Understanding Ransomware Attacks
It’s crucial for small businesses to fortify their defenses against escalating ransomware threats. These malicious cyberattacks have surged, posing an ever-increasing challenge to organizations globally. Particularly at risk are small enterprises, which are often seen as less fortified targets due to constrained cybersecurity resources. This guide offers a comprehensive ransomware prevention checklist. It is designed to bolster your system’s resilience and mitigate the risk of a devastating ransomware incident. Understanding the dynamics of ransomware attacks is the first step in crafting an effective defense strategy.
The Rising Threat of Ransomware
Ransomware, a type of malicious software, has rapidly evolved into one of the most significant cybersecurity threats in recent years. It operates by encrypting valuable data on a victim’s system. This renders the data inaccessible. The hacker then demands a ransom—usually in cryptocurrency—for its release. This form of cyber attack is increasingly targeting small businesses, exploiting vulnerabilities to infiltrate networks and capture sensitive information.
The escalation in ransomware attacks since 2022 is not just about frequency; it’s also about sophistication. Modern ransomware can evade traditional defenses, making previous security measures inadequate. These attacks can lead to data breaches and significant operational disruptions, emphasizing the need for robust ransomware prevention strategies. Businesses must recognize the severity of the threat. They need to take proactive steps to prepare their systems against these evolving security challenges.
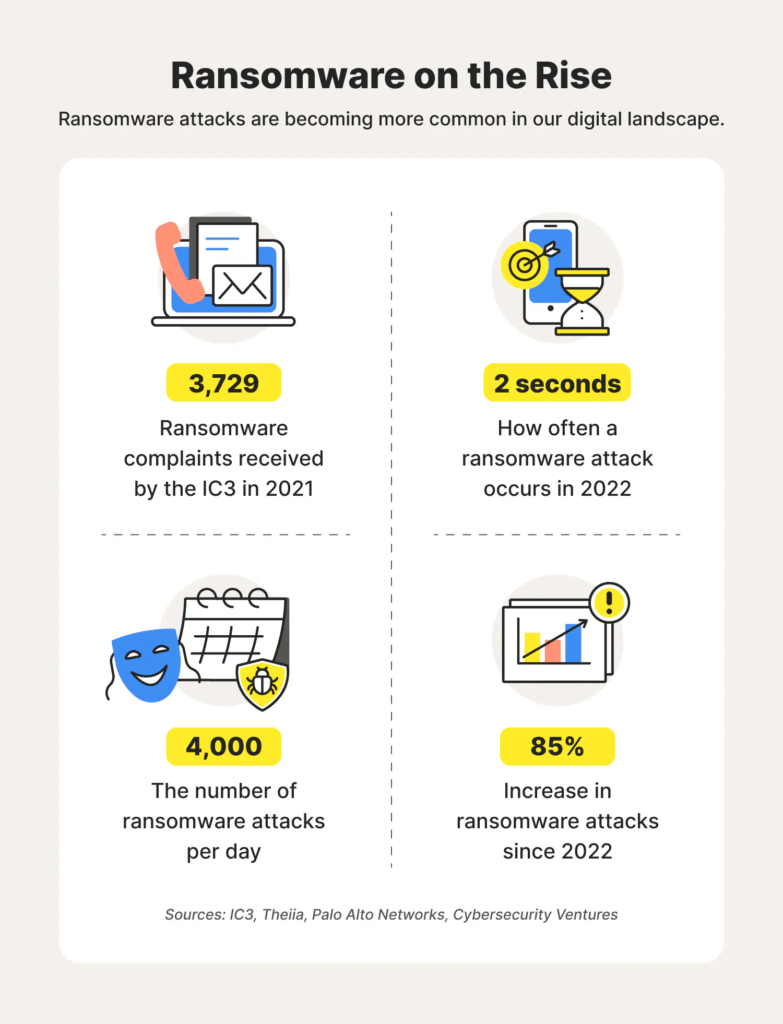
Source: 100+ ransomware statistics for 2023 and beyond – Norton
Why Small Businesses are Prime Targets
Large corporations boast dedicated IT teams and substantial security budgets. Contrast this with small businesses that often face constraints in implementing advanced cybersecurity measures. This disparity renders them more susceptible to cybercriminals who are constantly on the lookout for easier targets. Employing a ransomware prevention checklist is a strategic step for small enterprises to enhance their defenses. In doing so, they diminish their visibility on the radar of these malicious actors.
