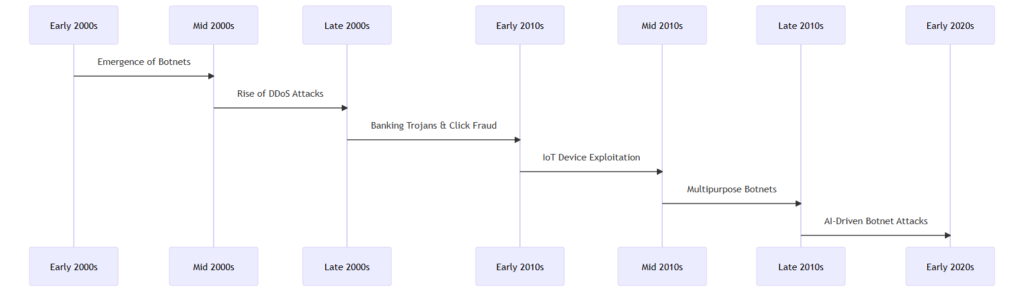
Introduction to Botnets and Their Impact
In the evolving landscape of cybersecurity threats, botnets have emerged as a formidable challenge. A botnet is a network of infected computers, or ‘bots’, controlled by a single entity, typically a hacker. Malware often infects regular computers, smartphones, or Internet of Things (IoT) devices, compromising them without the owner’s knowledge. Once integrated into a botnet, a device can launch Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks, send spam, or steal data.
Botnet attacks hold overwhelming significance in the current cybersecurity landscape. Botnets represent a unique threat because they harness the collective power of multiple infected devices, making their attacks more potent than those originating from a single source. Botnets often perpetrate large-scale attacks targeting critical infrastructure, disrupting services, and compromising sensitive data. The versatile nature of botnets means they can adapt to different types of attacks, making them particularly hard to detect and counter.
Moreover, the rise of IoT devices has expanded the potential for botnet growth. With more devices connecting to the internet, there are more opportunities for cybercriminals to exploit vulnerabilities and recruit new bots. This growing network of compromised computers presents a significant challenge to individuals and organizations, underscoring the need for robust botnet detection and prevention strategies.
In summary, understanding the nature of botnets and their impact is crucial for anyone concerned with cybersecurity. By grasping how these networks operate and the threats they pose, we can better prepare to defend against them, ensuring the security and integrity of our digital landscape.
What’s It All About?
This post delves into the complex world of botnets and the critical importance of botnet detection in cybersecurity. Botnets, networks of infected devices controlled by hackers, pose significant threats, including DDoS attacks, data breaches, and malware spread. Effective botnet detection is challenging due to their covert nature but is crucial for mitigating their impact. The post highlights the evolution of botnet detection techniques, from reactive methods like signature-based detection to proactive strategies using machine learning and AI, which analyze network patterns to identify potential threats. Key types of botnets – Financial, IoT, P2P, Spam, and DDoS – each require tailored detection and prevention strategies. Additionally, DNS-based detection plays a pivotal role in combating botnets. The article underscores the necessity of continuous innovation and adaptation in botnet detection methods to stay ahead of evolving cyber threats, ensuring digital security in an ever-changing landscape.
How is a Botnet Created?
A botnet is created through a multi-step process that typically involves the following stages:
- Malware Distribution: The initial step is the distribution of malware, which is often done through phishing emails, compromised websites, or exploiting vulnerabilities in software. This malware is designed to take control of the device and connect it to a botnet.
- Infection and Control: Once the malware is installed on a device, it establishes a connection to a command and control (C&C) server. This server remotely directs the infected device, turning it into a ‘bot.’
- Recruitment and Expansion: The network of bots grows as more devices are infected and recruited into the network. This expansion can be rapid, as each new bot can potentially spread the malware to additional devices.
- Activation for Malicious Activities: With a network of controlled bots established, the botnet operator can then use this network to carry out various malicious activities. These can include launching DDoS attacks, sending spam emails, stealing data, or distributing more malware.
Understanding the creation process of a botnet is crucial for developing effective strategies to prevent, detect, and mitigate such threats.
Understanding Botnet Detection: A Key to Cybersecurity

Bot detection is an essential component in the arsenal against cyber threats. It involves identifying the presence of a botnet within a network before it can cause harm. This process is challenging due to the covert nature of botnets, which are designed to remain hidden while performing malicious activities. Botnet detections will not only identify the existence of bots but also help in understanding their behavior, which is key in mitigating their impact.
