Introduction to IoT Security
In an era where interconnected technology has become the backbone of modern efficiency, the significance of securing Internet of Things (IoT) devices cannot be overstated. As these devices increasingly permeate every aspect of our daily lives, from smart home appliances to industrial machinery, the necessity for robust IoT security measures escalates. This article will help you understand the challenges in securing IoT endpoints and how to deal with them.
This burgeoning sector, often referred to as the IoT ecosystem, faces a unique set of security challenges. The sheer number of connected IoT devices – expected to reach billions in the coming years – presents a daunting task for ensuring comprehensive security. Each IoT device, whether it’s a sensor in a smart factory or a thermostat in your living room, potentially opens a gateway to security risks, making IoT security not just a technological concern but a critical safety issue.
Furthermore, the rapid growth of the IoT environment amplifies these challenges. As the scale of IoT expands, so does the complexity of maintaining network security. This expansion is not just in numbers; the diversity of IoT technology, from simple sensors to complex machinery, adds layers to the security puzzle. It’s no longer just about protecting data; it’s about ensuring the physical security of devices and the environments they operate in.
Post Summary
This post is about the critical challenges and best practices in securing IoT (Internet of Things) endpoints, offering a comprehensive guide on how to navigate and fortify the complex IoT security landscape.
Learn the common IoT security challenges, such as device vulnerabilities, incompatible protocols, and the need for scalable solutions, and illustrate these with real-world examples like the Mirai botnet attack. Then we talk about the practical strategies for securing IoT devices, including robust encryption and regular firmware updates, and underscores the importance of regular security assessments to identify and mitigate risks.
From there, you need to learn about the implementation of IoT security solutions, balancing custom and off-the-shelf options. Also learn how different industries can adapt to these challenges. Looking forward, we examine future trends in IoT security and the impact of policy and regulation in shaping IoT standards. The post concludes by emphasizing the ongoing nature of IoT security and the need for continuous adaptation and vigilance.
The Impact of the IoT on Industry
The Internet of Things (IoT) has seen significant growth in recent years and is projected to continue to do so, as shown in the chart below. This growth is driven by advancements in technology, increased internet connectivity, and the proliferation of smart devices. Key factors include:
- Technological Advancements: Improvements in sensors, processors, and connectivity options have made IoT devices more capable and affordable.
- Increased Connectivity: With more global internet access, IoT devices can be deployed in a wider range of locations.
- Smart Device Proliferation: The rise in smart home devices, wearables, and industrial IoT applications has contributed to this growth.
- Business and Consumer Demand: Both sectors have shown increased interest in IoT solutions for efficiency, data collection, and automation.
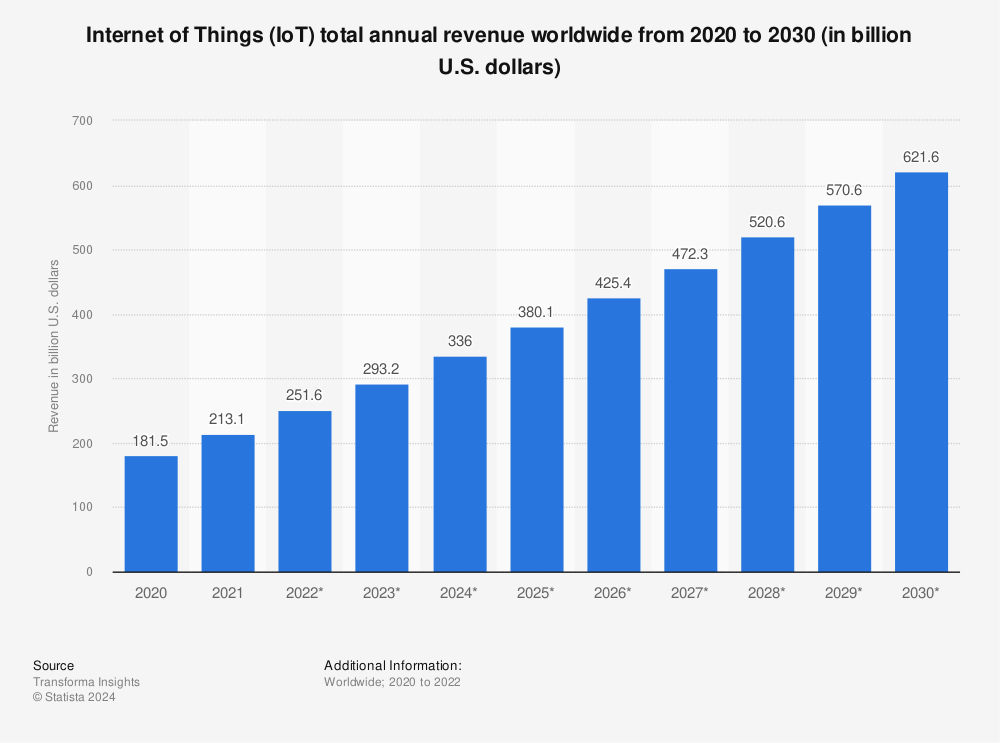
Find more statistics at Statista
This introduction sets the stage for a comprehensive exploration of IoT security challenges and best practices. We delve into the intricacies of securing the IoT, from the device level to the system as a whole, understanding that the security of IoT is paramount in an increasingly connected world.