Common Ransomware Attack Methods
Ransomware attacks, an ever-present threat in the cyber realm, often leverage a variety of tactics to infiltrate and paralyze systems. Phishing remains one of the most prevalent methods of entering a system. Attackers send deceptive emails that trick recipients into clicking malicious links or opening infected attachments. These emails often appear legitimate, making them a potent tool for spreading malware.
Exploit use is another common technique, targeting specific vulnerabilities in software or systems. Cybercriminals exploit these security gaps to gain unauthorized access and deploy ransomware. Regular software updates and patches are crucial in mitigating this threat, as they address known vulnerabilities.
Social engineering tactics also play a significant role in ransomware attacks. Here, attackers manipulate individuals into divulging sensitive information or performing actions that compromise security. This method preys on human psychology rather than technical vulnerabilities. This underscores the importance of comprehensive cybersecurity awareness and information security training within organizations.
Case Studies: Lessons from Real Incidents
The WannaCry Attack (2017)
The WannaCry ransomware attack serves as a harrowing example of how exploiting software vulnerabilities can lead to widespread chaos. It utilized a vulnerability in Microsoft Windows. This vulnerability had been patched but remained exposed in systems that hadn’t applied the update. This incident underscores the critical importance of keeping software up-to-date. Further, conducting regular system audits as outlined in any effective ransomware prevention checklist.
The Colonial Pipeline Attack (2021)
The attack on Colonial Pipeline highlights the real-world implications of ransomware attacks on critical infrastructure. The attackers were able to cripple a major fuel supply line by infiltrating the company’s systems through social engineering. This lead to significant economic and operational disruptions. This case study emphasizes the need for robust network security, regular data backups, and an incident response plan. These would have quickly addressed and mitigated the effects of such attacks.
Each of these incidents provides valuable insights into the methods used by cybercriminals and the profound impact ransomware can have. They reinforce the necessity of a multi-faceted approach to cybersecurity. By combining technical safeguards like endpoint security solutions and best practices for securing sensitive information with ongoing education and vigilance against social engineering and phishing attempts.
Preventing Incidents: A Comprehensive Ransomware Prevention Checklist
To effectively shield your business from ransomware, a comprehensive and dynamic approach is essential. This section introduces a detailed ransomware prevention checklist, tailored to reinforce your organization’s cyber defenses. By implementing these measures, small businesses can significantly bolster their security posture, turning potential vulnerabilities into strengths.
The Pillars of Proactive Ransomware Defense
Proactive defense against ransomware involves more than just technological solutions; it’s about cultivating a security-first mindset throughout your organization. Key pillars include:
- Continuous Employee Training: Regular training sessions act as the first line of defense. Doing so educates staff on recognizing and responding to cybersecurity threats like phishing emails.
- Strong Network Security Protocols: Implementing robust security measures to protect your network from unauthorized access.
- Up-to-date Systems and Software: Managing day-to-day system operations, utilizing management software to keep all systems and software patched and current to close off vulnerabilities that could be exploited by attackers.