The importance of botnet detection and removal in cybersecurity cannot be understated. Botnets are often responsible for significant disruptions, including large-scale DDoS attacks, data breaches, and the spread of malware. Detecting a botnet early can prevent these attacks or minimize their impact, protecting sensitive data and maintaining the integrity of affected systems. For businesses, this means safeguarding not just their operational infrastructure but also their reputation and customer trust.
The Evolution of Botnet Detection Technology
The evolution of botnet detection has been closely tied to advancements in technology. Early botnet detection techniques were largely reactive, relying on recognizing known patterns of botnet behavior. This approach, while effective against known threats, struggled to identify new or evolving botnets. The advent of machine learning and AI in cybersecurity has brought a paradigm shift. These technologies enable proactive detection, analyzing vast amounts of network data to identify unusual patterns that may indicate botnet activity. This shift from a reactive to a proactive stance significantly enhances the ability to detect novel and sophisticated botnets.
Moreover, the integration of machine learning algorithms allows for continuous learning and adaptation. As botnets evolve, so do the detection systems, constantly improving their ability to identify and neutralize threats. This ongoing advancement in botnet detection technology is a critical factor in staying ahead of cybercriminals in an ever-changing digital landscape.
In summary, understanding and implementing advanced botnet detection methods is paramount in cybersecurity. As technology continues to evolve, so does the sophistication of botnets, making continuous innovation in detection methods not just beneficial but necessary for ensuring digital security.
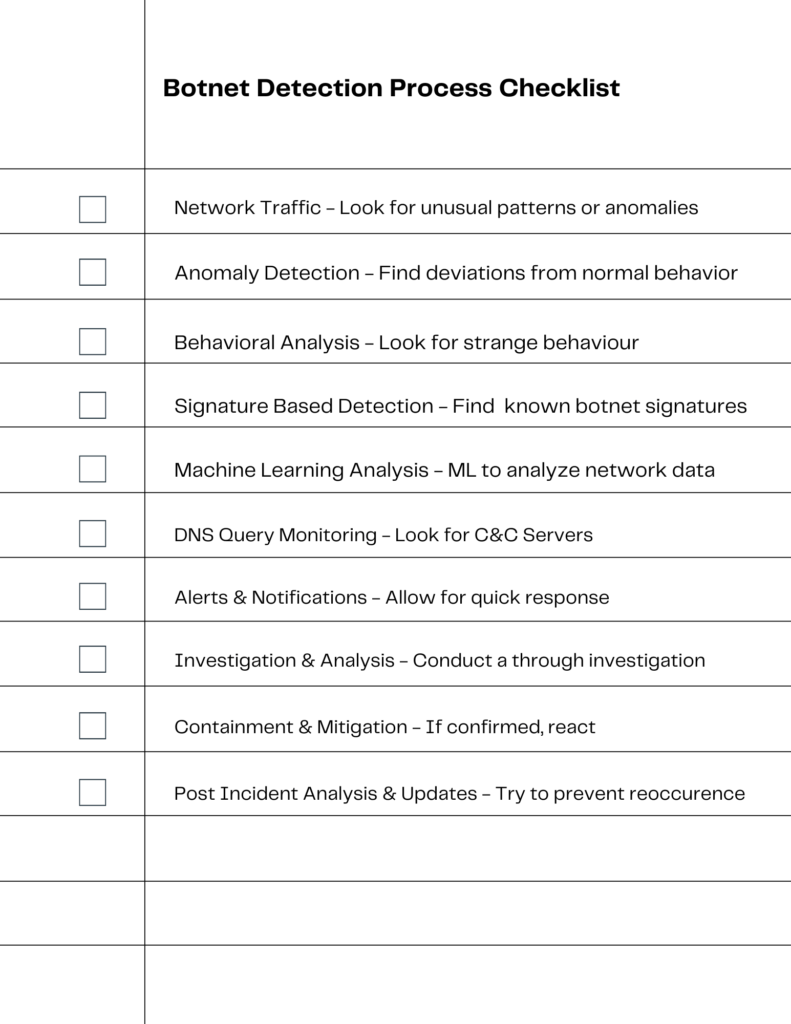
Botnet Detection Process
The checklist below shows a step-by-step list for the botnet detection process:
- Network Traffic Monitoring: Continuously monitor network traffic for unusual patterns or anomalies. This includes checking for unexpected data flows, high volumes of traffic, or communication with known malicious IP addresses.