Interested in a foundational understanding of IoT and endpoint security? our guides on A Comprehensive Guide to IoT and The Importance of Endpoint Security offer in-depth insights into these domains. These guides can serve as valuable resources in navigating the complexities of the digital world.
Understanding the Internet of Things Security Challenges
As the Internet of Things (IoT) continues to evolve, it brings a myriad of security challenges that impact both businesses and individual users. At the core of these challenges is the inherent vulnerability of IoT devices. Often, IoT devices are not designed with security as a primary focus, leading to potential gaps in protection. This lack of security can expose users to various risks, from data breaches to more serious security incidents.
The challenges are further compounded by the different protocols used by IoT devices, which can create inconsistencies in security standards. Moreover, the vast scale of IoT means that security solutions must be scalable and adaptable to different environments and needs. This scale of IoT, combined with its diversity, makes crafting universal security strategies a complex task.

The Top 5 IoT Security Challenges
It is crucial to identify and understand the specific challenges in IoT Security. The landscape of IoT security is marked by a diverse array of challenges, each posing unique threats to the integrity and functionality of IoT systems.
In this subsection, we’ll highlight the top five IoT security challenges that are most pressing in today’s digital environment. These challenges not only represent the most common vulnerabilities faced by IoT systems but also serve as key focus areas for developing robust security strategies. By examining these top challenges, we can better prepare and fortify our IoT ecosystems against potential threats.
- Insecure Network Connections: Many IoT devices connect to the internet via networks that lack robust security features, making them susceptible to attacks.
- Limited Security Features: Due to constraints in processing power and size, many IoT devices have minimal built-in security features, leaving them vulnerable.
- Inadequate Update Mechanisms: Regular security updates are crucial, but many IoT devices lack the capability or support to receive these updates, leading to outdated defenses.
- Physical Security Threats: The physical accessibility of some IoT devices makes them prone to tampering and direct attacks.
- Lack of Standardization: The IoT ecosystem is marked by a variety of devices with differing security protocols, making comprehensive protection challenging.
IoT Security Risks: A Closer Look

smallbizepp SEO create
In the ever-evolving landscape of the Internet of Things (IoT), understanding the array of security risks is crucial for developing effective defense strategies. This section takes a closer look at the various IoT security risks that pervade our connected world. From the subtle vulnerabilities in everyday devices to more overt threats that have led to significant breaches, we will examine the multifaceted nature of these risks. By exploring real-world incidents and case studies, such as the Mirai botnet attack and the Ring security camera breach, we gain deeper insights into how these risks manifest and the profound impact they can have. This exploration is not just about recognizing potential threats; it’s a crucial step towards building more resilient and secure IoT environments.
The Mirai Botnet Attack: Turning IoT Devices into Zombies
One of the most notorious examples of IoT security breaches was the Mirai botnet attack in 2016. This attack exploited weak security in IoT devices like cameras and routers, transforming them into a botnet that launched massive Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks. This incident underscored the serious security risks posed by insecure IoT devices and the need for robust security measures.
The Ring Security Camera Breach
Another significant incident was the breach of Ring security cameras, where attackers gained access to IoT devices, leading to privacy invasions and security concerns. This breach highlighted vulnerabilities in IoT device security and the importance of securing these devices to protect user privacy and safety.
IoT Security Best Practices
Navigating the complexities of IoT security requires a multifaceted approach, blending best practices with effective implementation strategies. To secure the IoT effectively, it’s crucial to adopt a holistic view that encompasses not just the technological aspects but also the human and process elements.
