With cybersecurity, it’s not just about purchasing the latest software like ESET Endpoint Protection. It’s about understanding why such an investment is crucial for your business. Understanding the intricacies of cybersecurity cost-benefit analysis has never been more crucial. Cyber threats have become increasingly sophisticated. As a result, small businesses find themselves at the crossroads of ensuring robust security while managing costs. But how does one strike a balance between investing in preventive measures and potential post-breach financial implications? This article delves deep into this pressing concern. It offers insights, real-world examples, and actionable strategies. This helps business managers navigate the complexities of cybersecurity investments. Join us as we unveil the secrets of making informed decisions. Decisions that not only safeguard your business but also ensure optimal financial outcomes.
Key Takeaways
- Balancing Costs and Security: Cybersecurity is a balance between investment with potential breach costs.
- Sophisticated Threats: Endpoint threats are becoming more advanced,. This requires equally sophisticated protection tools like ESET Endpoint Protection.
- Real-World Examples: Real-world cyber incidents highlight the critical need for robust cybersecurity measures. This will help to prevent financial and reputational damage.
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: Conduct a thorough cost-benefit analysis. This helps ensure that cybersecurity investments provide maximum protective value.
The Evolving Landscape of Cybersecurity in 2024
Today, businesses, technologies, and user behaviors are evolving. As they do, so do the threats that lurk in the shadows of the internet. This has showcased the profound impact of global events on the cybersecurity landscape.
The Impact of Global Events on Cyber Threats in 2023
The ripple effects of global events have always influenced cyber threats. However, 2023 has been particularly noteworthy. There has been a rise of remote work due to the lingering effects of the COVID-19 pandemic. Because of this, the boundaries between professional and personal digital spaces have blurred. This shift has opened new avenues for cyber attackers. It allows them to exploit vulnerabilities in less secure home networks and devices. Additionally, political tensions and economic shifts have given rise to nation-state attacks. True, they are targeting large corporations and governments. However, they are also targeting smaller entities caught in the crossfire. Natural disasters, too, have played a role. Cybercriminals take advantage of disrupted communication lines and emergency responses. This allows them to launch phishing attacks and scams.
Why Small Businesses are Prime Targets
A common misconception is that cyber attackers only set their sights on large corporations. However, small businesses have emerged as prime targets for several reasons. Firstly, they often lack the robust cybersecurity infrastructure that larger organizations possess. This makes them easier to breach. Their limited resources mean that they might not have dedicated IT personnel. This leads to potential oversights in security measures. Moreover, small businesses often work with larger corporations. This provides a backdoor entry point for attackers aiming for bigger prey. The perceived lower risk of significant repercussions also emboldens cybercriminals. For them, small businesses represent low-hanging fruit. These businesses are easier to compromise. Further, they won’t have the means for aggressive legal or retaliatory actions.
The Rise of Sophisticated Endpoint Threats and the Evolution of Protection Tools
Today more than ever, businesses and individuals have become more connected. The threats they face have grown in sophistication. Endpoint devices have become prime targets for cybercriminals. These threats are no longer just about viruses or malware. These threats include:
- ransomware
- zero-day exploits
- advanced persistent threats (APT)
Products like ESET Endpoint Protection have recognized this evolving threat landscape. They have continuously adapted to offer robust defenses. These tools employ advanced techniques like behavioral detection, machine learning, and cloud-based analysis. These tools help to identify and neutralize threats before they can cause harm. They’re about detecting known viruses. However, they are also about predicting and countering new, unseen cyber threats.
The importance of such advanced protection tools cannot be understated. However, it’s equally crucial for businesses to understand their return on investment (ROI). Investing in a product like ESET is more than just purchasing software. It’s about understanding the financial and operational repercussions of a breach versus the cost of the tool. It’s about recognizing the cost of recovery can far outweigh the proactive investment in a top-tier endpoint protection solution.