- Anomaly Detection: Utilize anomaly detection systems to identify deviations from normal network behavior. These systems can flag unusual activities that may indicate the presence of a botnet.
- Behavioral Analysis: Implement behavioral analysis tools to examine the behavior of devices on the network. Look for signs such as unexplained data transmissions, unexpected requests, or strange system behavior.
- Signature-Based Detection: Use signature-based detection tools to scan for known botnet signatures. This involves matching network activities against a database of known botnet characteristics and behaviors.
- Machine Learning Analysis: Apply machine learning algorithms to analyze network data. These algorithms can learn from existing data patterns to predict and identify potential botnet activity.
- DNS Query Monitoring: Monitor DNS queries to detect communication attempts with command and control (C&C) servers. Unusual or repeated DNS requests can be a sign of a botnet trying to establish or maintain control.
- Alerts and Notifications: Set up a system for alerts and notifications when potential botnet activity is detected. This allows for quick investigation and response.
- Investigation and Analysis: Once an alert is triggered, conduct a thorough investigation and analysis to confirm the presence of a botnet. This may involve examining logs, checking device integrity, and analyzing network traffic in more detail.
- Containment and Mitigation: If a botnet is confirmed, implement containment and mitigation strategies. This might include isolating infected devices, blocking malicious traffic, or updating security measures to neutralize the threat.
- Post-Incident Analysis and Updates: After addressing the immediate threat, perform a post-incident analysis to understand how the botnet penetrated the network and update security policies and tools to prevent future occurrences.
This outlines a comprehensive botnet detection process that provides a clear understanding of each step involved in identifying and responding to botnet threats.
Types of Botnets: Understanding the Variety and Complexity
Botnets come in various forms, each with its unique characteristics and threats. Understanding the diversity of botnets is key to recognizing and countering the different types of cyber threats they pose.
DDoS Botnets
One of the most common types of botnets, DDoS botnets are used to perform Distributed Denial of Service attacks. By harnessing the collective power of numerous infected devices, these botnets can overwhelm a target server or IP address with traffic, causing service disruptions. The infamous Mirai botnet, which primarily targeted IoT devices, is a notable example of a DDoS botnet.
Spam Botnets
These botnets are designed to send out massive amounts of spam emails. They can be used for distributing malware, phishing scams, or simply flooding inboxes to disrupt communications. Spam botnets often rely on a large number of bots to avoid detection.
Financial Botnets
Focused on monetary gain, these botnets are used for activities like stealing credit card information, and banking credentials, or conducting fraudulent transactions. They often employ sophisticated methods to evade detection by security systems.
IoT Botnets
With the proliferation of IoT devices, IoT botnets have become increasingly common. An IoT botnet may exploit vulnerabilities in IoT devices, which are often less secure than traditional computing devices. IoT botnets can be used for a variety of purposes, including DDoS attacks and data breaches.
P2P (Peer-to-Peer) Botnets
Unlike traditional botnets that rely on a central command and control (C&C) server, P2P botnets distribute their control mechanism across the botnet, making them harder to disrupt. They are resilient and can be used for various malicious activities, including DDoS attacks and information theft.
Each type of botnet poses unique threats based on its design and objectives. For instance, DDoS botnets can cripple critical online services, while financial botnets directly threaten financial assets. IoT botnets raise significant concerns due to the sheer number of vulnerable devices and their potential to cause widespread disruption.
Understanding the variety and complexity of botnets is crucial in developing effective countermeasures. It helps in tailoring detection and prevention strategies to the specific characteristics of different botnet types, thereby enhancing the overall security posture against these evolving cyber threats.
The Role of Machine Learning in Botnet Detection

Machine learning is revolutionizing the field of cybersecurity, particularly in botnet detection. By leveraging data-driven algorithms, machine learning offers dynamic and adaptive solutions to identify and counter botnet threats.
Transforming Detection Capabilities
Machine learning algorithms excel at analyzing vast quantities of data to identify patterns and anomalies. This capability is crucial in detecting botnet activity, which often involves subtle and complex network behaviors. For instance, machine learning techniques are employed to discern patterns in network traffic that may indicate botnet involvement. This approach is far more efficient and effective than traditional methods, which might struggle with the sheer volume and sophistication of modern cyber threats.
