
Why Endpoint Backup is Crucial in 2024
As we navigate the digital intricacies of 2024, the importance of endpoint backup has become undeniably paramount. This urgency is shaped by two dominant trends: the widespread adoption of remote work and a menacing cyber threat landscape. With an increasing number of employees accessing vital company data from a myriad of endpoint devices, businesses face heightened risks.
It may be the vulnerabilities of remote work environments or the escalating threats of ransomware attacks. In any case, having a robust endpoint backup strategy is no longer a luxury—it’s a critical necessity for safeguarding valuable business data and ensuring continuity.
Understanding the Basics of Endpoint Backup
Endpoint backup is a specialized process designed to safeguard data stored on endpoint devices. It does this by creating secure copies of that data. These copies can be restored in the event of data loss, corruption, or cyber threats. In the context of the modern digital workspace, it’s a foundational element of a comprehensive data protection strategy.
At its core, the essence of endpoint backup lies in its proactive approach. Instead of reacting to data loss incidents, businesses can preemptively secure their data. Thus, ensuring that even in the face of unforeseen challenges like ransomware attacks or hardware malfunctions, business operations remain uninterrupted.
In a world where data is often equated with currency, the significance of such a backup mechanism becomes clear. It’s not just about data recovery; it’s about business resilience and continuity.
But what exactly constitutes an endpoint? In the realm of IT, endpoint devices refer to any remote computing device that communicates back to a network. This includes:
- Laptops: Often the primary work device for many professionals, especially in remote work settings.
- Smartphones: Essential tools for communication and accessing business applications on the go.
- Tablets: Used for presentations, data access, and more.
- Desktops: Traditional workstations found in office settings.
Each of these devices, when connected to a business network, can access, store, and process business data. One has to deal with the diverse locations and network conditions that these devices operate under.
This is especially true in a work from home scenario. At home, they become potential entry points for cyber threats. Hence, ensuring they are backed up and protected is not a mere IT best practice—it’s a business imperative.
The Risks of Overlooking Endpoint Backup
In the digital age, data is the lifeblood of any business. However, without a robust backup strategy, organizations expose themselves to a myriad of risks that can have catastrophic consequences. Let’s delve into some of these risks and understand the pivotal role of backup in mitigating them.
Data Loss Scenarios and the Power of Backup
- Accidental Deletions: Imagine an employee inadvertently deleting a crucial project file. With a backup in place, such a file can be swiftly restored, ensuring no disruption to project timelines.
- Hardware Failures: Devices can malfunction. A sudden hard drive crash can wipe out months of work. But with endpoint backup, data can be retrieved from the most recent backup, minimizing downtime.
- Software Corruption: Software glitches or updates can sometimes corrupt files. Instead of losing valuable data, businesses with backup solutions can revert to a previous, uncorrupted version of the file.
- Lost or Stolen Devices: In a world where work is increasingly mobile, devices get lost or stolen. Endpoint backup ensures that the data on these devices is not lost forever and can be restored on a new device.
Ransomware: The Silent Threat
Ransomware attacks have become increasingly sophisticated. Cybercriminals encrypt user data, demanding a ransom for its decryption. However, organizations with a sound backup strategy can bypass this extortion. Instead of paying hefty ransoms, they can restore their data from the backup, rendering the ransomware attack ineffective.
Compliance and Legal Implications
Data breaches can lead to severe legal repercussions, especially with stringent data protection regulations in place globally. Non-compliance can result in hefty fines and a tarnished reputation.
Regular backups not only ensure data integrity but also play a crucial role in compliance monitoring. This prepares for the event of legal scrutiny or audits. Businesses can present their backup records as evidence of data management best practices, significantly reducing legal and compliance risks.
In conclusion, overlooking backup is a gamble no business can afford in today’s volatile digital landscape. Endpoint backup emerges as a non-negotiable business imperative. This is true from safeguarding against data loss scenarios to mitigating ransomware threats and ensuring compliance,
Diving Deep: The Technical Aspects of Backup
Backup strategies, while crucial for business operations, are underpinned by intricate technical details that determine their efficacy. Let’s delve into these technicalities to gain a deeper understanding of the backup process.
Data Encryption: The Shield of 256-bit AES
In the realm of data security, encryption stands as the first line of defense. 256-bit AES encryption is a widely recognized standard, offering a high level of security. Without delving too deep into cryptographic jargon, it’s essential to understand that the ‘256-bit’ denotes the encryption key’s size.
The larger the key, the tougher it is for cybercriminals to crack it. In practical terms, 256-bit AES encryption ensures that even if data is intercepted during the backup process, it remains indecipherable and secure.
