In today’s rapidly evolving cybersecurity landscape, one threat is making headlines for its stealth and sophistication: fileless malware. Recent statistics reveal an alarming 888% increase in fileless malware attacks over the past year. For small businesses, this isn’t just a tech issue; it’s a ticking time bomb that could jeopardize your entire operation. One source show that fileless malware attacks increased by 888% in 2020 compared to 2019. That’s why this post will discuss the best practices for protecting your system against fileless malware.
Key Takeaways
- Regularly update all software to close security loopholes.
- Use behavioral analysis tools to detect unusual activities.
- Implement network segmentation to contain malware spread.
This post will discuss best practices for protecting against fileless malware, offering actionable insights to safeguard your business.
What is Fileless Malware?
Fileless malware is a type of malicious software that operates directly from computer memory, bypassing the hard drive. Unlike traditional malware, it leaves no traceable files, making it harder to detect and remove. This stealthy approach allows it to infiltrate systems without triggering most antivirus solutions.
For a deeper dive into fileless malware, check out our previous post: What is Fileless Malware?
Why Traditional Malware Solutions Fall Short
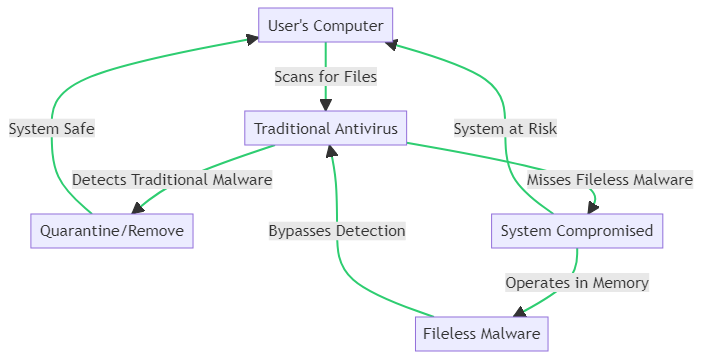
Traditional antivirus solutions are designed to scan files on your computer’s hard drive. They excel at detecting and removing traditional malware that relies on executable files. However, as the graphic above illustrates, these solutions often miss fileless malware. This type of malware operates directly in the computer’s memory, bypassing the hard drive entirely. As a result, it evades detection, leaving your system compromised and at risk.
For a more comprehensive understanding of why traditional solutions fall short, it’s crucial to recognize their limitations in the evolving landscape of fileless malware attacks.
Real-World Examples of Fileless Malware Attacks
While statistics and technical explanations provide valuable insights, nothing drives home the urgency of protecting against fileless malware like real-world examples. Although the following cases are hypothetical, they illustrate the devastating impact such attacks can have on small businesses.
Example 1: Local Bakery’s Payment System Compromised
A local bakery uses a point-of-sale (POS) system to process customer payments. Unbeknownst to them, a fileless malware infiltrates their POS through a seemingly harmless email attachment opened by an employee. The malware resides in the system’s memory, making it undetectable by traditional antivirus software. It captures credit card information from every transaction and sends it to a remote server.
Example 2: Law Firm’s Confidential Data Leaked
A small law firm specializing in family law becomes a victim of a fileless malware attack. An employee clicks on a malicious link in a phishing email, allowing the malware to execute PowerShell commands. It gains access to confidential client files and encrypts them, demanding a ransom for their release.
These examples underscore the stealthy and damaging nature of fileless malware, especially for small businesses with limited cybersecurity measures.
How Fileless Malware Infiltrates Your System
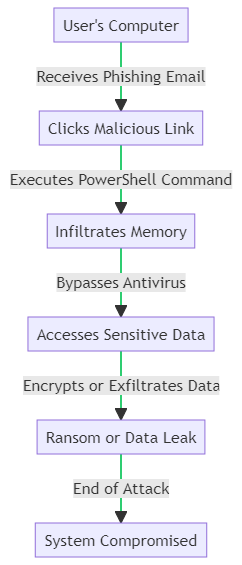
Understanding the mechanics of a fileless malware attack is crucial for effective prevention. As the flowchart above illustrates, the attack often starts with a phishing email containing a malicious link. Once clicked, it executes a PowerShell command that infiltrates your system’s memory, bypassing traditional antivirus software. From there, it can access sensitive data, encrypt it for ransom, or even exfiltrate it to a remote server, leaving your system compromised.
By comprehending these steps, you’re better equipped to identify vulnerabilities and implement protective measures.
The Anatomy of a Fileless Malware Attack
Fileless malware attacks are complex and multi-staged, designed to evade detection and maximize damage. Let’s break down the anatomy of such an attack, from the initial infection to its ultimate execution.
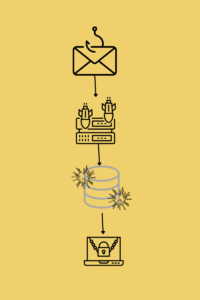
Stage 1: Infection Vector
The most common infection vectors are phishing emails, malicious websites, or infected USB drives. The attacker uses these methods to deliver a payload that initiates the attack.