Case Study: BredoLab Botnet Disruption
A notable example of machine learning in action is the disruption of the BredoLab botnet. By analyzing network traffic data, machine learning algorithms were able to detect unusual patterns indicative of botnet activity. This led to the identification and subsequent dismantling of the botnet, preventing further malicious activities.
Proactive Defense with Predictive Analysis
Machine learning isn’t just reactive; it’s also predictive. By analyzing current trends and data, machine learning models can forecast potential future botnet trends, allowing cybersecurity teams to preemptively bolster their defenses. This predictive capability was demonstrated in preparing defenses against the evolving tactics of the Ramnit botnet, enabling a more proactive cybersecurity stance.
Machine Learning in Intrusion Detection Systems
Incorporating machine learning into Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) has significantly improved the detection of botnet-related activities. These systems, trained on extensive datasets of both normal and malicious network behaviors, are adept at identifying even the subtlest indications of botnet infections. Such enhanced detection was pivotal in identifying variants of the Storm Worm botnet.
Deep Learning for Advanced Threats
Deep learning, an advanced branch of machine learning, is particularly effective against sophisticated botnets that might evade traditional detection methods. By analyzing complex and extensive datasets, deep learning models uncover intricate patterns that signal advanced botnet activities. The detection of the TrickBot botnet, known for its advanced evasion techniques, showcases the effectiveness of deep learning in this arena.
In conclusion, the role of machine learning in botnet detection is transformative. Its ability to analyze, predict, and adapt to the ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats makes it an invaluable tool in the fight against botnets. As machine learning technology continues to advance, so too will the capabilities to detect and neutralize these pervasive cyber threats.
Botnet Attack Detection: Comprehensive Tools and Techniques
In the realm of cybersecurity, a diverse array of tools and techniques have been developed for botnet attack detection. These range from basic signature-based methods to sophisticated behavioral analysis systems.
Signature-Based Detection Techniques
Signature-based detection, one of the earliest forms of botnet detection, relies on known patterns of malware and botnet behavior. These systems compare network activities against a database of known signatures or patterns associated with botnets. While effective against known threats, signature-based detection has limitations. It struggles to identify new or evolving botnets that don’t match existing signatures.
Behavioral Analysis and Anomaly Detection
Behavioral analysis and anomaly detection techniques have been developed in order to counter the limitations of signature-based systems. These methods analyze the normal behavior of a network and flag deviations that could indicate botnet activity. For example, a sudden spike in outgoing traffic from a device could be a sign of botnet involvement. These techniques are more dynamic and can detect previously unknown botnets.
Machine Learning and AI in Botnet Detection
Machine learning and AI have greatly enhanced botnet detection capabilities. These technologies analyze large data sets to learn and predict botnet behavior, offering a proactive approach to detection. They can adapt to new threats more rapidly than traditional methods, though they require substantial data and computational power.
Network Traffic Analysis
Analyzing network traffic is key in detecting botnet activity. Tools like intrusion detection systems (IDS) and network traffic analyzers can monitor data flows for signs of botnet involvement, such as unusual data packets or traffic patterns.
DNS Monitoring
Monitoring DNS queries can also reveal botnet activity, as many botnets rely on DNS to communicate with their command and control centers. Anomalies in DNS request patterns can be indicative of botnet activity.
Choosing the Right Detection Tools for Your Business
Selecting the right botnet detection tools is crucial for businesses of all sizes. The choice depends on several factors:
- Business Size and Network Complexity: Larger businesses with complex networks may require more advanced tools, such as AI-driven detection systems. Smaller businesses might benefit from simpler, less resource-intensive solutions.
- Type of Data and Assets to Protect: The nature of the data and assets a business needs to protect also influences the choice of tools. High-value assets may require more sophisticated protection strategies.
- Compliance Requirements: Businesses in certain industries might be subject to regulatory compliance requirements that dictate specific security measures, including botnet detection capabilities.
- Budget and Resources: The budget and IT resources available will also play a role in tool selection. While more advanced tools offer better protection, they also require more investment in terms of money and skilled personnel.
- Scalability: The chosen tools should be scalable to grow with the business and adapt to evolving threats.
Top Botnet Detection Tools
Here’s a brief overview of some of the top botnet detection tools available in 2023:
- Snort: An open-source tool known for its robust network traffic analysis and behavioral analytics capabilities. Snort is a favorite among many IT professionals for its versatility and community support.