In essence, as endpoint threats grow in complexity, the tools to combat them must evolve in tandem. But every investment should be backed by a clear understanding of its cost-benefit dynamics.
Understanding the nuances of cybersecurity risk management and its cost-benefit analysis is important. We’ll explore strategies and insights to help small businesses fortify their defenses. We need to keep in mind the costs so we don’t break the bank!
Demystifying Cost-Benefit Analysis in Cybersecurity
Cost-benefit analysis (CBA) stands as a time-tested tool. It helps leaders weigh the pros and cons of their choices. When applied to cybersecurity, CBA takes on a whole new dimension. It becomes an instrument in navigating cyber threats and defenses.
What is Cost-Benefit Analysis and Why is it Crucial?
Cost-benefit analysis provides a systematic framework. It enables one to estimate the strengths and weaknesses of alternatives. It involves evaluating the potential costs of security measures. Then compare these against the benefits they provide. But why is this so vital? As cyber threats evolve, businesses are faced with a myriad of security solutions, each with its own price tag. One must have a clear understanding of the return on investment. Without this, companies can end up overspending on redundant tools. Worse, they can underinvest and leave critical vulnerabilities exposed. CBA offers a structured way to make these informed decisions. Thus, ensuring that every dollar spent on cybersecurity yields the maximum protective value.
The Direct and Indirect Costs of Cybersecurity
It’s important to recognize both the direct and indirect expenses associated with cybersecurity.
- Direct Costs: These are the immediate, tangible expenses related to cybersecurity. They encompass hardware and software solutions. Solutions like:
- Indirect Costs: Indirect costs are often overlooked. However, they can have a significant impact on a business’s bottom line. They include:
- potential revenue losses from downtime during a cyber-attack
- reputational damage leading to lost business opportunities
- legal fees arising from data breaches
- the cost of lost productivity when employees are locked out of systems or when they need to adapt to new security protocols.
Understanding the balance between these direct and indirect costs is pivotal. It’s about how much you spend on cybersecurity solutions. But more than that, it’s also about the potential financial repercussions if those solutions fail or are insufficient.
As we continue, we’ll discover practical strategies. These will ensure that the smaller businesses get the best bang for their buck. Thus, safeguarding their digital assets without draining their resources.
The Real-World Implications: Cyber Attacks and Their Financial Toll
Understanding the theoretical aspects of cybersecurity risk management and cost-benefit analysis is essential. However, it’s the real-world examples that truly bring home the gravity of the situation. Today, understanding the tangible impacts of cyber breaches becomes paramount.
Recent Cyber Attack Case Studies and Their Financial Impact
- Small Retailer Ransomware Attack: A small online retailer recently fell victim to a ransomware attack. The attackers encrypted the company’s customer database. Then they demanded a ransom of $50,000. Beyond the immediate ransom amount, the retailer faced two days of downtime. This translated to a loss of approximately $20,000 in sales. Additionally, the cost of IT services to restore the systems amounted to another $10,000.
- Local Clinic Data Breach: A local health clinic experienced a data breach. In that breach, sensitive health information was exposed. The immediate legal fees and potential fines amounted to $100,000. The clinic also had to offer credit monitoring services to affected patients, costing an additional $25,000.
- Manufacturing Firm Phishing Scam: A small manufacturing firm’s accountant received a phishing email. It seemed to come from a trusted vendor. This lead to a fraudulent wire transfer of $200,000. The bank managed to recover half the amount. However, the company still faced a significant loss. Further, they suffered the costs associated with
Reputational Damage: The Hidden Cost of Cyber Breaches
The immediate financial implications of cyber-attacks are indeed daunting. However, the long-term reputational damage can be even more devastating. Customers entrust businesses with their data. This data can be credit card information, personal details, or health records. They should expect the utmost security. A breach not only signifies a failure in this trust but can also lead to a long-lasting perception of the company as unreliable.
For small businesses, this reputational damage can be particularly crippling. Word-of-mouth, community trust, and local reputation are often the lifeblood of their operations.