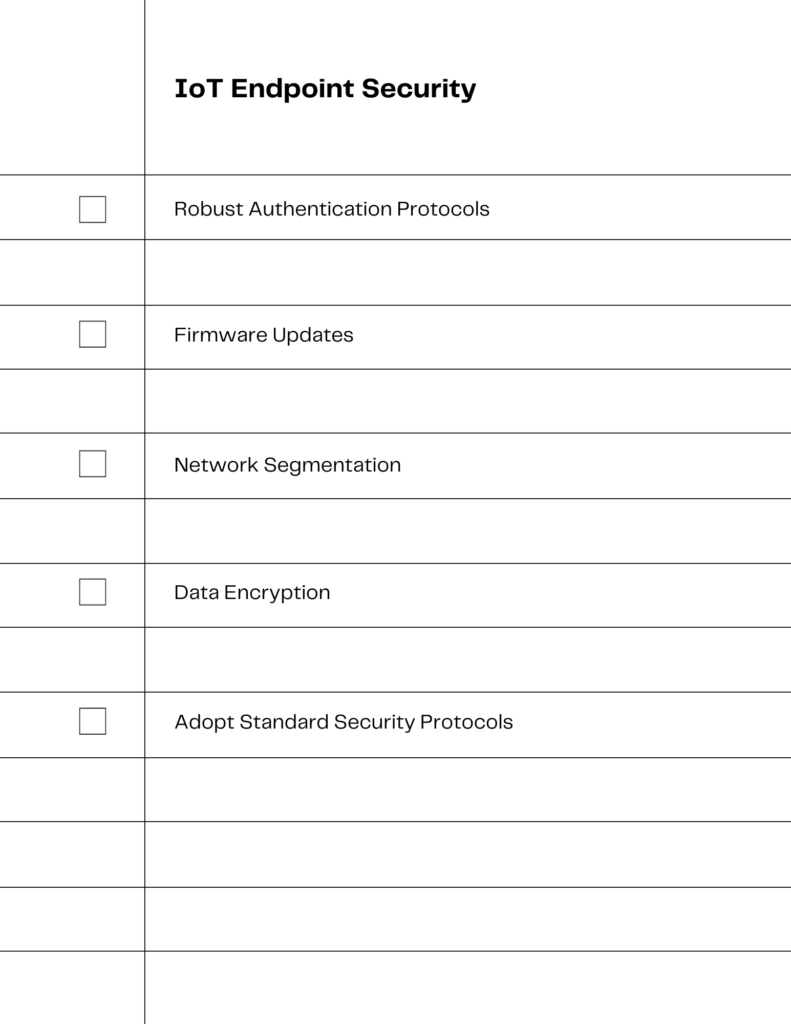
Security of IoT Devices: Strategies and Solutions
Securing IoT devices is a critical step in safeguarding the IoT ecosystem. Here are some key strategies and solutions:
- Implement Robust Authentication Protocols: Strong authentication mechanisms, like two-factor authentication, can significantly enhance the security of IoT devices.
- Regular Firmware Updates: Keeping the firmware of IoT devices updated is crucial for patching security vulnerabilities as they arise.
- Network Segmentation: Segregating IoT devices onto separate networks can limit the potential impact of a breach.
- Encryption of Data: Encrypting data transmitted by IoT devices ensures that even if intercepted, the information remains secure.
- Adopting Standard Security Protocols: Utilizing standard security protocols can help in maintaining a consistent level of security across different IoT devices.
| Solution | Features Specific to IoT Devices | Suitability |
|---|---|---|
| Symantec Endpoint Security | – IoT Device Discovery – IoT Risk Assessment – IoT Threat Defense | Suitable for businesses looking for comprehensive IoT device visibility and advanced threat protection. |
| McAfee Endpoint Security | – IoT Device Protection – Machine Learning Analysis for IoT – Integrated Firewall for IoT Devices | Ideal for businesses requiring robust IoT protection with integrated firewall and machine learning analysis. |
| Trend Micro IoT Security | – IoT Device Reputation – Vulnerability Shielding for IoT – Custom Defense for IoT | Best suited for businesses seeking custom defense and vulnerability shielding for IoT devices. |
| Kaspersky Endpoint Security | – IoT Threat Prevention – Adaptive Anomaly Control for IoT – Exploit Prevention for IoT Devices | Suitable for businesses looking for adaptive control and exploit prevention for IoT devices. |
| Bitdefender GravityZone | – Risk Management for IoT – IoT Anomaly Detection – Network Attack Defense for IoT | Ideal for enterprises needing advanced risk management and network attack defense for IoT devices. |
Importance of Regular Security Assessments
Regular security assessments are vital in identifying and mitigating potential vulnerabilities in an IoT environment. These assessments should be an ongoing process, adapting as the network evolves and as new threats emerge. Conducting these assessments involves:
- Vulnerability Scanning: Regularly scanning IoT devices and networks for vulnerabilities.