- Bro/Zeek: Offers both network traffic analysis and behavioral analytics. It’s scalable, making it suitable for businesses of various sizes.
- Darktrace: A leader in the realm of threat intelligence, Darktrace uses AI to provide real-time threat detection and autonomous response.
- Splunk: Known for its real-time monitoring capabilities, Splunk offers behavioral analytics and has a user-friendly interface, making it a popular choice for many organizations.
- Cisco Stealthwatch: This tool stands out for its IoT device monitoring feature. Alongside, it offers real-time monitoring, ensuring comprehensive network security.
| Tool | Features | Price | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Snort | Network Traffic Analysis, Behavioral Analytics | Open Source | Snort Website |
| Bro/Zeek | Network Traffic Analysis, Behavioral Analytics | Varies by Size | Zeek Website |
| Darktrace | Network Traffic Analysis, Threat Intelligence | Contact for Pricing | Darktrace Website |
| Splunk | Real-time Monitoring, Behavioral Analytics | Varies by Usage | Splunk Website |
| Cisco Stealthwatch | IoT Device Monitoring, Real-time Monitoring | Contact for Pricing | Cisco Website |
In summary, while there is a wide range of tools and techniques available for botnet attack detection, the effectiveness and suitability of each depend on the specific needs and circumstances of the business. A careful assessment of these factors will guide businesses in choosing the right tools to protect their digital assets effectively.
Identifying and Responding to Botnet Activity
In the ongoing battle against cyber threats, identifying signs of botnet activity and responding effectively are critical steps. Timely detection and appropriate response can mitigate the impact of a botnet attack.
Strategies for Identifying Signs of Botnet Activity
Detecting a botnet attack involves vigilance and the use of sophisticated detection tools. Key strategies include:
- Monitoring Network Traffic: Unusual patterns in network traffic, such as spikes in outbound traffic or increased requests to unknown servers, can be indicative of botnet activity. Tools like network analyzers play a crucial role in this monitoring process.
- Analyzing Server Logs: Server logs can reveal suspicious activities, like multiple failed login attempts or strange data requests, which might suggest a botnet’s presence.
- DNS Query Analysis: Since botnets often rely on DNS for command and control communications, unusual DNS query patterns can be a red flag.
- Utilizing Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): IDS can help identify potential botnet traffic by analyzing network data and comparing it against known threat signatures.
- Endpoint Security Solutions: These solutions monitor individual devices for signs of malware or botnet infection, such as unexpected software changes or system performance issues.
Best Practices for Responding to a Detected Botnet Attack
Once a botnet attack is detected, prompt and strategic response is essential to contain and neutralize the threat.
- Isolation of Affected Systems: Immediately isolate infected devices from the network to prevent the spread of the botnet.
- Engaging Incident Response Teams: Involve cybersecurity experts or incident response teams to analyze the attack and orchestrate a response.
- Updating Security Systems: Update firewalls, antivirus programs, and other security systems to counter the specific botnet characteristics identified.
- Notifying Stakeholders: Inform relevant stakeholders, including employees and, if necessary, customers, about the breach, especially if sensitive data is involved.
- Conducting a Thorough Investigation: A comprehensive investigation should follow to understand the botnet’s source, the extent of the damage, and vulnerabilities exploited.
- Implementing Remediation Measures: Based on the investigation, implement remediation measures to repair damage and strengthen network defenses against future attacks.
- Reviewing and Updating Security Policies: Post-attack, it’s crucial to review and update security policies and practices to prevent similar incidents.
In summary, proactive identification of botnet activity and a well-planned response strategy are vital in minimizing the impact of botnet attacks. Employing a combination of advanced tools and best practices ensures a robust defense against these pervasive cyber threats.
Detection and Prevention: A Dual Approach to Combat Botnets
Combating botnet threats effectively requires a dual approach that incorporates both detection and prevention. This synergy ensures not only the identification of existing threats but also the minimization of future vulnerabilities.
Synergy Between Detection and Prevention
Detection involves identifying botnet activities within a network, while prevention focuses on stopping these threats before they can cause harm. The two strategies complement each other: effective detection informs prevention strategies, and robust prevention reduces the burden on detection systems. For instance, understanding the behavior of a detected botnet can help in fortifying defenses against similar future attacks.