Backup Frequency and Policies: Striking the Right Balance
Determining how often backups should occur is a delicate balance between risk mitigation and cost-efficiency.
- Frequent Backups: While backing up data frequently (e.g., every hour) ensures minimal data loss in case of a mishap, it can be resource-intensive, leading to higher costs and potential system slowdowns.
- Infrequent Backups: Less frequent backups (e.g., weekly) might be cost-effective but risk significant data loss if a disaster strikes just before the next scheduled backup.
There are three primary types of backups
Full Backups
This involves backing up all data, ensuring a complete data snapshot. While comprehensive, it’s resource-intensive and might not be feasible to perform daily.
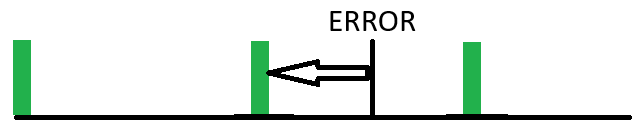
Here we see an example of a weekly full backup. Only one backup a week. So when an error occurs between backups requiring a restore, you have to go back to the last full backup and all of the data between that backup and the occurrence of the failure is lost. In the worst case, this could be close to a week.
Incremental Backups
Only the changes made since the last backup (whether full or incremental) are stored. This is quicker and requires less storage but can complicate the restoration process.
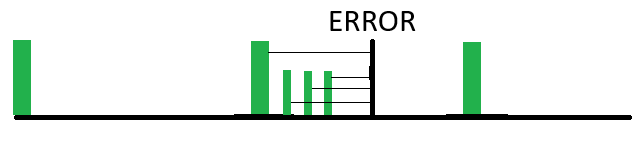
Here we see an example where in addition to the weekly full backups, on a daily basis the changes from the day before are backed up. So when an error occurs, the restoration process will get you all of the changes made up to the day before. The disadvantage of this over the full backup is that it takes up more storage and more processing time. Also, it takes more time to restore because you have to restore the full backup, then each incremental backup.
Differential Backups
This captures the changes made since the last full backup. It’s a middle ground between full and incremental backups in terms of speed and storage requirements.
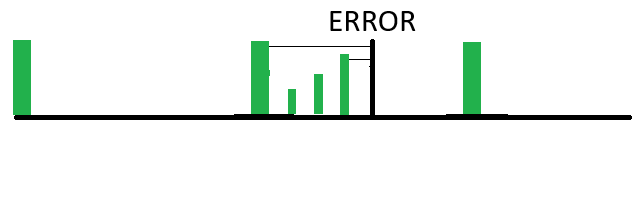
Here we see an example. There is a full backup each week. Between full backups, on a daily basis the changes since the last full backup are captured. So, when an error occurs, the restoration process will get you all the changes made up to the day before, and only require a two-step restoration process: the last full backup and the last incremental backup. The disadvantage is that it requires more storage and more time for each differential backup vs the incremental backup.
Cloud vs. On-Premise Backup: The 3-2-1 Rule
When considering backup storage, businesses often grapple with the choice between cloud and on-premise solutions. Each has its merits:
- Cloud Backup: Offers scalability, remote access, and eliminates the need for physical infrastructure. However, it’s dependent on internet connectivity and might have recurring costs.
- On-Premise Backup: Provides immediate data access and can be more secure, but requires hardware investment and is vulnerable to physical threats like fires or floods.
The 3-2-1 rule offers a balanced approach:
- Keep 3 copies of your data.
- Store 2 copies on different media or platforms.
- Ensure 1 copy is offsite (preferably on the cloud).
In essence, understanding the technical nuances of backup is pivotal for businesses to craft a strategy that’s both efficient and effective, ensuring data security and business continuity in the face of unforeseen challenges.
Comparing Backup Solutions in 2024
As businesses grapple with the complexities of data protection in 2024, choosing the right endpoint backup solution becomes paramount. Here are five key features to consider when evaluating your options:
- Robust Encryption: In an era rife with cyber threats, a backup solution must offer top-tier encryption standards, like 256-bit AES encryption, ensuring that data remains secure during both transit and storage.
- Flexible Backup Frequency: The solution should allow businesses to customize their backup schedules, balancing between risk mitigation and resource allocation. Whether it’s full, incremental, or differential backups, flexibility is key.
- Cloud Integration: With the increasing reliance on cloud infrastructure, an ideal backup solution should seamlessly integrate with popular cloud platforms, adhering to the 3-2-1 rule of backups.