A single cyber incident can lead to a strain of financial resources from:
- a mass exodus of customers
- negative reviews
- a tarnished brand image that can take years to rebuild
- the cost of PR campaigns
- customer outreach
- potential discounts or compensations to retain clientele
Understanding these real-world implications are crucial. It is true that it’s about the immediate costs. However, the long-term financial and reputational ramifications can determine a business’s survival.
Cybersecurity Risk Management: A Deep Dive
Understanding the nuances of cybersecurity risk management is paramount. It’s more than setting up firewalls or installing the latest antivirus software. Risk management is about a holistic approach. It needs to consider every potential vulnerability and the corresponding financial implications. Let’s delve deeper into this critical aspect of modern business operations.
Risk Assessment: The First Step to a Robust Strategy
Risk assessment is the cornerstone of any effective cybersecurity strategy. It involves:
- identifying potential threats
- evaluating the vulnerabilities within the system
- understanding the potential impact of a breach.
Here’s a step-by-step breakdown:
- Asset Identification: Determine what you’re protecting. This includes tangible assets like servers and computers. It also includes intangible ones like software, data, and intellectual property.
- Threat Identification: Recognize potential threats. Whether these threats are:
- hackers
- malware
- insider threats
- natural disasters that could disrupt IT infrastructure
- Vulnerability Assessment: Using tools and audits, identify weak points in your system. This could be outdated software, unsecured access points, or even employee behaviors.
- Impact Analysis: Understand the potential consequences of a breach. This involves estimating the financial loss, data compromise, and any operational disruptions.
- Risk Determination: Based on the vulnerabilities and potential impact, determine the level of risk. This will guide the prioritization of security measures.
Security Risk vs. Financial Risk: Striking the Balance
Risk management often becomes a tightrope walk between security risks and financial risks. Here’s how they compare:
- Security Risk: This pertains to the potential threats to your digital assets. High security risk could mean exposure to frequent cyberattacks or potential data breaches. Mitigating these risks often requires investments in security infrastructure, training, and regular audits.
- Financial Risk: This relates to the monetary implications of cybersecurity decisions. Over-investing in cybersecurity can strain a company’s finances. This can lead to potential cutbacks in other crucial areas. Conversely, under-investing can result in costly breaches, legal fees, and reputational damage.
Striking the right balance involves a thorough cost-benefit analysis. It’s about understanding the potential financial impact of a security breach. Then, compare it to the costs of preventive measures. For small businesses, this balance is even more critical. Budget constraints can often limit cybersecurity investments. However, it’s possible to achieve robust security without overburdening financial resources.
Understanding these dynamics is essential. It’s a continuous process of evaluation, investment, and adaptation. Doing so ensures that businesses remain shielded in an ever-evolving digital landscape.
The Trade-offs: Investing in Prevention vs. Post-Breach Cleanup
One of the most challenging decisions businesses face is the allocation of resources. Should they invest heavily in preventive measures? Or is it more cost-effective to deal with the aftermath of a breach? Let’s examine the trade-offs between these two approaches. We’ll highlight the importance of proactive investments. Finally, we’ll examine the long-term financial implications of reactive measures.
Evaluating the ROI of Preventive Cybersecurity Measures
Return on Investment (ROI) is a critical metric in any business decision. Cybersecurity is no exception to this rule.
Here’s how businesses can evaluate the ROI of their preventive measures:
- Cost of Implementation: Calculate the total cost of implementing the preventive measures. This includes software, hardware, training, and any third-party services.
- Potential Loss Prevention: Estimate the potential financial losses that these measures could prevent. Consider factors like potential downtime, data loss, and the cost of restoring services.
- Operational Efficiency: Proactive measures often lead to smoother operations. For instance, regular system updates can improve performance. Another example, employee training can reduce the chances of human error.
- Reputational Benefits: Today, having a robust cybersecurity posture can enhance a business’s reputation. This can lead to increased customer trust and loyalty.