Creating a Robust Defense Strategy
- Regular Network Monitoring: Consistently monitoring network traffic for unusual patterns is crucial in early detection of botnet activity.
- Implementing Strong Security Protocols: This includes using firewalls, antivirus programs, and intrusion detection systems that are regularly updated.
- Employee Training and Awareness: Educating staff about cybersecurity best practices can prevent inadvertent breaches that lead to botnet infections.
- Regular Software Updates and Patch Management: Keeping software and systems up-to-date reduces vulnerabilities that botnets often exploit.
- Using Advanced Threat Intelligence: Leveraging threat intelligence services can provide insights into emerging botnet trends and prevention strategies.
Implementing DNS-based Botnet Detection
DNS-based detection is a powerful tool in identifying and disrupting botnet activities. This approach involves monitoring DNS queries to detect anomalies that may indicate botnet communication.
How DNS-based Detection Works
- Monitoring DNS Requests: By analyzing DNS query patterns, it’s possible to identify suspicious activities, such as frequent requests to known malicious domains.
- DNS Sinkholing: Redirecting traffic from suspicious domains to a controlled server can prevent botnets from communicating with their command and control centers.
- Analyzing DNS Traffic Patterns: Large volumes of DNS requests or unusual patterns can be indicative of a botnet attempting to establish or maintain control over infected devices.
Case Studies Demonstrating DNS-based Detection Impact
- The Conficker Botnet: Utilizing DNS sinkholing, security experts were able to disrupt this botnet’s communication channels, significantly limiting its spread and impact.
- Gameover Zeus Disruption: Collaborative efforts using DNS-based detection methods were pivotal in dismantling the command and control infrastructure of this financially motivated botnet.
- Mirai Botnet Analysis: DNS query analysis helped in identifying infected IoT devices, providing crucial data for developing countermeasures against this large-scale botnet.
In summary, combining detection and prevention strategies offers a comprehensive approach to managing botnet threats. Implementing DNS-based detection, in particular, has proven effective in identifying and mitigating botnet activities, showcasing its importance in the broader cybersecurity strategy.
Botnet Detection: Emerging Trends and Predictions
As cyber threats evolve, so do the strategies and technologies for detecting botnets. Staying ahead of these changes is essential for effective cybersecurity. This section delves into the current trends in botnet detection and offers predictions for future developments.
Current Trends in Botnet Detection
- Increased Use of Machine Learning and AI: Detection using artificial intelligence and machine learning in botnet detection is rapidly growing. These technologies are becoming more adept at analyzing patterns in data to predict and identify botnet activities.
- Focus on detection in IoT Security: With the proliferation of IoT devices, there’s an increasing emphasis on securing these devices against botnet attacks. This includes developing specialized detection methods tailored to the unique vulnerabilities of IoT technology.
- Rise of Autonomous Response Solutions: Automated response mechanisms that can independently react to detected threats are becoming more prevalent. These systems can quickly isolate affected parts of a network to minimize damage from botnet attacks.
- Integration of Threat Intelligence Platforms: There’s a growing trend of integrating threat intelligence platforms into detection systems. These platforms provide real-time data and insights about emerging threats, enhancing the ability to detect and respond to botnets.
Predictions for Future Developments
- Advanced Predictive Analytics: The future of botnet detection likely includes more sophisticated predictive analytics, using machine learning algorithms to forecast future attack patterns and prepare defenses accordingly.
- Enhanced Deep Learning Capabilities: Deep learning models, which can analyze more complex data sets, are expected to play a bigger role in detecting advanced botnets that evade traditional detection methods.
- Greater Emphasis on Behavioral Analysis: Behavioral analysis, as opposed to signature-based detection, will become more prominent. This shift will help in identifying new and evolving botnets based on their behavior rather than known signatures.
- Blockchain in Botnet Defense: The use of blockchain technology for securing networks against botnets may emerge as a trend. Blockchain can potentially enhance the integrity and security of communication within networks.
The Role of Emerging Technologies
Emerging technologies are poised to significantly enhance botnet detection capabilities. For instance, the integration of AI and machine learning not only improves the accuracy of detection but also speeds up the response to threats. The use of cloud computing and big data analytics offers the potential for more robust and scalable detection solutions. Additionally, advancements in network security, such as next-generation firewalls and advanced endpoint protection, are set to provide stronger defenses against botnet infiltrations.