Stage 2: Initial Execution
Upon successful delivery, the payload often exploits vulnerabilities in commonly used applications like Microsoft Word or Adobe Reader to execute the initial code.
Stage 3: Memory Exploitation
The malware then moves to the system’s memory, avoiding the hard drive where traditional antivirus software scans for threats.
Stage 4: Evasion Techniques
Fileless malware employs various evasion techniques, such as polymorphic coding and credential harvesting, to remain undetected.
Stage 5: Execution of Malicious Activities
Once securely in the system, the malware can perform a range of activities, from data exfiltration to encryption for ransom demands.
Stage 6: Covering Tracks
Finally, the malware often deletes any temporary files and logs to cover its tracks, making post-attack forensics more challenging.
Understanding the anatomy of a fileless malware attack can empower you to take proactive steps in safeguarding your system.
Best Practices for Protecting Against Fileless Malware

Protecting your small business from fileless malware requires a multi-layered approach. While we’ll delve into an infographic summarizing these best practices, let’s explore them in detail.
Keep Your Systems Updated
Regular updates are crucial for closing security loopholes that malware exploits. Ensure all software, including your operating system and third-party applications, are up-to-date.
Employ Behavioral Analysis Tools
Traditional antivirus solutions may not catch fileless malware, but behavioral analysis tools like Darktrace or Cynet can. These tools monitor system behavior in real-time, flagging unusual activities that could indicate a fileless malware attack. They analyze patterns and can trigger alerts or even automated responses to halt suspicious actions.
Implement Network Segmentation
Network segmentation divides your network into isolated segments. This limits the spread of malware by restricting its access to only certain parts of the network. If one segment is compromised, the malware can’t easily move to another.
By adopting these best practices, you’re taking significant steps to protect your small business from the growing threat of fileless malware.
Tools and Solutions for Enhanced Protection
In the ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats, relying solely on traditional methods is insufficient. Here are some advanced tools and solutions that can offer enhanced protection against fileless malware.
Endpoint Security Solutions
Endpoint security plays a pivotal role in protecting individual devices like computers, smartphones, and tablets. Solutions like McAfee Endpoint Security, Symantec Endpoint Protection, or ESET Endpoint Security offer advanced features, including real-time scanning and behavioral analysis, specifically designed to catch fileless malware.
Cloud-Based Security Options
Cloud-based solutions like Cisco Umbrella or Zscaler offer the flexibility and scalability that small businesses need. These solutions provide real-time threat intelligence and can be easily integrated with existing security infrastructure. The cloud-based nature allows for quick updates, ensuring you’re always protected against the latest threats.
Comparison of Recommended Tools and Solutions for Enhanced Protection
| Feature/Tool | McAfee Endpoint Security | Symantec Endpoint Protection | Cisco Umbrella | Zscaler |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type of Solution | Endpoint Security | Endpoint Security | Cloud-Based | Cloud-Based |
| Real-Time Scanning | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Behavioral Analysis | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| Threat Intelligence | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Scalability | Moderate | Moderate | High | High |
| Ease of Integration | Moderate | Moderate | Easy | Easy |
| Automatic Updates | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
By comparing these tools based on key features, you can make an informed decision on the best fit for your small business’s cybersecurity needs.
By incorporating these advanced tools and solutions into your cybersecurity strategy, you’re fortifying your small business against not just fileless malware but a range of cyber threats.
Expert Tips and Tricks for Protecting Against Fileless Malware
Navigating the cybersecurity landscape can be challenging, especially with the rise of sophisticated threats like fileless malware. Fortunately, experts in the field offer valuable insights that can help fortify your defenses.
Don’t Click on Suspicious Links
Being cautious with links, especially in emails and messages, is crucial. A single click can trigger a fileless malware attack.
Keep Your Software Updated
Outdated software is a breeding ground for attacks. Regular updates serve as a preventive measure against various types of malware, including fileless ones.
Use Antivirus Software Wisely
Not all antivirus solutions are created equal. Choose software that offers behavioral analysis features for more comprehensive protection against fileless malware.
By implementing these expert tips, you can significantly reduce the risk of falling victim to a fileless malware attack.
Conclusion and Next Steps
Fileless malware is a growing threat that traditional security measures often fail to address. From understanding its anatomy to implementing advanced tools and solutions, taking a proactive approach is crucial. Don’t underestimate the value of keeping your systems updated and employing behavioral analysis tools.
Now you’re armed with expert tips and best practices for protecting against fileless malware. Now, it’s time to take action. Secure your small business against this insidious form of malware today.
We encourage you to share this post with others who might find it valuable. If you have additional tips or questions, please feel free to engage in the comments section below. Your input could help someone else protect their business.
Questions? We Have Answers.
Get answers to a list of the most Frequently Asked Questions.

Experienced cybersecurity analyst, software engineer, patent attorney, worked with Linux, Windows, AWS, lots of security tools. Hope to help people do the right things and do the things right!