- Calculate ROI:
- This formula can give businesses ROI of their preventive measures:
[(Net Profit from Investment – Cost of Investment) / Cost of Investment]
The Long-Term Financial Benefits of Proactive Cybersecurity
The immediate costs of preventive measures can be daunting. However, the long-term financial benefits often outweigh the initial investment:
- Reduced Cleanup Costs: The aftermath of a cyber breach can be expensive. Costs include restoring systems to legal fees and potential fines. These costs can quickly escalate. Proactive measures significantly reduce these potential expenses.
- Business Continuity: Downtime can lead to significant revenue losses. By investing in preventive measures, businesses can ensure continuity, avoiding potential operational disruptions.
- Customer Retention: In the wake of a breach, businesses often face customer attrition. Proactive measures can prevent this. Further, these measures can also lead to increased customer acquisition due to enhanced trust.
- Competitive Advantage: Having robust preventive measures can offer a competitive edge. It can attract partnerships and collaborations.
With cybersecurity risk management cost-benefit analysis, understanding the trade-offs is crucial. The allure of cutting costs in the short term can be tempting. However, there are long-term benefits for proactive cybersecurity. This often makes it the more financially sound choice.
Practical Steps to Implementing Cost-Benefit Analysis
Navigating the complexities of cybersecurity investments requires a structured approach. Implementing a cost-benefit analysis in this domain starts with crunching numbers. But more than that, it’s about understanding the broader implications of each decision. Let’s explore the practical steps businesses can take to effectively implement this analysis. This will ensure that every cybersecurity investment is both strategic and impactful.
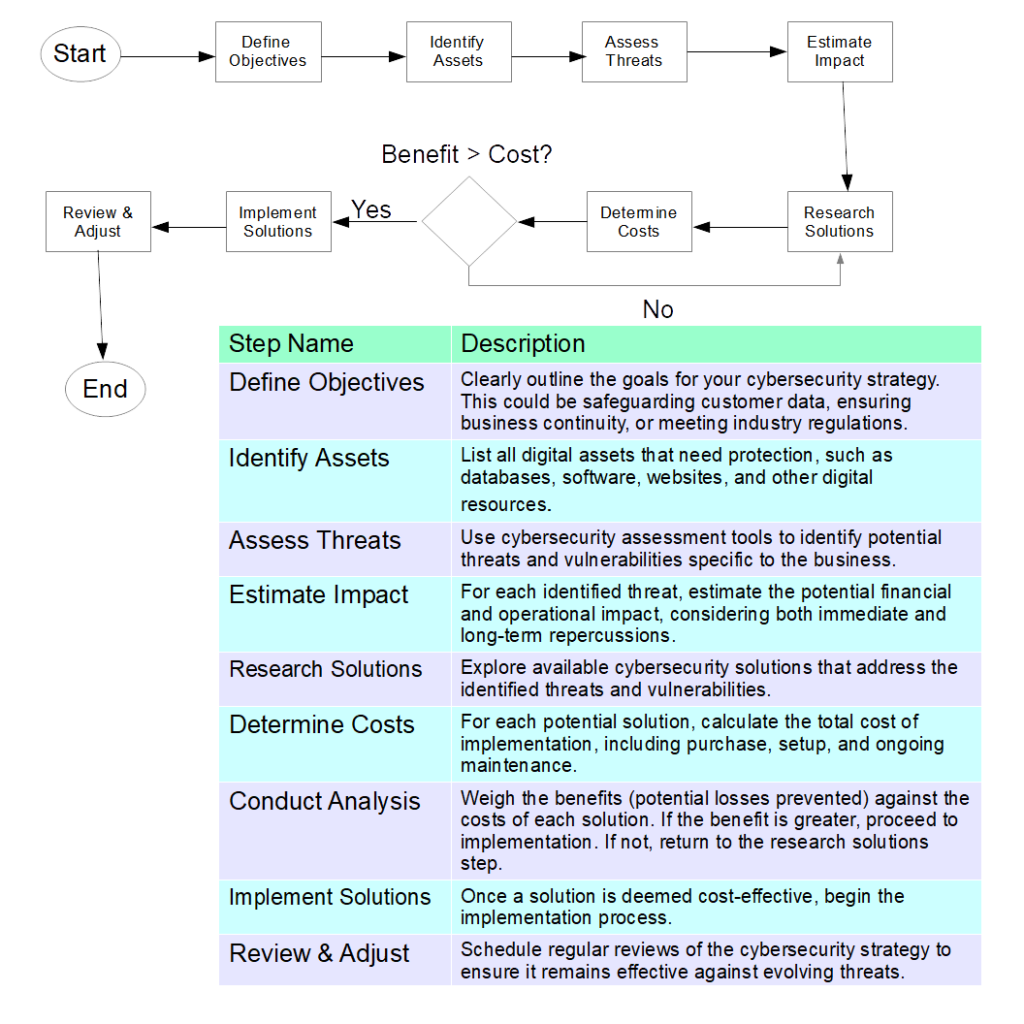
Tools and Frameworks for Effective Analysis
Let’s explore several tools and cost-benefit analysis frameworks.. These are designed to assist businesses, specifically for cybersecurity:
- Cybersecurity Assessment Tools: These tools help businesses identify vulnerabilities in their systems. They provide a clear picture of potential risks. These tools assist in understanding these vulnerabilities. By doing so, businesses can better estimate the costs associated with potential breaches.
- ROI Calculators for Cybersecurity: These can factor in both the direct and indirect costs. Thus, helping businesses determine the potential return on their investments.