In conclusion, the field of botnet detection is evolving rapidly, driven by technological advancements and changing cyber threat landscapes. Staying informed about these trends and predictions is crucial for developing effective strategies to combat botnet attacks in the future.
How to Prevent Your Network from Becoming Part of a Zombie Botnet
Zombie botnets, networks of compromised devices controlled by a central source, pose a significant threat to both individual users and organizations. Understanding how to prevent your network from becoming a part of such a botnet is crucial for maintaining cybersecurity.
What are Zombie Botnets?
Zombie botnets are made up of infected devices, known as ‘zombies,’ that are remotely controlled by a cybercriminal, often referred to as a botmaster. These botnets can be used for various malicious activities, including launching DDoS attacks, sending spam, or spreading malware. The ‘zombie’ devices can range from personal computers to IoT devices, all covertly contributing to the botnet’s malicious activities.
Preventative Measures Against Zombie Botnets
- Regular Software Updates: Keeping all software, especially antivirus and malware protection, updated can close security gaps that botnets exploit.
- Strong Network Security: Implementing robust network security measures like firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and secure Wi-Fi networks.
- Employee Education and Training: Regularly training employees on identifying phishing attempts and suspicious activities can prevent inadvertent downloading of botnet malware.
- Monitoring Network Traffic: Keeping an eye on network traffic for unusual activities can help in early detection of botnet infections.
- Implementing Access Controls: Limiting user access to essential systems and data can reduce the risk of internal infections leading to botnet recruitment.
- Regular Security Audits: Conducting security audits can help identify and rectify vulnerabilities in the network.
Understanding the Process of Creating a Botnet and How to Counteract It
Creating a botnet typically involves infecting multiple devices with malware that allows remote control. This is often achieved through phishing emails, exploiting network vulnerabilities, or distributing malware-laden software. Once infected, these devices can be controlled without the knowledge of their owners.
Importance of Understanding Botnet Creation for Prevention
- Identifying Vulnerabilities: Understanding how devices are infected aids in fortifying defenses against those specific threats.
- Developing Targeted Security Measures: Knowledge of botnet creation processes enables the development of more effective, targeted security measures.
- Proactive Defense Strategies: Awareness of the botnet lifecycle empowers organizations to implement proactive defenses, rather than reacting post-infection.
In summary, preventing your network from becoming part of a zombie botnet requires a combination of technical safeguards, regular maintenance, and awareness. Understanding the process behind botnet creation is fundamental to designing effective prevention strategies, ensuring that networks remain secure and resilient against these insidious threats.
Conclusion: Staying One Step Ahead of Botnets
As we navigate the complex and ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity, understanding the dynamics of botnet threats and the strategies for their detection and prevention is crucial. This article has explored various facets of botnets, offering insights into how we can safeguard our digital environments against these pervasive threats.
The crucial steps to take if one suspects a botnet infection are:
- 1. Suspect Botnet Infection: Recognizing unusual behavior in your network or devices.
- 2. Isolate Affected Devices: Preventing the potential spread of the infection.
- 3. Scan for Malware: Using reliable tools to detect threats.
- 4. Remove Detected Threats: Ensuring complete removal of malware.
- 5. Update All Software & Firmware: Keeping systems up-to-date.
- 6. Change All Passwords: Securing all accounts.
- 7. Monitor Network Traffic: Watching for unusual activity.
- 8. Educate & Train Employees: Keeping the team informed.
- 9. Implement Multi-factor Authentication: Adding an extra layer of security.
- 10. Regularly Backup Data: Safeguarding critical data.
We began by defining botnets and their significant impact on the cybersecurity landscape, emphasizing the need for effective botnet detection strategies. The role of machine learning in enhancing botnet detection capabilities was highlighted, showcasing its importance in identifying and mitigating sophisticated cyber threats.
We delved into the different types of botnets, including DDoS, spam, financial, IoT, and P2P botnets, each presenting unique challenges and requiring tailored detection and prevention strategies. The article also covered the comprehensive tools and techniques for botnet attack detection, discussing both their effectiveness and limitations.
The synergy between detection and prevention was stressed, underscoring the importance of a dual approach in combating botnet threats. We also explored the application of DNS-based detection in identifying and disrupting botnet activities, supported by real-world case studies.

Experienced cybersecurity analyst, software engineer, patent attorney, worked with Linux, Windows, AWS, lots of security tools. Hope to help people do the right things and do the things right!