- User-Friendly Restoration: In the event of data loss, swift and hassle-free data restoration is crucial. The backup solution should offer intuitive tools for data retrieval, minimizing downtime.
- Compliance and Monitoring Tools: Given the stringent data protection regulations, backup solutions should come equipped with compliance monitoring features, ensuring businesses adhere to legal standards and can swiftly respond to audits or legal holds.
In 2024, as the digital landscape continues to evolve, these features stand out as non-negotiables, ensuring businesses have a robust, efficient, and compliant backup strategy in place.
Real-world Scenarios: The Importance of Endpoint Backup in Action
In 2019, a prominent U.S. healthcare institution fell victim to a ransomware attack, with encrypted patient records and crucial data held hostage. Thanks to their robust endpoint backup strategy, they restored the data from recent backups, bypassing the ransom and ensuring uninterrupted patient care.
Meanwhile, in 2018, an executive from a global corporation faced a potential crisis when her laptop, containing sensitive company data, was stolen during an international trip. The company’s endpoint backup system came to the rescue, allowing data restoration to a new device and a remote wipe of the stolen laptop.
In another incident in 2020, a major European university’s software update led to widespread data corruption. Their differential backup system proved invaluable, restoring corrupted data and preventing academic disruptions.
Endpoint Backup for the Remote Workforce
The shift to remote work, while offering unparalleled flexibility, has ushered in a unique set of challenges for businesses. One of the primary concerns is the increased vulnerability of endpoint devices connected to less secure home networks, heightening the risk of cyberattacks. Additionally, the physical security of devices becomes a concern, with laptops and other equipment susceptible to theft or damage in non-office environments. Furthermore, the blend of personal and professional data on a single device can lead to accidental data mishandling or breaches.
To navigate these challenges, businesses are adopting several best practices. Implementing 256-bit AES encryption ensures that data remains secure during transit between home networks and company servers. Regular training sessions for employees emphasize the importance of data security, equipping them with tools and knowledge to identify and thwart potential threats. Lastly, adopting a robust endpoint backup strategy is non-negotiable.
By ensuring that data from all endpoint devices is backed up regularly, businesses can swiftly recover from data loss incidents, be it from cyberattacks, device malfunctions, or human errors. In the era of remote work, a proactive approach to data security, underpinned by endpoint backup, is the cornerstone of business resilience.
Future of Endpoint Backup: What Lies Ahead
As we navigate the evolving digital landscape, several emerging trends and innovations in the backup domain are poised to redefine how businesses safeguard their data. One notable shift is the rise of Hybrid Cloud Backup Solutions. Businesses are increasingly leaning towards solutions that merge the immediacy of on-premise storage with the disaster recovery capabilities of the cloud, offering a balanced approach to data protection.
Furthermore, the integration of Artificial Intelligence in backup processes is gaining momentum. AI-enhanced backup systems can intelligently predict optimal backup schedules, swiftly detect potential data breaches, and streamline the restoration process. This automation ensures businesses experience minimal disruptions during unforeseen data loss incidents.
Ransomware, a looming threat in the cyber realm, is driving the demand for immutable backups. These unalterable backup copies act as a failsafe, ensuring data remains untouched even if primary datasets are compromised. Additionally, the ‘as a Service’ model is making waves in the backup sector, with Backup as a Service (BaaS) offerings providing robust backup capabilities without the complexities of managing underlying infrastructures.
Lastly, with the remote work paradigm becoming ubiquitous, there’s an amplified focus on endpoint backup. Innovations are veering towards real-time backup solutions for endpoint devices, ensuring continuous data protection, irrespective of an employee’s location.
Wrapping Up: Taking the Next Steps in Your Endpoint Backup Journey
In the dynamic world of digital data, staying updated and proactive in your endpoint backup strategies is not just a recommendation—it’s a necessity. As we’ve explored, the landscape of backup solutions is continuously evolving, driven by technological advancements and ever-changing business needs. Ensuring that your data is safeguarded against potential threats requires both vigilance and adaptability. We encourage all our readers to remain at the forefront of these developments, ensuring that your backup strategies are always a step ahead of potential challenges.
Moreover, we recognize that every business has its unique journey, filled with its own set of experiences, challenges, and success stories. We invite you to share your tales from the trenches—whether it’s a backup challenge you’ve overcome, an innovation you’ve implemented, or a success story that can inspire others. Together, as a community, we can learn, grow, and fortify our defenses in this digital age.

Experienced cybersecurity analyst, software engineer, patent attorney, worked with Linux, Windows, AWS, lots of security tools. Hope to help people do the right things and do the things right!