- Industry-specific Guidelines: Specific industries might have specific guidelines or best practices. These can help guide the cost-benefit analysis process.
The Role of the NIST Cybersecurity Framework and the Gordon-Loeb Model
- NIST Cybersecurity Framework: Developed by the National Institute of Standards and Technology, this framework provides a set of best practices, standards, and guidelines for improving cybersecurity. It offers a structured approach to understanding current security postures, setting goals, and measuring progress. By aligning with the NIST framework, businesses can ensure that their cybersecurity investments are both comprehensive and aligned with industry standards.
- Gordon-Loeb Model: This model posits the optimal amount to invest in cybersecurity. It says that it should be a fraction of the expected loss that would result from a breach. It provides a mathematical approach to determine how much to invest in cybersecurity. It does this by weighing the potential loss from a cyber incident against the cost of preventive measures.
Step-by-Step Plan for Implementing a Cost-Benefit Analysis in Cybersecurity
- Define Objectives: Clearly outline what you aim to achieve with your cybersecurity investments. This could range from safeguarding customer data to ensuring business continuity.
- Identify Assets: Determine the digital assets that need protection. This includes databases, websites, software, and any other digital resources.
- Assess Potential Threats: Using cybersecurity assessment tools, identify potential threats and vulnerabilities.
- Estimate Potential Loss: Calculate the potential financial loss from each identified threat. This should include both direct costs, like recovery efforts. It should also include indirect costs, like reputational damage.
- Determine Investment Costs: Calculate the costs associated with each preventive measure or solution being considered.
- Apply the Gordon-Loeb Model: Use the model to determine the optimal investment amount for each preventive measure.
- Align with the NIST Framework: Ensure that the chosen measures align with the guidelines and best practices. These are as outlined in the NIST Cybersecurity Framework.
- Implement Solutions: Once the analysis is complete, implement the chosen cybersecurity solutions.
- Regularly Review and Adjust: Cyber threats are ever-evolving. Regularly review and adjust your cybersecurity strategy and investments. Do this based on new threats, business changes, and technological advancements.
This approach can ensure that the cost-benefit analysis is both comprehensive and effective. Thus, leading to informed investment decisions that safeguard their digital assets.
