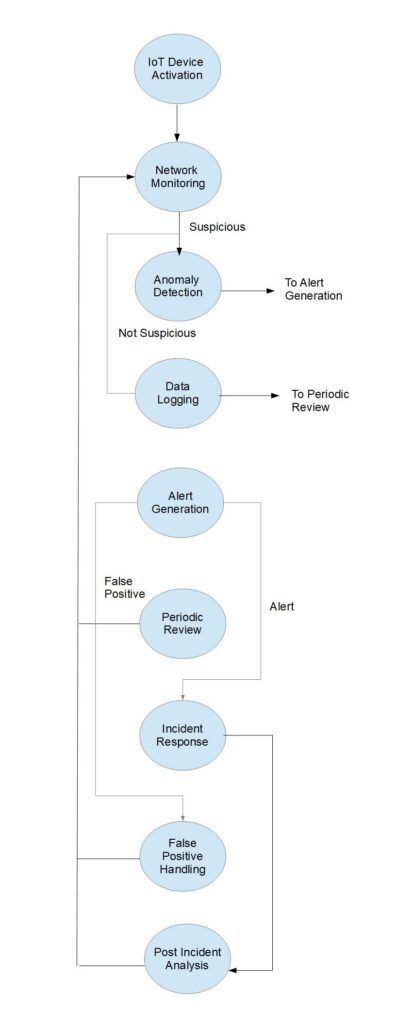
As illustrated in the workflow diagram, IDS systems can be adapted to monitor the unique types of network traffic that IoT devices produce. The flowchart outlines the entire lifecycle of IDS integration in an IoT environment, from initial device activation to ongoing monitoring and incident response.
For instance, after IoT Device Activation (Step 1), the IDS begins Network Monitoring (Step 2). Depending on whether suspicious activity is detected, the system either moves to Anomaly Detection (Step 3) or Data Logging (Step 4). This cycle continues, adapting and responding to various conditions as outlined in the table.
Challenges and Solutions
While implementing IDS in IoT comes with its own set of challenges, such as compatibility and scalability, solutions like cloud-based IDS and machine learning algorithms are making it easier to overcome these hurdles.
Future Outlook
As IoT continues to evolve, the role of IDS in securing these devices will only become more significant. Ongoing research and technological advancements are likely to produce more sophisticated IDS solutions tailored for IoT security.
Understanding the role of IDS in IoT is crucial for any organization that relies on these devices. As we’ve seen, IDS not only protects traditional networks but is also evolving to meet the unique challenges posed by the Internet of Things.
In the next section, we’ll look at some best practices for maintaining and updating your IDS to ensure long-term effectiveness.
How IDS Complements Other Security Measures
In the complex landscape of cybersecurity, no single tool can offer complete protection. A robust security strategy requires a multi-layered approach, incorporating various tools and measures that work in harmony. Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) are a vital component of this strategy, but they are most effective when used in conjunction with other security measures.

As depicted in the diagram above, IDS is one of several interconnected elements that make up a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy. Let’s delve into how IDS complements other key security tools:
Firewalls
Firewalls act as the first line of defense, blocking unauthorized access to your network. While they are excellent at preventing known threats, they may not catch new, more sophisticated attacks. This is where IDS comes in. It monitors network traffic for suspicious activity that may have bypassed the firewall, providing an additional layer of security.
Antivirus Software
Antivirus software scans files and programs for known malware signatures. However, zero-day attacks or custom malware can evade these traditional scans. IDS complements antivirus software by monitoring network behavior, detecting anomalies that could indicate an unknown form of malware.
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs)
VPNs encrypt your data transmission, making it difficult for attackers to intercept sensitive information. However, if malware has already infiltrated your system, a VPN alone can’t stop it from transmitting data back to the attacker. IDS can identify such unauthorized data transmissions, alerting you to the presence of malware.
Other Security Measures
In addition to these, IDS can work alongside other security tools like Data Loss Prevention (DLP) systems, Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) solutions, and more. The key is to integrate IDS into your broader security architecture, ensuring that it complements and enhances other security measures.
By understanding how IDS fits into your overall cybersecurity strategy, as illustrated in the graphic, you can maximize its effectiveness and ensure a more secure environment.