- Risk Analysis: Assessing the potential impact of identified vulnerabilities on the overall IoT network.
- Security Audits: Conduct thorough audits of the IoT ecosystem, including hardware, software, and network components.
- Incident Response Planning: Developing and updating an incident response plan to quickly address security breaches or vulnerabilities.
- Employee Training: Educating employees on security best practices and the latest threats can significantly reduce the risk of breaches due to human error.
Implementing IoT Security Solutions
Successfully implementing IoT security solutions requires a strategic approach, balancing between custom-developed and off-the-shelf solutions. Each option has its merits and challenges, making it crucial to choose the one that aligns best with specific IoT security needs.
Custom Solutions vs. Off-the-Shelf Solutions
Custom Solutions offer the advantage of being tailored specifically to your IoT environment’s unique requirements. They can be designed to integrate seamlessly with existing systems, providing a level of security that is specifically suited to your IoT devices and network. However, they can be more costly and time-consuming to develop and maintain.
Off-the-Shelf Solutions, on the other hand, are generally more cost-effective and quicker to deploy. They are built to cater to common security needs and are regularly updated to address new threats. The downside is that they might not address every unique aspect of your IoT environment, potentially leaving gaps in your security strategy.
The flow chart below gives one implementation of a process for implementing IoT security solutions.
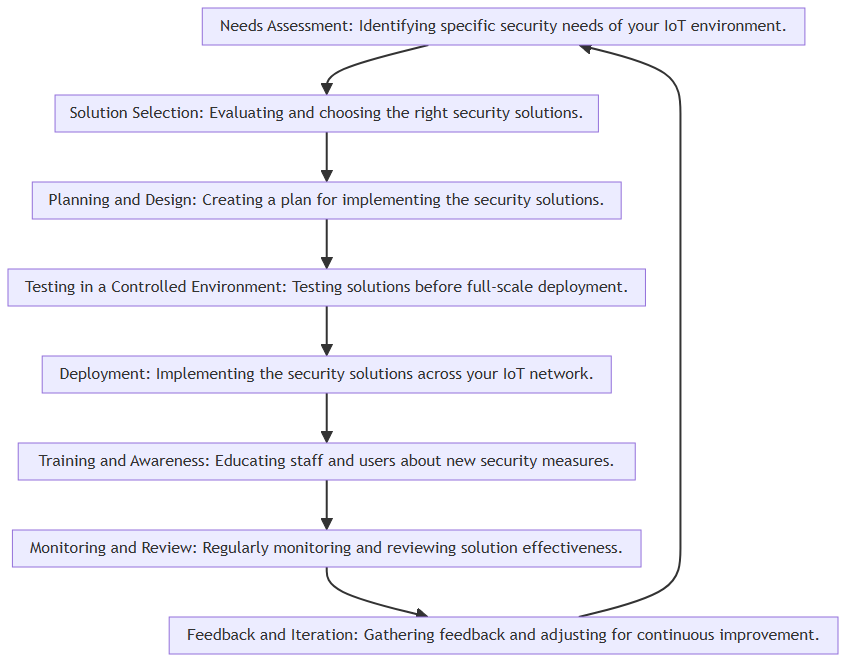
Overcoming Implementation Challenges
The following two hypothetical examples illustrate how different industries that use IoT devices may implement security to prevent potential security issues.
Case Study: A Retail Chain’s IoT Security Upgrade
A notable example of overcoming these challenges comes from a large retail chain. They faced significant security vulnerabilities in their IoT system, which included a wide range of devices from different vendors. The solution involved deploying a combination of custom and off-the-shelf security solutions, integrated through a centralized management platform. This approach not only enhanced their IoT security but also streamlined the management of their IoT devices.