The Future of Cybersecurity: Predictions and Preparations
The cybersecurity landscape is in a constant state of flux. With every technological advancement comes a new set of challenges. However, it is accompanied by a wave of innovative solutions. You must ensure that businesses remain resilient in the face of these evolving threats. So it’s crucial to both anticipate the future and be prepared to adapt. Let’s explore the predictions and preparations that will shape the future of cybersecurity.
Emerging Threats and How to Stay Ahead
The digital age, while filled with opportunities, is also rife with challenges. Here are some of the emerging threats and strategies to stay ahead:
- AI-Powered Cyber Attacks: Artificial intelligence is becoming more sophisticated. Cybercriminals are leveraging it to launch more targeted and complex attacks. Stay ahead by investing in AI-driven security solutions. Solutions can predict and counteract AI-based threats. Thus, ensuring that your defenses evolve at the same pace as the threats.
- Deepfakes in Phishing Scams: Deepfakes, or AI-generated fake videos or audio recordings, are becoming a tool for phishing scams, tricking individuals into revealing sensitive information. Stay ahead of this by organizing regular training sessions for employees to recognize and report potential deepfake content, combined with AI tools that can detect manipulated media.
- Quantum Computing Threats: The rise of quantum computing poses a threat to current encryption methods, potentially making them obsolete. Stay ahead of this by doing research and investing in quantum-resistant encryption methods to ensure data remains secure as quantum technology becomes more prevalent.
- IoT Vulnerabilities: As the Internet of Things (IoT) expands, so does the potential attack surface for cybercriminals. Stay ahead of this by ensuring that all IoT devices are regularly updated, change default passwords, and segment IoT devices on separate networks.
- Supply Chain Attacks: Cybercriminals are targeting vulnerabilities in the supply chain. This allows them to breach larger organizations through smaller ones. Stay ahead of this by assessing the cybersecurity measures of suppliers and partners. Thus, ensuring they meet your security standards.
Innovations in Cybersecurity Solutions for Small Businesses
As threats evolve, so do the solutions designed to combat them. Here are some of the latest innovations tailored for small businesses:
- Zero Trust Architectures: Move away from the traditional perimeter-based security. Zero Trust ensures that every access request is fully authenticated. Authenticated regardless of where it originates.
- Security-as-a-Service (SECaaS): Cloud-based solutions can offer small businesses top-tier subscription-based security measures. Thus, eliminating the need for heavy upfront investments.
- Automated Threat Hunting: AI-driven tools proactively search for and neutralize threats. Thus, ensuring that breaches are addressed even before they can cause damage.
- Behavioral Analytics: Tools that monitor user behavior to detect anomalies. They can offer an additional layer of security. They do this by identifying potential insider threats or compromised accounts.
- Decentralized Security Systems: Blockchain technology can distribute data across a network. Thus, making it harder for cybercriminals to launch targeted attacks on a single point.
The future of cost-benefit analysis in cybersecurity will be shaped by both the challenges and the solutions that arise. Stay informed and proactive. By doing so, businesses can ensure they remain one step ahead. Thus, safeguarding their assets and ensuring continued growth in the digital age.
Actionable Takeaways: Your Next Steps
From here, it’s time to translate this knowledge into actionable steps. The following provides a clear roadmap to ensure your business remains resilient in the face of evolving digital threats.
Checklist for Implementing a Cost-Benefit Analysis Approach
- Define Your Objectives: Clearly outline what you aim to achieve with your cybersecurity strategy. This could be:
- safeguarding customer data
- ensuring business continuity
- complying with industry regulations
- Asset Inventory: Catalog all your digital assets to understand what you’re protecting. This should include hardware and software to databases and intellectual property.
- Threat Identification: Use cybersecurity assessment tools to identify potential threats and vulnerabilities specific to your business and industry.
- Estimate Potential Impact: For each identified threat, calculate the potential financial and operational impact. Consider both immediate and long-term repercussions.