False Positives and False Negatives: Understanding the Limitations
While Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) are an invaluable asset in cybersecurity, they are not without their limitations. Understanding these limitations, particularly the phenomena of false positives and false negatives, is crucial for effectively managing and interpreting IDS alerts.
| Scenario | Description | Leads to False Positive or False Negative |
|---|---|---|
| Outdated Signature Files | IDS is using outdated signature files, missing new attack patterns. | False Negative |
| Overly Broad Signatures | IDS signatures are too broad, flagging benign activities as malicious. | False Positive |
| High Network Traffic | During peak usage, IDS might miss some activities due to overload. | False Negative |
| Encrypted Traffic | IDS cannot inspect encrypted packets, potentially missing malicious activity. | False Negative |
| User Error | Misconfiguration or lack of understanding of IDS settings. | Both |
| Software Bugs | Bugs within the IDS software may lead to incorrect flagging. | Both |
| Legitimate Tool Usage | Usage of tools like port scanners by authorized personnel. | False Positive |
| Sophisticated Malware | Advanced malware designed to evade detection. | False Negative |
As outlined in the table above, various scenarios can lead to false positives and negatives:
Outdated Signature Files
When IDS uses outdated signature files, it can miss new attack patterns, leading to false negatives. Regularly updating your IDS can mitigate this issue.
Overly Broad Signatures
If the IDS signatures are too broad, they may flag benign activities as malicious, resulting in false positives. Fine-tuning your IDS settings can help minimize this.
High Network Traffic
During periods of high network traffic, IDS might miss some activities due to overload, causing false negatives. Employing additional IDS sensors can help in such cases.
Encrypted Traffic
IDS cannot inspect encrypted packets, potentially missing malicious activity and leading to false negatives. Using IDS solutions that can decrypt traffic for inspection can address this limitation.
User Error
Misconfiguration or a lack of understanding of IDS settings can lead to both false positives and negatives. Proper training and documentation can alleviate this issue.
Software Bugs
Bugs within the IDS software may lead to incorrect flagging, causing both false positives and negatives. Keeping your IDS software up to date can help minimize this risk.
Legitimate Tool Usage
When authorized personnel use tools like port scanners for legitimate purposes, IDS may flag these as malicious activities, causing false positives. Listing allowed tools can prevent this.
Sophisticated Malware
Advanced malware designed to evade detection can result in false negatives. Employing a multi-layered security approach can offer additional protection.
By understanding these limitations and taking proactive steps to mitigate them, you can make more informed decisions and enhance your cybersecurity posture.
Implementing IDS: A Step-by-Step Guide for Small Businesses
Implementing an Intrusion Detection System (IDS) can seem like a daunting task, especially for small businesses with limited resources. However, with the right approach, it’s entirely feasible and highly beneficial. This section aims to provide a practical guide to help you navigate the process of IDS implementation.
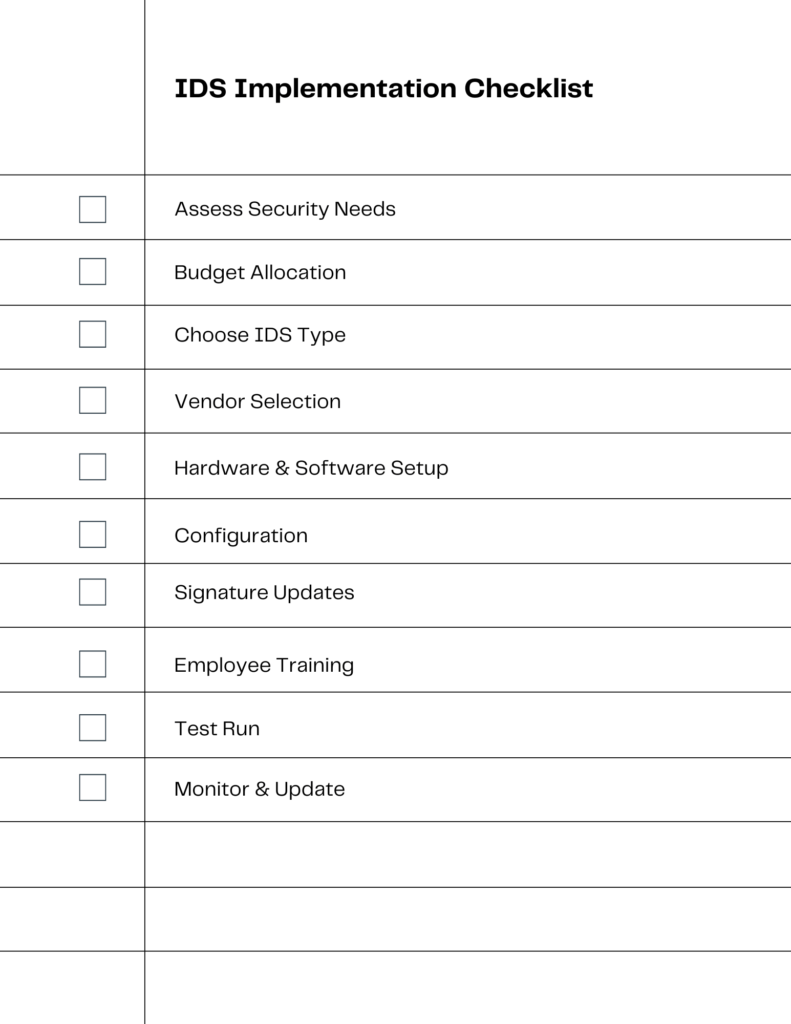
Assess Security Needs
Before diving into the world of IDS, it’s crucial to assess your business’s specific security needs. Identify the vulnerabilities in your current system and understand what you require from an IDS.