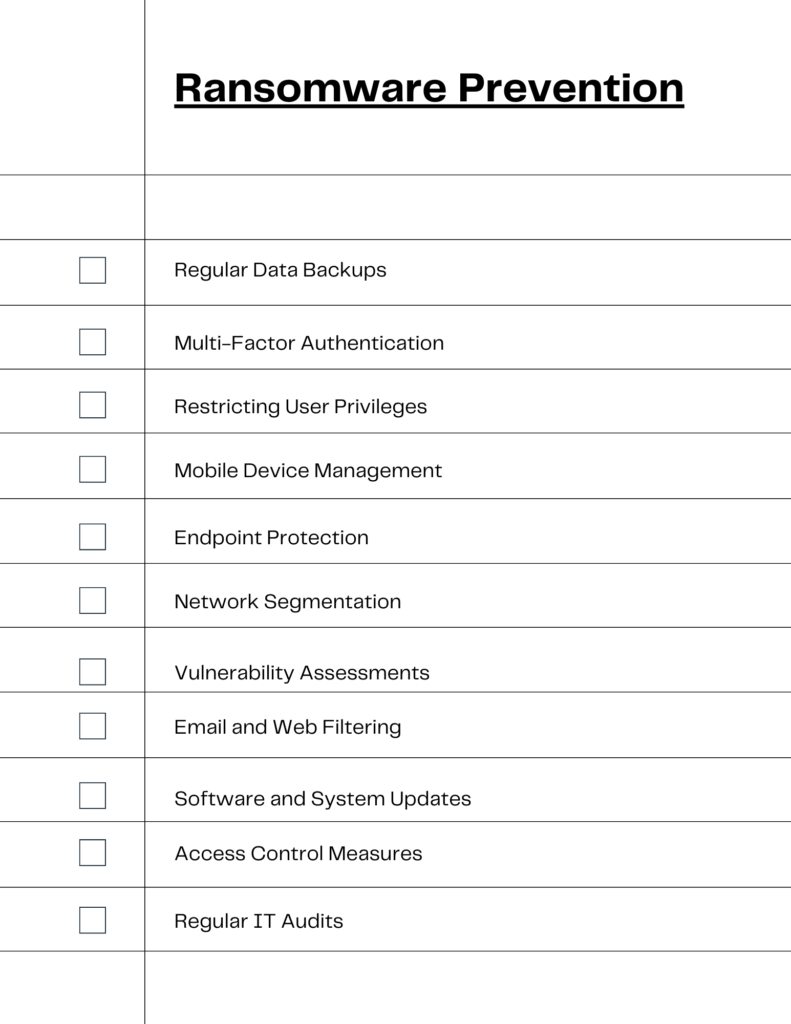
Essential Components of a Ransomware Prevention Checklist
Your ransomware prevention checklist should encompass a range of strategies to cover all aspects of your IT infrastructure. Essential components include:
- Regular Data Backups: Regularly backup data, maintaining frequent and secure backups of critical data, stored separately from your main network.
- Multi-factor Authentication: Implementing multi-factor authentication requires two or more pieces of evidence for verification. Doing this adds an extra layer of security for user logins.
- User Privilege Restriction: Restricting access privileges and access to data to essential personnel minimizes the impact of potential breaches.
- Mobile Device Management: Ensure all mobile devices are secured and managed to prevent them from being the weak link in your security.
- Endpoint Protection: Utilize advanced endpoint protection tools to detect and neutralize threats at the device level.
- Network Segmentation: Divide your network into secure segments to isolate and contain potential breaches. This helps prevent stolen data and contains breaches, reducing the spread of ransomware within the network.
- Vulnerability Assessments: Conduct regular checks to identify and rectify security weaknesses in your systems.
- Email and Web Filtering: Enhance email security by deploying an filtering system to block phishing emails and restrict access to malicious websites.
- Software and System Updates: Regular updates help organizations keep all systems and software secure and up to date.
- Access Control Measures: Implement and regularly review access control policies to manage data access effectively.
- Regular IT Audits: Perform comprehensive audits of your IT infrastructure to ensure continuous security and compliance.
Integrate these elements into your cybersecurity framework. By doing so, you create a multi-layered defense strategy against ransomware. This significantly reduces the risk of falling victim to these disruptive attacks. Remember, ransomware prevention is not a one-time effort but an ongoing process that evolves with the changing cyber threat landscape.
Implementing Effective Access Management
Effective access management is a critical component in preventing unauthorized data access, serving as a fundamental safeguard in your ransomware prevention strategy. This subsection explores the role of access controls and how they contribute to a stronger defense against ransomware attacks.