- Research Solutions: Investigate the available cybersecurity solutions that address your identified threats and vulnerabilities. Before investing in solutions like ESET, understand each product’s features, benefits, and how it aligns with the identified threats and vulnerabilities of your business.
- Determine Investment Costs: For each potential solution, calculate the total cost of implementation, including purchase, setup, and ongoing maintenance.
- Apply Cost-Benefit Analysis: Weigh the costs of each solution against the potential losses it could prevent. Use tools or frameworks like the Gordon-Loeb Model to guide your analysis.
- Implementation: Once you’ve determined the most cost-effective solutions, begin the implementation process, ensuring each measure is correctly set up and integrated.
- Training and Awareness: Educate your team about the new measures, ensuring they understand their roles in maintaining cybersecurity.
- Regular Reviews: Cyber threats are constantly evolving. Schedule regular reviews of your cybersecurity strategy to ensure it remains effective and up-to-date.
Recommended Resources and Tools to Get Started
- NIST Cybersecurity Framework: A comprehensive guide offering best practices, standards, and guidelines for improving cybersecurity.
- Gordon-Loeb Model Calculator: An online tool to help businesses determine the optimal amount to invest in cybersecurity based on potential loss.
- Cybersecurity Assessment Tools: Platforms like Nessus or OpenVAS can help identify vulnerabilities in your systems.
- ROI Calculators for Cybersecurity: Tools that help businesses determine the potential return on their cybersecurity investments, factoring in both direct and indirect costs.
- Industry-specific Forums and Communities: Platforms like ISACA or Cybersecurity Insiders offer insights, discussions, and updates tailored to specific industries.
- Online Training Platforms: Websites like Cybrary or Pluralsight offer courses on various cybersecurity topics, ensuring your team remains informed and updated.
- Endpoint Protection Solutions: Tools like ESET or Symantec provide comprehensive protection for devices, ensuring threats are neutralized before they can infiltrate your network.
By following the above checklist and leveraging the recommended resources, businesses can ensure they adopt a comprehensive and cost-effective approach to cybersecurity. Remember, in the realm of cybersecurity risk management cost-benefit analysis, proactive measures not only safeguard your assets but also ensure long-term financial stability and growth.
Conclusion: Embracing the Future of Cybersecurity
In the intricate dance of cybersecurity, the stakes have never been higher. As we’ve journeyed through the evolving landscape of 2023, a few key takeaways emerge. Endpoint threats are growing in sophistication, making tools like ESET Endpoint Protection invaluable. However, it’s not just about having the right tools; it’s about understanding their true value through a meticulous cost-benefit analysis. Blind investments can strain resources, but informed decisions, grounded in a clear understanding of ROI, can fortify a business against the ever-present cyber threats.
But what’s the path forward? The digital realm is in constant flux, and the threats of today might evolve or be replaced by newer, more complex challenges tomorrow. This brings us to the importance of continuous learning and adaptation. Cybersecurity isn’t a one-time effort; it’s a continuous journey of learning, adapting, and evolving. Regularly updating one’s knowledge, staying abreast of the latest threats, and adapting strategies accordingly is paramount.
As you move forward, armed with the insights from this article, remember to approach cybersecurity as a dynamic field. Regularly review and refine your strategies, invest in continuous learning, and always be prepared to adapt. In the world of digital defense, the best armor is a combination of the right tools and an ever-evolving strategy.
Engaging the Community: Sharing Experiences and Challenges
I would encourage you to comment about recommendations or stories you know about small business using cost benefit analysis for cybersecurity. What worked and what didn’t?
Also, how cost benefit analysis and be used to foster a cybersecurity community in your organization, as it requires a lot of cooperation between disparate groups.
Questions? We Have Answers.
Get answers to a list of the most Frequently Asked Questions.

Experienced cybersecurity analyst, software engineer, patent attorney, worked with Linux, Windows, AWS, lots of security tools. Hope to help people do the right things and do the things right!