Budget Allocation
Setting aside a budget is the next step. IDS solutions come in various price ranges, so knowing your budget will help you narrow down your options.
Choose IDS Type
There are different types of IDS—Host-based (HIDS), Network-based (NIDS), and hybrid. Choose the one that best suits your business needs.
Vendor Selection
Once you’ve decided on the type of IDS, it’s time to choose a vendor. Research and opt for a reputable vendor that aligns with your requirements and budget.
Hardware & Software Setup
After selecting a vendor, you’ll need to set up the necessary hardware and software. This could range from installing a simple software application to setting up dedicated hardware.
Configuration
Fine-tuning the IDS settings to suit your specific environment is crucial for effective detection. This involves setting up signatures, defining alert thresholds, and more.
Signature Updates
Keeping the IDS signatures up to date is essential for detecting new types of attacks. Make sure to regularly update your IDS to stay ahead of potential threats.
Employee Training
Educate your staff on how to use the IDS and what to do in case of alerts. A well-trained team can make all the difference in effective threat detection and response.
Test Run
Before fully integrating the IDS into your operations, run tests to ensure it’s functioning as expected. Make adjustments as necessary.
Monitor & Update
Once implemented, the work isn’t over. Regular monitoring and updates are crucial for maintaining an effective IDS.
By following this step-by-step guide, small businesses can successfully implement an IDS, enhancing their cybersecurity posture. The checklist above serves as a handy reference to ensure you don’t miss any crucial steps.
Conclusion: The Future of IDS and Why It Matters to You
In today’s rapidly evolving cybersecurity landscape, Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) serve as an indispensable tool for safeguarding your business assets. From understanding the limitations of IDS, such as false positives and negatives, to diving deep into the types and detection methods, we’ve covered a comprehensive range of topics to equip you with the knowledge you need.
As we look to the future, IDS technology is set to become even more sophisticated. With advancements in machine learning and artificial intelligence, we can expect more accurate and adaptive systems that can better counter emerging threats. The integration of IDS in Internet of Things (IoT) environments is another exciting frontier, offering a new layer of security for interconnected devices.
Implementing an IDS may seem like a complex task, but with the right planning and resources, it’s entirely achievable, especially for small businesses. Our step-by-step guide and checklist aim to simplify this process, ensuring you can enhance your cybersecurity measures effectively.
We encourage you to share your experiences or any questions you may have in the comments section below. Your insights could be invaluable to others in the community who are on their own journey of implementing an Intrusion Detection System.
Thank you for reading, and here’s to a more secure future for your business!
Additional Resources
Questions? We Have Answers.
Get answers to a list of the most Frequently Asked Questions.

Experienced cybersecurity analyst, software engineer, patent attorney, worked with Linux, Windows, AWS, lots of security tools. Hope to help people do the right things and do the things right!