Access controls are policies and technologies that restrict user access to networks, systems, and data. They are essential for ensuring that only authorized individuals can access highly sensitive data and information, thus significantly reducing the risk of internal and external breaches.
Role-Based Access Controls (RBAC)
Implementing RBAC ensures that employees have access only to the resources necessary for their job functions. This minimizes the potential damage from compromised user credentials or internal threats.
Least Privilege Principle
Adhering to the least privilege principle, where users are granted the minimum levels of access—or permissions—needed to perform their job functions. Assigning privileges based on the level of sensitivity of data is crucial to maintain a secure environment.
User Authentication and Authorization
Strengthening authentication processes, possibly through multi-factor authentication, enhances security by verifying the identities of users attempting to access the system. Proper authorization ensures that each user can only access data and resources appropriate to their role.
Regular Audits of Access Controls
Conducting regular audits of access control systems helps in identifying and addressing any potential weaknesses. This also involves monitoring user activities and access logs to detect any unusual or unauthorized activities.
Integration with Incident Response Plan
Incorporating access control strategies into your broader incident response plan can help in quickly identifying and isolating affected systems in the event of a ransomware attack.
By effectively managing, continuously monitoring and assigning access controls, organizations can significantly reduce their vulnerability to ransomware attacks. This proactive approach to access management not only safeguards against unauthorized data access but also reinforces the overall security posture of the organization.
Encouraging Cybersecurity Best Practices in Your Organization
Cybersecurity is not just a concern for IT departments; it is a critical responsibility shared by every member of an organization. This section emphasizes the need for cultivating a cybersecurity-conscious culture and outlines strategies that can be employed across the organization to enhance overall security. By encouraging best practices and integrating robust security measures, businesses can create a more resilient and aware workplace, better equipped to face the challenges of the digital age.
Building a Cybersecurity-Conscious Culture
Creating a cybersecurity-conscious culture involves more than just implementing policies; it requires a shift in mindset and behavior at every level of the organization. This can be achieved through:
- Regular Cybersecurity Training and Education: Conduct ongoing training sessions to provide staff with information about ransomware and keep them updated on the latest cybersecurity threats and prevention techniques. This includes educating them about ransomware, phishing scams, and safe internet practices.
- Encouraging Open Communication: Fostering an environment where employees feel comfortable reporting potential security threats or breaches without fear of repercussions.
- Promoting Safe Cyber Practices: Regularly communicating tips and reminders about strong password policies, safe browsing habits, and the importance of software updates.
- Leadership Involvement: Having the organization’s leadership actively promote and participate in cybersecurity initiatives to demonstrate its importance.

Key Strategies for Organizational Cybersecurity
In preparing for and mitigating the risks of cyber attacks, organizations should adopt a holistic approach:
- Conducting Regular Vendor Audits: Regularly evaluate the security protocols of third-party vendors to ensure they meet your organization’s cybersecurity standards.
- Developing and Testing Incident Response Plans: Having a clear, tested response plan for different types of cyber incidents, including ransomware attacks.
- Implementing Network Security Measures: Such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and regular network monitoring.
The Role of Multi-Factor Authentication
Multifactor authentication (MFA) plays a pivotal role in enhancing an organization’s security framework:
- Reinforcing User Identity Verification: MFA an extra layer of security, including key management, by requiring two or more verification methods, significantly reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
- Broad Implementation Across Systems: Ensuring MFA is used not only for network access but also for email, cloud services, and other critical applications.
- Regularly Updating and Reviewing Authentication Protocols: Keeping up with technological advancements in authentication methods to stay ahead of potential threats.
By embedding these practices and measures within the organizational structure, businesses can substantially elevate their defense against cyber threats, making cybersecurity a shared and integral part of their corporate culture.