Learning from the Healthcare Industry
Another insightful example is from the healthcare industry, where hospitals have successfully navigated the complexities of IoT security. Hospitals often use a mix of legacy systems and modern IoT devices, making security a critical concern. By implementing robust network security protocols and regular security audits, alongside staff training programs, they have managed to create a more secure and reliable IoT environment.
Securing the Future of the Internet of Things

As we venture deeper into the digital era, the future of IoT security appears both challenging and promising. Advancements in technology not only bring new security challenges but also innovative solutions.
Predicting Future Trends in IoT Security
- AI and Machine Learning: The use of artificial intelligence and machine learning in enhancing IoT security is likely to grow. These technologies can help in detecting and responding to threats more efficiently.
- Blockchain for Security: Blockchain technology could play a significant role in securing IoT devices and networks by providing decentralized security mechanisms.
- Increased Focus on Edge Computing: As edge computing becomes more prevalent, ensuring the security of edge devices will become a critical aspect of IoT security.
- Development of Universal Security Standards: The IoT industry may see the development of more universal security standards to address the diversity and scalability challenges.
- Greater Emphasis on Data Privacy: With increasing awareness about data privacy, IoT security will likely see a stronger focus on protecting user data.
The Role of Policy and Regulation in IoT Security
As the Internet of Things (IoT) continues to expand its influence across various sectors, the role of policy and regulation in shaping the security landscape becomes increasingly significant. This subsection delves into how governmental policies and industry regulations are instrumental in defining and enforcing IoT security standards.
We will explore the dynamic interplay between technological innovation and regulatory frameworks, examining how laws and guidelines are evolving to address the unique challenges posed by IoT. From setting baseline security requirements to influencing the design and development of IoT devices, policy and regulation play a pivotal role in ensuring a safer IoT ecosystem. Understanding this aspect is key to comprehending the full spectrum of IoT security and its future direction.
Shaping IoT Security Standards Through Legislation
Government policies and regulations are increasingly playing a pivotal role in shaping IoT security standards. Regulations like the IoT Cybersecurity Improvement Act aim to establish baseline security standards for IoT devices used by the government, influencing the broader IoT market.
Global Variations and Challenges
The approach to IoT security regulation varies globally, with different countries and regions implementing their own standards. This variation presents both challenges and opportunities for standardizing IoT security measures.
The Impact on Manufacturers and Users
For IoT device manufacturers, these regulations necessitate compliance with various security standards, potentially impacting design and development processes. For users, these regulations promise better security and reliability of IoT devices, enhancing overall trust in IoT technology.
Conclusion: Secure the IoT, Secure the Future
The journey through the complex and evolving world of Internet of Things (IoT) security brings us to a critical realization: the security of IoT is not just a technological concern; it’s a fundamental necessity for the safe and efficient operation of countless systems that define our modern world. From individual smart home devices to vast industrial networks, securing IoT endpoints is paramount.
The Importance of IoT Security
IoT devices often function in a diverse range of environments, making the challenge of ensuring their security all the more complex. IoT security issues is crucial in this regard, as they can significantly impact the overall effectiveness of IoT solutions. This is especially true in a world brimming with connected devices, where each addition to the network potentially introduces new security challenges.
Looking Ahead: Best Practices and Future Considerations
As we look to the future, it’s evident that IoT security will continue to be a dynamic field, shaped by technological advancements and regulatory changes. Such measures are pivotal in mitigating attacks on IoT systems, which are becoming increasingly sophisticated and frequent.
The future of IoT security will likely see increased integration of AI and machine learning for threat detection, a greater focus on edge computing security, and the development of universal security standards. Prioritizing data security in IoT systems will be a significant aspect of these advancements, ensuring that personal and corporate data remains protected.
In conclusion, securing the IoT is an ongoing process that requires vigilance, innovation, and collaboration. By staying informed and proactive, we can navigate the challenges and harness the full potential of this transformative technology, ensuring a secure and prosperous future.
Additional Resources
We have additional resources for you to explore on these to interconnected subjects:
- OWASP Top 10 IoT Vulnerabilities
- Guide to IoT
- IoT Security Risks
- IoT Security Best Practices
- Host Endpoint Security

Experienced cybersecurity analyst, software engineer, patent attorney, worked with Linux, Windows, AWS, lots of security tools. Hope to help people do the right things and do the things right!