Endpoint Security Solutions and Zero-Trust Approach in Ransomware Prevention
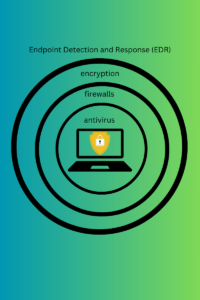
(click to enlarge)
Today, cyber threats are becoming increasingly sophisticated. Relying solely on traditional security measures is no longer sufficient. This section delves into advanced endpoint security solutions and the zero-trust approach, both critical in enhancing an organization’s resilience against ransomware by taking appropriate security precautions and reduce the chance of a successful attack. These strategies represent a shift towards more dynamic and adaptive security frameworks, crucial for safeguarding against evolving cyber threats.
Advanced Endpoint Security Technologies
Endpoint security solutions are integral to a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy, to prevent ransomware effectively:
- Robust Malware Detection and Prevention: Modern endpoint security systems employ advanced algorithms to detect and neutralize malware, effectively working to protect systems, including ransomware, before it can cause harm.
- Integration with Overall Security Infrastructure: Effective endpoint protection is not standalone; it integrates with the broader security infrastructure for a unified defense strategy.
- Continuous Monitoring and Response: These technologies continuously monitor endpoints for suspicious activities, offering real-time responses to potential threats.
- User Behavior Analytics (UBA): Utilizing UBA to identify abnormal or potentially malicious behavior that could indicate a security breach, enhancing the ability to preemptively address threats.
Understanding and Implementing Zero-Trust Security
The zero trust security model operates on the principle of “never trust, always verify,” a critical stance in today’s security landscape:
- Eliminating Implicit Trust: Zero trust requires verification of every user and device attempting to access resources in a network, regardless of their location or previous interactions.
- Micro-Segmentation of Networks: This approach involves dividing networks into small, manageable segments based on where critical data resides. This can provide a path for more controlled access and monitoring, making it harder for ransomware to move laterally across the system.
- Continuous Verification Processes: Implementing regular checks and balances to ensure that the security status of users and devices is consistently maintained.
Regular Software Updates and Data Scans
Maintaining the health and security of IT systems requires diligence in routine maintenance tasks:
- Regular Patch Management: Implementing security controls to keep all software and systems up-to-date with the latest patches is critical in closing security gaps that can be exploited by ransomware.
- Frequent Data Scans: Implementing routine scans of systems and networks for vulnerabilities and signs of intrusion helps in early detection and prevention of ransomware attacks.
- Automated Security Updates and Scans: Automating these processes ensures they occur consistently and without fail, enhancing the overall security posture.
By integrating these advanced technologies and approaches into their cybersecurity strategies, organizations can significantly strengthen their defenses against the sophisticated and ever-evolving nature of ransomware attacks.
Developing a Robust Ransomware Incident Response Plan
In the realm of cybersecurity, being prepared for potential ransomware attacks is just as important as prevention. This section focuses on the critical aspect of preparedness: developing a robust ransomware incident response plan. Such a plan is essential for quick and effective action in the event of an attack, minimizing potential damage and ensuring business continuity. We’ll explore the components of an effective plan, the steps involved in responding to an attack, and the importance of continually refining these strategies.
Crafting an Effective Incident Response Plan
A well-crafted incident response plan is a blueprint for action during a cybersecurity emergency. Its importance lies in:
- Defining Clear Roles and Responsibilities: Establishing who is responsible for what actions during an incident, ensuring a coordinated and efficient response.
- Setting Procedures for Different Scenarios: Tailoring responses to different types of ransomware attacks, considering various factors like the scale of the attack and the data affected.
- Ensuring Compliance with Legal and Regulatory Requirements: Including steps to comply with data breach notification laws and other relevant regulations.
- Establish Communication Strategies: Outlining how and when to communicate with internal stakeholders and external entities, such as law enforcement or customers, during an incident.
Key Steps in Responding to Ransomware Attacks
Responding effectively to a ransomware attack involves several key steps:
- Detection and Identification: Quickly identifying the presence of ransomware is crucial for limiting its spread and impact.
- Containment: Isolating affected systems to prevent further spread of the ransomware.
- Eradication and Recovery: Removing the ransomware from the affected systems and restoring data from backups.
- Post-Incident Analysis: Conducting a thorough analysis to understand how the breach occurred and how similar incidents can be prevented in the future.
Continuous Improvement of Response Strategies
Cyber threats are continually evolving, making it imperative to regularly update and refine the incident response plan:
- Regular Audits and Reviews: Assessing and updating the response plan to ensure it remains effective against new and evolving ransomware threats.
- Training and Drills: Utilizing tools like Active Directory in training sessions and simulated attacks to ensure that the response team and other employees are prepared and know what to do in the event of an actual attack.
- Learning from Past Incidents: Incorporating lessons learned from previous attacks into the response plan to continuously improve its effectiveness.
By establishing and regularly updating a comprehensive incident response plan, organizations can significantly mitigate the risks and impacts of ransomware attacks, ensuring they are well-prepared to handle such incidents efficiently and effectively.
Securing Your Future: Following a Ransomware Prevention Checklist Keeps You One Step Ahead of Threats
As we navigate the complex and ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity, it becomes increasingly clear that vigilance and adaptation are not just recommendations; they are necessities. The threat of ransomware is a persistent and growing challenge, one that demands continuous attention and a dynamic approach. In this guide, we’ve explored a comprehensive ransomware prevention checklist, delved into the importance of cultivating a cybersecurity-conscious culture, and emphasized the need for robust incident response planning.
However, the journey does not end here. Cybersecurity is a continuous process of learning, implementing, and adapting. Technologies advance, and so do the tactics of cybercriminals. To stay one step ahead of ransomware threats, it’s imperative for organizations, especially small businesses, to remain proactive in their cybersecurity efforts. This means regularly updating and reviewing security protocols, staying informed about the latest cyber threats, and fostering an environment within your organization where cybersecurity is a shared responsibility of all.
Remember, the goal is not just to respond to threats, but to anticipate and prevent them. By embracing a forward-thinking mindset, consulting with security authorities, investing in the right tools and training, and adhering to best practices, you can significantly enhance your organization’s resilience against ransomware. Let this guide be a starting point, a foundation upon which you build a more secure and confident future for your business in the digital world.
In conclusion, securing your organization against ransomware is a journey, not a destination. It requires commitment, collaboration, and the willingness to evolve. With these principles in mind, you can create a robust defense against ransomware, safeguarding your valuable data, and ensuring the continuity and success of your business.

Experienced cybersecurity analyst, software engineer, patent attorney, worked with Linux, Windows, AWS, lots of security tools. Hope to help people do the right things and do the things right!



Hello, I’ve been reading your article about ransomware prevention, and I find it extremely relevant given the increasing threat of cyberattacks. I’m new to the topic of cybersecurity, but I’m eager to learn more about protecting businesses from ransomware. The checklist you’ve provided is quite comprehensive and covers various aspects of prevention.
One thing that caught my attention is the concept of network segmentation as a defense strategy. Could you explain more about how network segmentation works and how it can effectively prevent ransomware attacks? How does it limit the spread of threats and enhance security?
Thank you for sharing your insights!
Thank you for your thoughtful comment!
Network segmentation sets up logical boundaries around parts of a network. It limits the traffic inside and out. That way it prevents the journey of a bad actor through a system.
There are parts of a system that are always weaker than others.
For example, one might have a very long development project that requires the use of software that is inherently vulnerable to attack. Rather than stop using it, which may be financially damaging to a company, they are willing to take some risk.
What you can do to manage the risk is isolate it on a part of the network. That way it is not accessible from the outside world. It can be put on its own subnet and only accessible through a gateway that requires authentication. So isolating it, it becomes less accessible to bad actors who might want to do a ransomware attack on the network through a weaker link.
You can also increase monitoring on that part of the network to be able to see such things as attempts by potential ransomware bots to “phone home”; trying to send messages to known ransomware addresses. This is one way to prevent an attack.
This is really what cybersecurity is all about. Managing risk.